- Search Search Please fill out this field.

What Is Market Research?
- How It Works
- Primary vs. Secondary
- How to Conduct Research
The Bottom Line
- Marketing Essentials
How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/dd453b82d4ef4ce8aac2e858ed00a114__alexandra_twin-5bfc262b46e0fb0026006b77.jpeg)
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example CURRENT ARTICLE
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, How To Create One
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons
- Best Startup Business Loans
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros & Cons, and Differences From an LLC
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types
- What is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide
Joules Garcia / Investopedia
Market research examines consumer behavior and trends in the economy to help a business develop and fine-tune its business idea and strategy. It helps a business understand its target market by gathering and analyzing data.
Market research is the process of evaluating the viability of a new service or product through research conducted directly with potential customers. It allows a company to define its target market and get opinions and other feedback from consumers about their interest in a product or service.
Research may be conducted in-house or by a third party that specializes in market research. It can be done through surveys and focus groups, among other ways. Test subjects are usually compensated with product samples or a small stipend for their time.
Key Takeaways
- Companies conduct market research before introducing new products to determine their appeal to potential customers.
- Tools include focus groups, telephone interviews, and questionnaires.
- The results of market research inform the final design of the product and determine how it will be positioned in the marketplace.
- Market research usually combines primary information, gathered directly from consumers, and secondary information, which is data available from external sources.
Market Research
How market research works.
Market research is used to determine the viability of a new product or service. The results may be used to revise the product design and fine-tune the strategy for introducing it to the public. This can include information gathered for the purpose of determining market segmentation . It also informs product differentiation , which is used to tailor advertising.
A business engages in various tasks to complete the market research process. It gathers information based on the market sector being targeted by the product. This information is then analyzed and relevant data points are interpreted to draw conclusions about how the product may be optimally designed and marketed to the market segment for which it is intended.
It is a critical component in the research and development (R&D) phase of a new product or service introduction. Market research can be conducted in many different ways, including surveys, product testing, interviews, and focus groups.
Market research is a critical tool that companies use to understand what consumers want, develop products that those consumers will use, and maintain a competitive advantage over other companies in their industry.
Primary Market Research vs. Secondary Market Research
Market research usually consists of a combination of:
- Primary research, gathered by the company or by an outside company that it hires
- Secondary research, which draws on external sources of data
Primary Market Research
Primary research generally falls into two categories: exploratory and specific research.
- Exploratory research is less structured and functions via open-ended questions. The questions may be posed in a focus group setting, telephone interviews, or questionnaires. It results in questions or issues that the company needs to address about a product that it has under development.
- Specific research delves more deeply into the problems or issues identified in exploratory research.
Secondary Market Research
All market research is informed by the findings of other researchers about the needs and wants of consumers. Today, much of this research can be found online.
Secondary research can include population information from government census data , trade association research reports , polling results, and research from other businesses operating in the same market sector.
History of Market Research
Formal market research began in Germany during the 1920s. In the United States, it soon took off with the advent of the Golden Age of Radio.
Companies that created advertisements for this new entertainment medium began to look at the demographics of the audiences who listened to each of the radio plays, music programs, and comedy skits that were presented.
They had once tried to reach the widest possible audience by placing their messages on billboards or in the most popular magazines. With radio programming, they had the chance to target rural or urban consumers, teenagers or families, and judge the results by the sales numbers that followed.
Types of Market Research
Face-to-face interviews.
From their earliest days, market research companies would interview people on the street about the newspapers and magazines that they read regularly and ask whether they recalled any of the ads or brands that were published in them. Data collected from these interviews were compared to the circulation of the publication to determine the effectiveness of those ads.
Market research and surveys were adapted from these early techniques.
To get a strong understanding of your market, it’s essential to understand demand, market size, economic indicators, location, market saturation, and pricing.
Focus Groups
A focus group is a small number of representative consumers chosen to try a product or watch an advertisement.
Afterward, the group is asked for feedback on their perceptions of the product, the company’s brand, or competing products. The company then takes that information and makes decisions about what to do with the product or service, whether that's releasing it, making changes, or abandoning it altogether.
Phone Research
The man-on-the-street interview technique soon gave way to the telephone interview. A telephone interviewer could collect information in a more efficient and cost-effective fashion.
Telephone research was a preferred tactic of market researchers for many years. It has become much more difficult in recent years as landline phone service dwindles and is replaced by less accessible mobile phones.
Survey Research
As an alternative to focus groups, surveys represent a cost-effective way to determine consumer attitudes without having to interview anyone in person. Consumers are sent surveys in the mail, usually with a coupon or voucher to incentivize participation. These surveys help determine how consumers feel about the product, brand, and price point.
Online Market Research
With people spending more time online, market research activities have shifted online as well. Data collection still uses a survey-style form. But instead of companies actively seeking participants by finding them on the street or cold calling them on the phone, people can choose to sign up, take surveys, and offer opinions when they have time.
This makes the process far less intrusive and less rushed, since people can participate on their own time and of their own volition.
How to Conduct Market Research
The first step to effective market research is to determine the goals of the study. Each study should seek to answer a clear, well-defined problem. For example, a company might seek to identify consumer preferences, brand recognition, or the comparative effectiveness of different types of ad campaigns.
After that, the next step is to determine who will be included in the research. Market research is an expensive process, and a company cannot waste resources collecting unnecessary data. The firm should decide in advance which types of consumers will be included in the research, and how the data will be collected. They should also account for the probability of statistical errors or sampling bias .
The next step is to collect the data and analyze the results. If the two previous steps have been completed accurately, this should be straightforward. The researchers will collect the results of their study, keeping track of the ages, gender, and other relevant data of each respondent. This is then analyzed in a marketing report that explains the results of their research.
The last step is for company executives to use their market research to make business decisions. Depending on the results of their research, they may choose to target a different group of consumers, or they may change their price point or some product features.
The results of these changes may eventually be measured in further market research, and the process will begin all over again.
Benefits of Market Research
Market research is essential for developing brand loyalty and customer satisfaction. Since it is unlikely for a product to appeal equally to every consumer, a strong market research program can help identify the key demographics and market segments that are most likely to use a given product.
Market research is also important for developing a company’s advertising efforts. For example, if a company’s market research determines that its consumers are more likely to use Facebook than X (formerly Twitter), it can then target its advertisements to one platform instead of another. Or, if they determine that their target market is value-sensitive rather than price-sensitive, they can work on improving the product rather than reducing their prices.
Market research only works when subjects are honest and open to participating.
Example of Market Research
Many companies use market research to test new products or get information from consumers about what kinds of products or services they need and don’t currently have.
For example, a company that’s considering starting a business might conduct market research to test the viability of its product or service. If the market research confirms consumer interest, the business can proceed confidently with its business plan . If not, the company can use the results of the market research to make adjustments to the product to bring it in line with customer desires.
What Are the Main Types of Market Research?
The main types of market research are primary research and secondary research. Primary research includes focus groups, polls, and surveys. Secondary research includes academic articles, infographics, and white papers.
Qualitative research gives insights into how customers feel and think. Quantitative research uses data and statistics such as website views, social media engagement, and subscriber numbers.
What Is Online Market Research?
Online market research uses the same strategies and techniques as traditional primary and secondary market research, but it is conducted on the Internet. Potential customers may be asked to participate in a survey or give feedback on a product. The responses may help the researchers create a profile of the likely customer for a new product.
What Are Paid Market Research Surveys?
Paid market research involves rewarding individuals who agree to participate in a study. They may be offered a small payment for their time or a discount coupon in return for filling out a questionnaire or participating in a focus group.
What Is a Market Study?
A market study is an analysis of consumer demand for a product or service. It looks at all of the factors that influence demand for a product or service. These include the product’s price, location, competition, and substitutes as well as general economic factors that could influence the new product’s adoption, for better or worse.
Market research is a key component of a company’s research and development (R&D) stage. It helps companies understand in advance the viability of a new product that they have in development and to see how it might perform in the real world.
Britannica Money. “ Market Research .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Market Research and Competitive Analysis .”
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Primary-Image-best-sba-loans-for-startups-of-2023-7509414-3703c627841444c9a1771e122d4be33b.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
How to Do Market Research: The Complete Guide
Learn how to do market research with this step-by-step guide, complete with templates, tools and real-world examples.
Access best-in-class company data
Get trusted first-party funding data, revenue data and firmographics
Market research is the systematic process of gathering, analyzing and interpreting information about a specific market or industry.
What are your customers’ needs? How does your product compare to the competition? What are the emerging trends and opportunities in your industry? If these questions keep you up at night, it’s time to conduct market research.
Market research plays a pivotal role in your ability to stay competitive and relevant, helping you anticipate shifts in consumer behavior and industry dynamics. It involves gathering these insights using a wide range of techniques, from surveys and interviews to data analysis and observational studies.
In this guide, we’ll explore why market research is crucial, the various types of market research, the methods used in data collection, and how to effectively conduct market research to drive informed decision-making and success.
What is market research?
The purpose of market research is to offer valuable insight into the preferences and behaviors of your target audience, and anticipate shifts in market trends and the competitive landscape. This information helps you make data-driven decisions, develop effective strategies for your business, and maximize your chances of long-term growth.

Why is market research important?
By understanding the significance of market research, you can make sure you’re asking the right questions and using the process to your advantage. Some of the benefits of market research include:
- Informed decision-making: Market research provides you with the data and insights you need to make smart decisions for your business. It helps you identify opportunities, assess risks and tailor your strategies to meet the demands of the market. Without market research, decisions are often based on assumptions or guesswork, leading to costly mistakes.
- Customer-centric approach: A cornerstone of market research involves developing a deep understanding of customer needs and preferences. This gives you valuable insights into your target audience, helping you develop products, services and marketing campaigns that resonate with your customers.
- Competitive advantage: By conducting market research, you’ll gain a competitive edge. You’ll be able to identify gaps in the market, analyze competitor strengths and weaknesses, and position your business strategically. This enables you to create unique value propositions, differentiate yourself from competitors, and seize opportunities that others may overlook.
- Risk mitigation: Market research helps you anticipate market shifts and potential challenges. By identifying threats early, you can proactively adjust their strategies to mitigate risks and respond effectively to changing circumstances. This proactive approach is particularly valuable in volatile industries.
- Resource optimization: Conducting market research allows organizations to allocate their time, money and resources more efficiently. It ensures that investments are made in areas with the highest potential return on investment, reducing wasted resources and improving overall business performance.
- Adaptation to market trends: Markets evolve rapidly, driven by technological advancements, cultural shifts and changing consumer attitudes. Market research ensures that you stay ahead of these trends and adapt your offerings accordingly so you can avoid becoming obsolete.
As you can see, market research empowers businesses to make data-driven decisions, cater to customer needs, outperform competitors, mitigate risks, optimize resources and stay agile in a dynamic marketplace. These benefits make it a huge industry; the global market research services market is expected to grow from $76.37 billion in 2021 to $108.57 billion in 2026 . Now, let’s dig into the different types of market research that can help you achieve these benefits.
Types of market research
- Qualitative research
- Quantitative research
- Exploratory research
- Descriptive research
- Causal research
- Cross-sectional research
- Longitudinal research
Despite its advantages, 23% of organizations don’t have a clear market research strategy. Part of developing a strategy involves choosing the right type of market research for your business goals. The most commonly used approaches include:
1. Qualitative research
Qualitative research focuses on understanding the underlying motivations, attitudes and perceptions of individuals or groups. It is typically conducted through techniques like in-depth interviews, focus groups and content analysis — methods we’ll discuss further in the sections below. Qualitative research provides rich, nuanced insights that can inform product development, marketing strategies and brand positioning.
2. Quantitative research
Quantitative research, in contrast to qualitative research, involves the collection and analysis of numerical data, often through surveys, experiments and structured questionnaires. This approach allows for statistical analysis and the measurement of trends, making it suitable for large-scale market studies and hypothesis testing. While it’s worthwhile using a mix of qualitative and quantitative research, most businesses prioritize the latter because it is scientific, measurable and easily replicated across different experiments.
3. Exploratory research
Whether you’re conducting qualitative or quantitative research or a mix of both, exploratory research is often the first step. Its primary goal is to help you understand a market or problem so you can gain insights and identify potential issues or opportunities. This type of market research is less structured and is typically conducted through open-ended interviews, focus groups or secondary data analysis. Exploratory research is valuable when entering new markets or exploring new product ideas.
4. Descriptive research
As its name implies, descriptive research seeks to describe a market, population or phenomenon in detail. It involves collecting and summarizing data to answer questions about audience demographics and behaviors, market size, and current trends. Surveys, observational studies and content analysis are common methods used in descriptive research.
5. Causal research
Causal research aims to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables. It investigates whether changes in one variable result in changes in another. Experimental designs, A/B testing and regression analysis are common causal research methods. This sheds light on how specific marketing strategies or product changes impact consumer behavior.
6. Cross-sectional research
Cross-sectional market research involves collecting data from a sample of the population at a single point in time. It is used to analyze differences, relationships or trends among various groups within a population. Cross-sectional studies are helpful for market segmentation, identifying target audiences and assessing market trends at a specific moment.
7. Longitudinal research
Longitudinal research, in contrast to cross-sectional research, collects data from the same subjects over an extended period. This allows for the analysis of trends, changes and developments over time. Longitudinal studies are useful for tracking long-term developments in consumer preferences, brand loyalty and market dynamics.
Each type of market research has its strengths and weaknesses, and the method you choose depends on your specific research goals and the depth of understanding you’re aiming to achieve. In the following sections, we’ll delve into primary and secondary research approaches and specific research methods.
Primary vs. secondary market research
Market research of all types can be broadly categorized into two main approaches: primary research and secondary research. By understanding the differences between these approaches, you can better determine the most appropriate research method for your specific goals.
Primary market research
Primary research involves the collection of original data straight from the source. Typically, this involves communicating directly with your target audience — through surveys, interviews, focus groups and more — to gather information. Here are some key attributes of primary market research:
- Customized data: Primary research provides data that is tailored to your research needs. You design a custom research study and gather information specific to your goals.
- Up-to-date insights: Because primary research involves communicating with customers, the data you collect reflects the most current market conditions and consumer behaviors.
- Time-consuming and resource-intensive: Despite its advantages, primary research can be labor-intensive and costly, especially when dealing with large sample sizes or complex study designs. Whether you hire a market research consultant, agency or use an in-house team, primary research studies consume a large amount of resources and time.
Secondary market research
Secondary research, on the other hand, involves analyzing data that has already been compiled by third-party sources, such as online research tools, databases, news sites, industry reports and academic studies.

Here are the main characteristics of secondary market research:
- Cost-effective: Secondary research is generally more cost-effective than primary research since it doesn’t require building a research plan from scratch. You and your team can look at databases, websites and publications on an ongoing basis, without needing to design a custom experiment or hire a consultant.
- Leverages multiple sources: Data tools and software extract data from multiple places across the web, and then consolidate that information within a single platform. This means you’ll get a greater amount of data and a wider scope from secondary research.
- Quick to access: You can access a wide range of information rapidly — often in seconds — if you’re using online research tools and databases. Because of this, you can act on insights sooner, rather than taking the time to develop an experiment.
So, when should you use primary vs. secondary research? In practice, many market research projects incorporate both primary and secondary research to take advantage of the strengths of each approach.
One rule of thumb is to focus on secondary research to obtain background information, market trends or industry benchmarks. It is especially valuable for conducting preliminary research, competitor analysis, or when time and budget constraints are tight. Then, if you still have knowledge gaps or need to answer specific questions unique to your business model, use primary research to create a custom experiment.
Market research methods
- Surveys and questionnaires
- Focus groups
- Observational research
- Online research tools
- Experiments
- Content analysis
- Ethnographic research
How do primary and secondary research approaches translate into specific research methods? Let’s take a look at the different ways you can gather data:
1. Surveys and questionnaires
Surveys and questionnaires are popular methods for collecting structured data from a large number of respondents. They involve a set of predetermined questions that participants answer. Surveys can be conducted through various channels, including online tools, telephone interviews and in-person or online questionnaires. They are useful for gathering quantitative data and assessing customer demographics, opinions, preferences and needs. On average, customer surveys have a 33% response rate , so keep that in mind as you consider your sample size.
2. Interviews
Interviews are in-depth conversations with individuals or groups to gather qualitative insights. They can be structured (with predefined questions) or unstructured (with open-ended discussions). Interviews are valuable for exploring complex topics, uncovering motivations and obtaining detailed feedback.
3. Focus groups
The most common primary research methods are in-depth webcam interviews and focus groups. Focus groups are a small gathering of participants who discuss a specific topic or product under the guidance of a moderator. These discussions are valuable for primary market research because they reveal insights into consumer attitudes, perceptions and emotions. Focus groups are especially useful for idea generation, concept testing and understanding group dynamics within your target audience.
4. Observational research
Observational research involves observing and recording participant behavior in a natural setting. This method is particularly valuable when studying consumer behavior in physical spaces, such as retail stores or public places. In some types of observational research, participants are aware you’re watching them; in other cases, you discreetly watch consumers without their knowledge, as they use your product. Either way, observational research provides firsthand insights into how people interact with products or environments.
5. Online research tools
You and your team can do your own secondary market research using online tools. These tools include data prospecting platforms and databases, as well as online surveys, social media listening, web analytics and sentiment analysis platforms. They help you gather data from online sources, monitor industry trends, track competitors, understand consumer preferences and keep tabs on online behavior. We’ll talk more about choosing the right market research tools in the sections that follow.
6. Experiments
Market research experiments are controlled tests of variables to determine causal relationships. While experiments are often associated with scientific research, they are also used in market research to assess the impact of specific marketing strategies, product features, or pricing and packaging changes.
7. Content analysis
Content analysis involves the systematic examination of textual, visual or audio content to identify patterns, themes and trends. It’s commonly applied to customer reviews, social media posts and other forms of online content to analyze consumer opinions and sentiments.
8. Ethnographic research
Ethnographic research immerses researchers into the daily lives of consumers to understand their behavior and culture. This method is particularly valuable when studying niche markets or exploring the cultural context of consumer choices.
How to do market research
- Set clear objectives
- Identify your target audience
- Choose your research methods
- Use the right market research tools
- Collect data
- Analyze data
- Interpret your findings
- Identify opportunities and challenges
- Make informed business decisions
- Monitor and adapt
Now that you have gained insights into the various market research methods at your disposal, let’s delve into the practical aspects of how to conduct market research effectively. Here’s a quick step-by-step overview, from defining objectives to monitoring market shifts.
1. Set clear objectives
When you set clear and specific goals, you’re essentially creating a compass to guide your research questions and methodology. Start by precisely defining what you want to achieve. Are you launching a new product and want to understand its viability in the market? Are you evaluating customer satisfaction with a product redesign?
Start by creating SMART goals — objectives that are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound. Not only will this clarify your research focus from the outset, but it will also help you track progress and benchmark your success throughout the process.
You should also consult with key stakeholders and team members to ensure alignment on your research objectives before diving into data collecting. This will help you gain diverse perspectives and insights that will shape your research approach.
2. Identify your target audience
Next, you’ll need to pinpoint your target audience to determine who should be included in your research. Begin by creating detailed buyer personas or stakeholder profiles. Consider demographic factors like age, gender, income and location, but also delve into psychographics, such as interests, values and pain points.
The more specific your target audience, the more accurate and actionable your research will be. Additionally, segment your audience if your research objectives involve studying different groups, such as current customers and potential leads.
If you already have existing customers, you can also hold conversations with them to better understand your target market. From there, you can refine your buyer personas and tailor your research methods accordingly.
3. Choose your research methods
Selecting the right research methods is crucial for gathering high-quality data. Start by considering the nature of your research objectives. If you’re exploring consumer preferences, surveys and interviews can provide valuable insights. For in-depth understanding, focus groups or observational research might be suitable. Consider using a mix of quantitative and qualitative methods to gain a well-rounded perspective.
You’ll also need to consider your budget. Think about what you can realistically achieve using the time and resources available to you. If you have a fairly generous budget, you may want to try a mix of primary and secondary research approaches. If you’re doing market research for a startup , on the other hand, chances are your budget is somewhat limited. If that’s the case, try addressing your goals with secondary research tools before investing time and effort in a primary research study.
4. Use the right market research tools
Whether you’re conducting primary or secondary research, you’ll need to choose the right tools. These can help you do anything from sending surveys to customers to monitoring trends and analyzing data. Here are some examples of popular market research tools:
- Market research software: Crunchbase is a platform that provides best-in-class company data, making it valuable for market research on growing companies and industries. You can use Crunchbase to access trusted, first-party funding data, revenue data, news and firmographics, enabling you to monitor industry trends and understand customer needs.
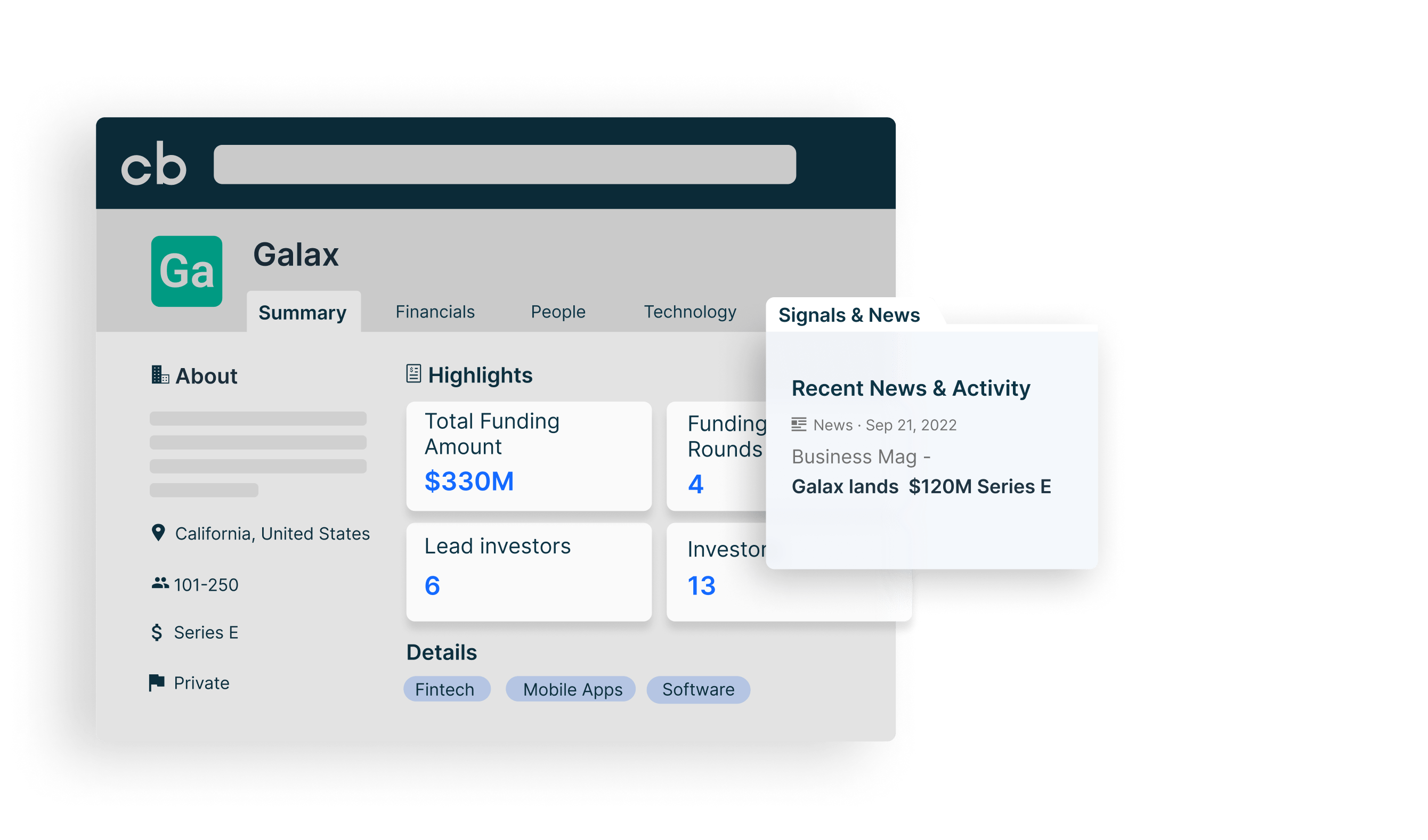
- Survey and questionnaire tools: SurveyMonkey is a widely used online survey platform that allows you to create, distribute and analyze surveys. Google Forms is a free tool that lets you create surveys and collect responses through Google Drive.
- Data analysis software: Microsoft Excel and Google Sheets are useful for conducting statistical analyses. SPSS is a powerful statistical analysis software used for data processing, analysis and reporting.
- Social listening tools: Brandwatch is a social listening and analytics platform that helps you monitor social media conversations, track sentiment and analyze trends. Mention is a media monitoring tool that allows you to track mentions of your brand, competitors and keywords across various online sources.
- Data visualization platforms: Tableau is a data visualization tool that helps you create interactive and shareable dashboards and reports. Power BI by Microsoft is a business analytics tool for creating interactive visualizations and reports.
5. Collect data
There’s an infinite amount of data you could be collecting using these tools, so you’ll need to be intentional about going after the data that aligns with your research goals. Implement your chosen research methods, whether it’s distributing surveys, conducting interviews or pulling from secondary research platforms. Pay close attention to data quality and accuracy, and stick to a standardized process to streamline data capture and reduce errors.
6. Analyze data
Once data is collected, you’ll need to analyze it systematically. Use statistical software or analysis tools to identify patterns, trends and correlations. For qualitative data, employ thematic analysis to extract common themes and insights. Visualize your findings with charts, graphs and tables to make complex data more understandable.
If you’re not proficient in data analysis, consider outsourcing or collaborating with a data analyst who can assist in processing and interpreting your data accurately.

7. Interpret your findings
Interpreting your market research findings involves understanding what the data means in the context of your objectives. Are there significant trends that uncover the answers to your initial research questions? Consider the implications of your findings on your business strategy. It’s essential to move beyond raw data and extract actionable insights that inform decision-making.
Hold a cross-functional meeting or workshop with relevant team members to collectively interpret the findings. Different perspectives can lead to more comprehensive insights and innovative solutions.
8. Identify opportunities and challenges
Use your research findings to identify potential growth opportunities and challenges within your market. What segments of your audience are underserved or overlooked? Are there emerging trends you can capitalize on? Conversely, what obstacles or competitors could hinder your progress?
Lay out this information in a clear and organized way by conducting a SWOT analysis, which stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. Jot down notes for each of these areas to provide a structured overview of gaps and hurdles in the market.
9. Make informed business decisions
Market research is only valuable if it leads to informed decisions for your company. Based on your insights, devise actionable strategies and initiatives that align with your research objectives. Whether it’s refining your product, targeting new customer segments or adjusting pricing, ensure your decisions are rooted in the data.
At this point, it’s also crucial to keep your team aligned and accountable. Create an action plan that outlines specific steps, responsibilities and timelines for implementing the recommendations derived from your research.
10. Monitor and adapt
Market research isn’t a one-time activity; it’s an ongoing process. Continuously monitor market conditions, customer behaviors and industry trends. Set up mechanisms to collect real-time data and feedback. As you gather new information, be prepared to adapt your strategies and tactics accordingly. Regularly revisiting your research ensures your business remains agile and reflects changing market dynamics and consumer preferences.
Online market research sources
As you go through the steps above, you’ll want to turn to trusted, reputable sources to gather your data. Here’s a list to get you started:
- Crunchbase: As mentioned above, Crunchbase is an online platform with an extensive dataset, allowing you to access in-depth insights on market trends, consumer behavior and competitive analysis. You can also customize your search options to tailor your research to specific industries, geographic regions or customer personas.
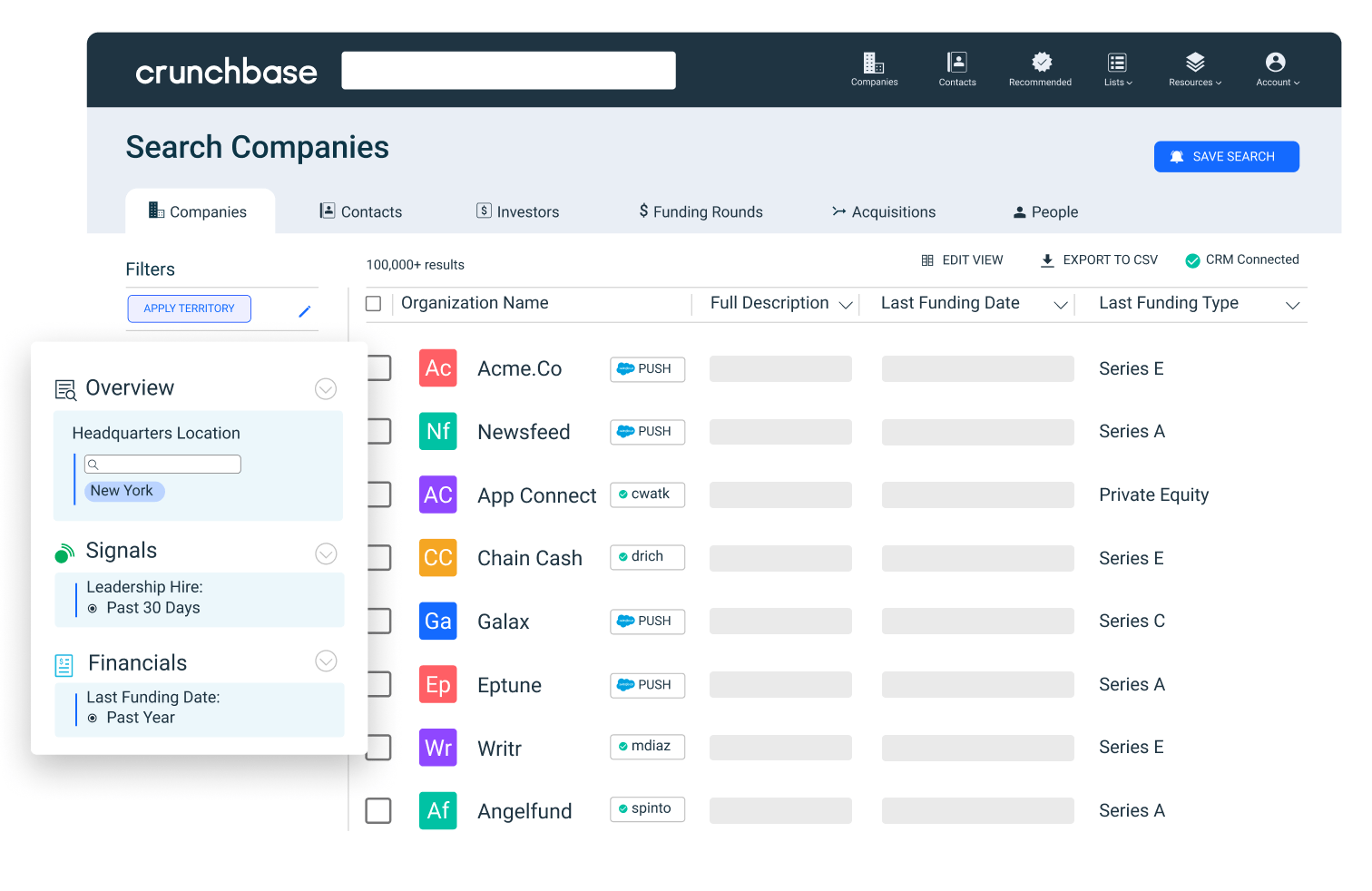
- Academic databases: Academic databases, such as ProQuest and JSTOR , are treasure troves of scholarly research papers, studies and academic journals. They offer in-depth analyses of various subjects, including market trends, consumer preferences and industry-specific insights. Researchers can access a wealth of peer-reviewed publications to gain a deeper understanding of their research topics.
- Government and NGO databases: Government agencies, nongovernmental organizations and other institutions frequently maintain databases containing valuable economic, demographic and industry-related data. These sources offer credible statistics and reports on a wide range of topics, making them essential for market researchers. Examples include the U.S. Census Bureau , the Bureau of Labor Statistics and the Pew Research Center .
- Industry reports: Industry reports and market studies are comprehensive documents prepared by research firms, industry associations and consulting companies. They provide in-depth insights into specific markets, including market size, trends, competitive analysis and consumer behavior. You can find this information by looking at relevant industry association databases; examples include the American Marketing Association and the National Retail Federation .
- Social media and online communities: Social media platforms like LinkedIn or Twitter (X) , forums such as Reddit and Quora , and review platforms such as G2 can provide real-time insights into consumer sentiment, opinions and trends.
Market research examples
At this point, you have market research tools and data sources — but how do you act on the data you gather? Let’s go over some real-world examples that illustrate the practical application of market research across various industries. These examples showcase how market research can lead to smart decision-making and successful business decisions.
Example 1: Apple’s iPhone launch
Apple ’s iconic iPhone launch in 2007 serves as a prime example of market research driving product innovation in tech. Before the iPhone’s release, Apple conducted extensive market research to understand consumer preferences, pain points and unmet needs in the mobile phone industry. This research led to the development of a touchscreen smartphone with a user-friendly interface, addressing consumer demands for a more intuitive and versatile device. The result was a revolutionary product that disrupted the market and redefined the smartphone industry.

Example 2: McDonald’s global expansion
McDonald’s successful global expansion strategy demonstrates the importance of market research when expanding into new territories. Before entering a new market, McDonald’s conducts thorough research to understand local tastes, preferences and cultural nuances. This research informs menu customization, marketing strategies and store design. For instance, in India, McDonald’s offers a menu tailored to local preferences, including vegetarian options. This market-specific approach has enabled McDonald’s to adapt and thrive in diverse global markets.
Example 3: Organic and sustainable farming
The shift toward organic and sustainable farming practices in the food industry is driven by market research that indicates increased consumer demand for healthier and environmentally friendly food options. As a result, food producers and retailers invest in sustainable sourcing and organic product lines — such as with these sustainable seafood startups — to align with this shift in consumer values.
The bottom line? Market research has multiple use cases and is a critical practice for any industry. Whether it’s launching groundbreaking products, entering new markets or responding to changing consumer preferences, you can use market research to shape successful strategies and outcomes.
Market research templates
You finally have a strong understanding of how to do market research and apply it in the real world. Before we wrap up, here are some market research templates that you can use as a starting point for your projects:
- Smartsheet competitive analysis templates : These spreadsheets can serve as a framework for gathering information about the competitive landscape and obtaining valuable lessons to apply to your business strategy.
- SurveyMonkey product survey template : Customize the questions on this survey based on what you want to learn from your target customers.
- HubSpot templates : HubSpot offers a wide range of free templates you can use for market research, business planning and more.
- SCORE templates : SCORE is a nonprofit organization that provides templates for business plans, market analysis and financial projections.
- SBA.gov : The U.S. Small Business Administration offers templates for every aspect of your business, including market research, and is particularly valuable for new startups.
Strengthen your business with market research
When conducted effectively, market research is like a guiding star. Equipped with the right tools and techniques, you can uncover valuable insights, stay competitive, foster innovation and navigate the complexities of your industry.
Throughout this guide, we’ve discussed the definition of market research, different research methods, and how to conduct it effectively. We’ve also explored various types of market research and shared practical insights and templates for getting started.
Now, it’s time to start the research process. Trust in data, listen to the market and make informed decisions that guide your company toward lasting success.
Related Articles

- Entrepreneurs
- 15 min read
What Is Competitive Analysis and How to Do It Effectively
Rebecca Strehlow, Copywriter at Crunchbase
17 Best Sales Intelligence Tools for 2024

- Market research
- 10 min read
How to Do Market Research for a Startup: Tips for Success
Jaclyn Robinson, Senior Manager of Content Marketing at Crunchbase
Search less. Close more.
Grow your revenue with Crunchbase, the all-in-one prospecting solution. Start your free trial.
Market Research: A How-To Guide and Template
Discover the different types of market research, how to conduct your own market research, and use a free template to help you along the way.

MARKET RESEARCH KIT
5 Research and Planning Templates + a Free Guide on How to Use Them in Your Market Research

Updated: 02/21/24
Published: 03/30/16
Today's consumers have a lot of power. As a business, you must have a deep understanding of who your buyers are and what influences their purchase decisions.
Enter: Market Research.
![market research example of → Download Now: Market Research Templates [Free Kit]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/6ba52ce7-bb69-4b63-965b-4ea21ba905da.png)
Whether you're new to market research or not, I created this guide to help you conduct a thorough study of your market, target audience, competition, and more. Let’s dive in.
Table of Contents
What is market research?
Primary vs. secondary research, types of market research, how to do market research, market research report template, market research examples.
Market research is the process of gathering information about your target market and customers to verify the success of a new product, help your team iterate on an existing product, or understand brand perception to ensure your team is effectively communicating your company's value effectively.
Market research can answer various questions about the state of an industry. But if you ask me, it's hardly a crystal ball that marketers can rely on for insights on their customers.
Market researchers investigate several areas of the market, and it can take weeks or even months to paint an accurate picture of the business landscape.
However, researching just one of those areas can make you more intuitive to who your buyers are and how to deliver value that no other business is offering them right now.
How? Consider these two things:
- Your competitors also have experienced individuals in the industry and a customer base. It‘s very possible that your immediate resources are, in many ways, equal to those of your competition’s immediate resources. Seeking a larger sample size for answers can provide a better edge.
- Your customers don't represent the attitudes of an entire market. They represent the attitudes of the part of the market that is already drawn to your brand.
The market research services market is growing rapidly, which signifies a strong interest in market research as we enter 2024. The market is expected to grow from roughly $75 billion in 2021 to $90.79 billion in 2025 .
.png)
Free Market Research Kit
- SWOT Analysis Template
- Survey Template
- Focus Group Template
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Why do market research?
Market research allows you to meet your buyer where they are.
As our world becomes louder and demands more of our attention, this proves invaluable.
By understanding your buyer's problems, pain points, and desired solutions, you can aptly craft your product or service to naturally appeal to them.
Market research also provides insight into the following:
- Where your target audience and current customers conduct their product or service research
- Which of your competitors your target audience looks to for information, options, or purchases
- What's trending in your industry and in the eyes of your buyer
- Who makes up your market and what their challenges are
- What influences purchases and conversions among your target audience
- Consumer attitudes about a particular topic, pain, product, or brand
- Whether there‘s demand for the business initiatives you’re investing in
- Unaddressed or underserved customer needs that can be flipped into selling opportunity
- Attitudes about pricing for a particular product or service
Ultimately, market research allows you to get information from a larger sample size of your target audience, eliminating bias and assumptions so that you can get to the heart of consumer attitudes.
As a result, you can make better business decisions.
To give you an idea of how extensive market research can get , consider that it can either be qualitative or quantitative in nature — depending on the studies you conduct and what you're trying to learn about your industry.
Qualitative research is concerned with public opinion, and explores how the market feels about the products currently available in that market.
Quantitative research is concerned with data, and looks for relevant trends in the information that's gathered from public records.
That said, there are two main types of market research that your business can conduct to collect actionable information on your products: primary research and secondary research.
Primary Research
Primary research is the pursuit of first-hand information about your market and the customers within your market.
It's useful when segmenting your market and establishing your buyer personas.
Primary market research tends to fall into one of two buckets:
- Exploratory Primary Research: This kind of primary market research normally takes place as a first step — before any specific research has been performed — and may involve open-ended interviews or surveys with small numbers of people.
- Specific Primary Research: This type of research often follows exploratory research. In specific research, you take a smaller or more precise segment of your audience and ask questions aimed at solving a suspected problem.
Secondary Research
Secondary research is all the data and public records you have at your disposal to draw conclusions from (e.g. trend reports, market statistics, industry content, and sales data you already have on your business).
Secondary research is particularly useful for analyzing your competitors . The main buckets your secondary market research will fall into include:
- Public Sources: These sources are your first and most-accessible layer of material when conducting secondary market research. They're often free to find and review — like government statistics (e.g., from the U.S. Census Bureau ).
- Commercial Sources: These sources often come in the form of pay-to-access market reports, consisting of industry insight compiled by a research agency like Pew , Gartner , or Forrester .
- Internal Sources: This is the market data your organization already has like average revenue per sale, customer retention rates, and other historical data that can help you draw conclusions on buyer needs.
- Focus Groups
- Product/ Service Use Research
- Observation-Based Research
- Buyer Persona Research
- Market Segmentation Research
- Pricing Research
- Competitive Analysis Research
- Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty Research
- Brand Awareness Research
- Campaign Research
1. Interviews
Interviews allow for face-to-face discussions so you can allow for a natural flow of conversation. Your interviewees can answer questions about themselves to help you design your buyer personas and shape your entire marketing strategy.
2. Focus Groups
Focus groups provide you with a handful of carefully-selected people that can test out your product and provide feedback. This type of market research can give you ideas for product differentiation.
3. Product/Service Use Research
Product or service use research offers insight into how and why your audience uses your product or service. This type of market research also gives you an idea of the product or service's usability for your target audience.
4. Observation-Based Research
Observation-based research allows you to sit back and watch the ways in which your target audience members go about using your product or service, what works well in terms of UX , and which aspects of it could be improved.
5. Buyer Persona Research
Buyer persona research gives you a realistic look at who makes up your target audience, what their challenges are, why they want your product or service, and what they need from your business or brand.
6. Market Segmentation Research
Market segmentation research allows you to categorize your target audience into different groups (or segments) based on specific and defining characteristics. This way, you can determine effective ways to meet their needs.
7. Pricing Research
Pricing research helps you define your pricing strategy . It gives you an idea of what similar products or services in your market sell for and what your target audience is willing to pay.
8. Competitive Analysis
Competitive analyses give you a deep understanding of the competition in your market and industry. You can learn about what's doing well in your industry and how you can separate yourself from the competition .
9. Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty Research
Customer satisfaction and loyalty research gives you a look into how you can get current customers to return for more business and what will motivate them to do so (e.g., loyalty programs , rewards, remarkable customer service).
10. Brand Awareness Research
Brand awareness research tells you what your target audience knows about and recognizes from your brand. It tells you about the associations people make when they think about your business.
11. Campaign Research
Campaign research entails looking into your past campaigns and analyzing their success among your target audience and current customers. The goal is to use these learnings to inform future campaigns.
- Define your buyer persona.
- Identify a persona group to engage.
- Prepare research questions for your market research participants.
- List your primary competitors.
- Summarize your findings.
1. Define your buyer persona.
You have to understand who your customers are and how customers in your industry make buying decisions.
This is where your buyer personas come in handy. Buyer personas — sometimes referred to as marketing personas — are fictional, generalized representations of your ideal customers.
Use a free tool to create a buyer persona that your entire company can use to market, sell, and serve better.

10 Free Competitive Analysis Templates
Track and analyze your competitors with these ten free planning templates.
- SWOT Analysis
- Battle Cards
- Feature Comparison
- Strategic Overview
Identifying Content Competitors
Search engines are your best friends in this area of secondary market research.
To find the online publications with which you compete, take the overarching industry term you identified in the section above, and come up with a handful of more specific industry terms your company identifies with.
A catering business, for example, might generally be a “food service” company, but also consider itself a vendor in “event catering,” “cake catering,” or “baked goods.” Once you have this list, do the following:
- Google it. Don't underestimate the value in seeing which websites come up when you run a search on Google for the industry terms that describe your company. You might find a mix of product developers, blogs, magazines, and more.
- Compare your search results against your buyer persona. If the content the website publishes seems like the stuff your buyer persona would want to see, it's a potential competitor, and should be added to your list of competitors.
5. Summarize your findings.
Feeling overwhelmed by the notes you took? We suggest looking for common themes that will help you tell a story and create a list of action items.
To make the process easier, try using your favorite presentation software to make a report, as it will make it easy to add in quotes, diagrams, or call clips.
Feel free to add your own flair, but the following outline should help you craft a clear summary:
- Background: Your goals and why you conducted this study.
- Participants: Who you talked to. A table works well so you can break groups down by persona and customer/prospect.
- Executive Summary : What were the most interesting things you learned? What do you plan to do about it?
- Awareness: Describe the common triggers that lead someone to enter into an evaluation. (Quotes can be very powerful.)
- Consideration: Provide the main themes you uncovered, as well as the detailed sources buyers use when conducting their evaluation.
- Decision: Paint the picture of how a decision is really made by including the people at the center of influence and any product features or information that can make or break a deal.
- Action Plan: Your analysis probably uncovered a few campaigns you can run to get your brand in front of buyers earlier and/or more effectively. Provide your list of priorities, a timeline, and the impact it will have on your business.
Within a market research kit, there are a number of critical pieces of information for your business‘s success. Let’s take a look at these elements.
Pro Tip: Upon downloading HubSpot's free Market Research Kit , you'll receive editable templates for each of the given parts of the kit, instructions on how to use the kit, and a mock presentation that you can edit and customize.

What Is a Competitive Analysis — and How Do You Conduct One?
![market research example of The Beginner's Guide to the Competitive Matrix [+ Templates]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/competitive-matrix-1-20240828-9831599.webp)
The Beginner's Guide to the Competitive Matrix [+ Templates]
![market research example of 9 Best Marketing Research Methods to Know Your Buyer Better [+ Examples]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/marketing-research-methods-featured.png)
9 Best Marketing Research Methods to Know Your Buyer Better [+ Examples]
![market research example of SWOT Analysis: How To Do One [With Template & Examples]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/marketingplan_20.webp)
SWOT Analysis: How To Do One [With Template & Examples]

28 Tools & Resources for Conducting Market Research

TAM, SAM & SOM: What Do They Mean & How Do You Calculate Them?
![market research example of How to Run a Competitor Analysis [Free Guide]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/Google%20Drive%20Integration/how%20to%20do%20a%20competitor%20analysis_122022.jpeg)
How to Run a Competitor Analysis [Free Guide]
![market research example of 5 Challenges Marketers Face in Understanding Audiences [New Data + Market Researcher Tips]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/challenges%20marketers%20face%20in%20understanding%20the%20customer%20.png)
5 Challenges Marketers Face in Understanding Audiences [New Data + Market Researcher Tips]

Causal Research: The Complete Guide

Total Addressable Market (TAM): What It Is & How You Can Calculate It
Free Guide & Templates to Help Your Market Research
The weekly email to help take your career to the next level. No fluff, only first-hand expert advice & useful marketing trends.
Must enter a valid email
We're committed to your privacy. HubSpot uses the information you provide to us to contact you about our relevant content, products, and services. You may unsubscribe from these communications at any time. For more information, check out our privacy policy .
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
You've been subscribed

IMAGES
VIDEO