
- Productivity
- Thoughtful learning

Become a better critical thinker with these 7 critical thinking exercises

Critical thinking is a skill you can use in any situation. Whether you're a student, entrepreneur, or business executive, critical thinking can help you make better decisions and solve problems.
But learning critical thinking skills isn't always an easy task. Many tools, techniques, and strategies are available, and choosing the right one can be challenging. Vague suggestions on the internet like "read more" aren't very helpful, and elaborate business examples don’t apply to many of us.
As average problem-solvers, we need actionable thinking exercises to improve our critical thinking skills and enhance our thinking processes. Regularly performing exercises that specifically stretch our decision-making and reasoning skills is the most effective method of improving our thinking abilities.
This article will explore several exercises that will help you develop critical thinking skills. Whether you are preparing for an exam, making an influential decision for your business, or going about your daily life, these fun activities can build your reasoning skills and creative problem-solving abilities.
Boost your logical thinking skills and start practicing a critical mindset with these 10 critical thinking exercises.
A Quick Look at Critical Thinking
As a thoughtful learner, you likely already understand the basics of critical thinking, but here's a quick refresher.
Critical thinking involves analyzing problems or issues objectively and rationally. Critical thinkers are able to understand their own biases and assumptions, as well as those of others. They’re also able to see the world from a different point of view and understand how their experiences impact their thinking.
Developing critical thinking skills is essential because it allows us to see things from multiple perspectives, identify biases and errors in reasoning, and be open to possible solutions. Making informed decisions is easier when we have a better understanding of the world around us.
Why We Need to Practice Critical Thinking

We aren't born with critical thinking skills, and they don’t naturally develop beyond survival-level thinking. To master critical thinking, we must practice it and develop it over time.
However, learning to think critically isn't as easy as learning to ride a bicycle. There aren't any step-by-step procedures to follow or supportive guides to fall back on, and it is not taught in public schools consistently or reliably. To ensure students' success, teachers must know higher-order thinking skills (HOTS) and how to teach them, research says.
Unfortunately, although teachers understand the importance of HOTS and attempt to teach it, studies show that their capacity to measure students' HOTS is low. Educator and author Dr. Kulvarn Atwal says, "It seems that we are becoming successful at producing students who are able to jump through hoops and pass tests."
As critical thinking skills become more important in higher grades, some students find it challenging to understand the concept of critical thinking. To develop necessary thinking skills, we must set aside our assumptions and beliefs. This allows us to explore and question topics from a "blank page" point of view and distinguish fact from opinion.
Be the first to try it out!
We're developing ABLE, a powerful tool for building your personal knowledge, capturing information from the web, conducting research, taking notes, and writing content.
7 Critical Thinking Exercises To Improve Your Critical Thinking Skills

The good news is that by assessing, analyzing, and evaluating our thought processes, we can improve our skills. Critical thinking exercises are key to this improvement. Our critical thinking builds and improves with regular practice, just like a muscle that gets stronger with use.
If you want to become a better critical thinker , here are some critical thinking exercises to try:
Exercise #1: The Ladder of Inference
You can exercise your critical thinking skills by using the Ladder of Inference model . This thinking model was developed by renowned organizational psychologist Chris Argyris. Each rung on the ladder of inference represents a step you take to arrive at your conclusions.
The decision-making process starts when we are faced with a problem or situation. As soon as we observe something problematic or important, we presume what is causing it, and then we use that assumption to draw conclusions. Based on those conclusions, we take action.
For example, say you're at a party and see a friend across the room. You catch their eye and wave, but they turn and walk away. Using the ladder, you might climb the rungs as follows:
- Observe that your friend walked away.
- Select a few details of the situation, including your wave and your assumption that they saw you.
- Meaning is attached based on the environment, making you think your friend must have other people to talk to at the party.
- Assumptions are made based on that meaning, assuming that means your friend doesn’t like you as much as them.
- Conclusions are drawn from the assumption, and you determine that your friend must be mad at you or doesn't want you to be at the party.
- Beliefs are formed, making you think you're not welcome.
- Action is taken, and you leave the party.
In this example, you started with a situation (someone walking away at a crowded party) and made a series of inferences to arrive at a conclusion (that the person is mad at you and doesn't want you there).
The Ladder of Inference can be a helpful tool to frame your thinking because it encourages you to examine each step of your thought process and avoid jumping to conclusions. It's easy to make assumptions without realizing it, as in this scene. Perhaps your friend never even saw you wave from across the crowded room.
Exercise #2: The Five Whys
The "Five Whys" technique is an analytical skill that can help you uncover the source of a problem. The activity was created by Sakichi Toyoda, the founder of Toyota, and consists of repeatedly asking “why?” when a problem is encountered to determine its root cause.
This exercise can be difficult because knowing if you've discovered the source of your problem is challenging. The "five" in "Five Whys" is just a guideline — you may need to ask more. When you can't ask anything else, and your response is related to the original issue, you've probably arrived at the end.
Even if you need several rounds of questioning, just keep going. The important part that helps you practice critical thinking is the process of asking "why?" and uncovering the deeper issues affecting the situation.
For instance, say you're trying to figure out why your computer keeps crashing.
- You ask " why ," and the answer is that there's a software problem.
- Why? Because the computer keeps running out of memory.
- Why? Because too many programs are running at the same time.
- Why? Because too many browser tabs are open .
- Why? Because multitasking is fragmenting your focus, you're doing too many things at once.
In this example, working through the "why's" revealed the underlying cause. As a result, you can find the best solution, which is concentrating on just one thing at a time.
Exercise #3: Inversion

Inversion is another critical thinking exercise that you can use in any situation. Inversion is sort of like taking on the role of the devil's advocate. In this exercise, adopt the opposite view of whatever issue you're exploring and consider the potential arguments for that side. This will help broaden your critical thinking skills and enable you to see other perspectives on a situation or topic more clearly.
For example, let's say you're thinking about starting your own business. Using inversion, you would explore all of the potential arguments for why starting your own business is bad. This might include concerns like:
- You could end up in debt.
- The business might fail.
- It's a lot of work.
- You might not have time for anything else.
By exploring these potentially adverse outcomes, you can identify the potential risks involved in starting your own business and make a more sound decision. You might realize that now is not the right time for you to become an entrepreneur. And if you do start the company, you'll be better prepared to deal with the issues you identified when they occur.
Exercise #4: Argument Mapping
Argument mapping can be a beneficial exercise for enhancing critical thinking skills. Like mind mapping, argument mapping is a method of visually representing an argument's structure. It helps analyze and evaluate ideas as well as develop new ones.
In critical thinking textbooks, argument diagramming is often presented to introduce students to argument constructions. It can be an effective way to build mental templates or schema for argument structures, which researchers think may make critical evaluation easier .
Argument maps typically include the following:
- Conclusion: What is being argued for or against
- Premises: The reasons given to support the conclusion
- Inferences: The connections made between the premises and conclusion
The argument map should be as clear and concise as possible, with a single word or phrase representing each element. This will help you make connections more easily. After the map is completed, you can use it to identify any weak points in the argument. If any areas aren't well-supported, additional premises can be added.
Argument mapping can be applied to any situation that requires critical thinking skills. The more time you take to map out an argument, the better you'll understand how the pieces fit together. Ultimately, this will help you think more creatively and critically, and make more informed decisions.
Exercise #5: Opinion vs. Fact
Critical thinking activities that focus on opinions and facts are particularly valuable and relevant new learning opportunities. Our constantly-connected world makes it easy to confuse opinions and facts , especially with sensationalist news articles and click-bait headlines.
How can you tell a fact from an opinion? Facts are generally objective and established, whereas opinions are subjective and unproven. For example, "the cloud is in the air" is a fact. "That dress looks good on you" is an opinion.
Practice your critical thinking skills by reading or listening to the news. See if you can identify when someone is stating an opinion rather than a fact. Ask yourself the following questions:
- Who is saying what? What reasons might be behind their statements?
- Does the claim make sense? Who would disagree with it and why?
- How can you tell if the data is reliable? Can it be fact-checked? Has it been shared by other credible publishers?
- How do you know whether or not the presenter is biased? What kind of language is being used?
This powerful exercise can train your mind to start asking questions whenever presented with a new claim. This will help you think critically about the information you're taking in and question what you're hearing before accepting it as truth.
Exercise #6: Autonomy of an Object
In her book " The Critical Thinking Tool Kit ," Dr. Marlene Caroselli describes a critical thinking exercise called "Living Problems, Lively Solutions." This exercise uses the autonomy of an object as a problem-solving tool to find a possible solution.
To do this, you'll personify your problem and place it in another context — a different time or place. This allows you to uncover unique solutions to the problem that might be tied to your mental associations with that setting.
For example, if your problem is poor time management , you might personify the issue as a thief of your time. The idea of a thief could make you think of jail, which might prompt thoughts of locking up specific distractions in your life. The idea of jail could also make you think of guards and lead you to the possible solution of checking in with an accountability buddy who can make sure you're sticking to your schedule.
The autonomy-of-object technique works because it stimulates thoughts you wouldn’t have considered without the particular context in which you place the problem.
Exercise #7: The Six Thinking Hats
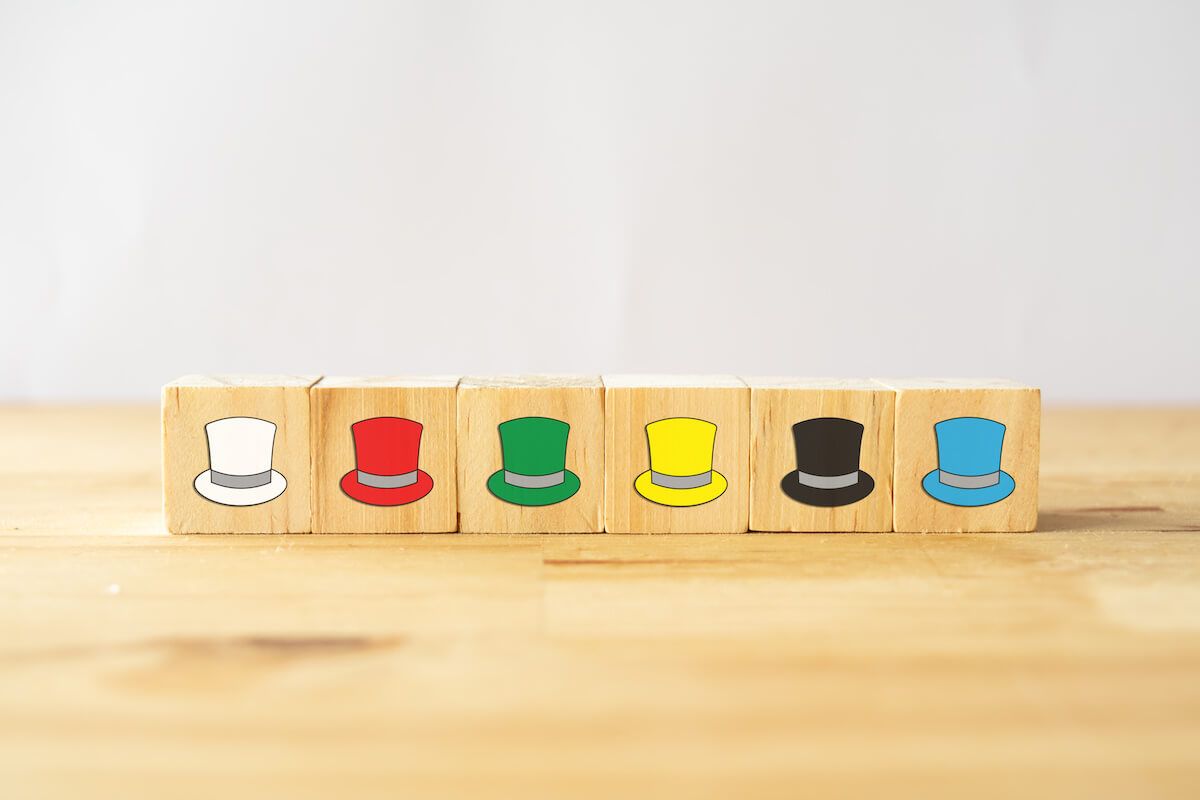

Designed by Edward de Bono, the Six Thinking Hats is a critical thinking exercise that was created as a tool for groups to use when exploring different perspectives on an issue. When people use other thinking processes, meetings can become challenging rather than beneficial.
To help teams work more productively and mindfully, de Bono suggests dividing up different styles of thinking into six categories, represented as hats:
- The white hat is objective and focuses on facts and logic
- The red hat is intuitive, focusing on emotion and instinct
- The black hat is cautious and predicts negative outcomes
- The yellow hat is optimistic and encourages positive outcomes
- The green hat is creative, with numerous ideas and little criticism
- The blue hat is the control hat used for management and organization
With each team member wearing a different hat, a group can examine an issue or problem from many different angles, preventing one viewpoint (or individual) from dominating the meeting or discussion. This means that decisions and solutions reached using the Six Thinking Hats approach will likely be more robust and effective, and everyone’s creative thinking skills will benefit.
Train Your Brain With Critical Thinking Exercises
Using critical thinking regularly in various situations can improve our ability to evaluate and analyze information. These seven critical thinking exercises train your brain for better critical thinking skills . With daily practice, they can become habits that will help you think more critically each day.
Improve your critical thinking with ABLE
Ask better questions and get better answers with ABLEs integrated web search, annotation and note-taking features. Check how ABLE helps you to improve your critical thinking.
I hope you have enjoyed reading this article. Feel free to share, recommend and connect 🙏
Connect with me on Twitter 👉 https://twitter.com/iamborisv
And follow Able's journey on Twitter: https://twitter.com/meet_able
And subscribe to our newsletter to read more valuable articles before it gets published on our blog.
Now we're building a Discord community of like-minded people, and we would be honoured and delighted to see you there.

Straight from the ABLE team: how we work and what we build. Thoughts, learnings, notes, experiences and what really matters.
Read more posts by this author
follow me :
Mental models: 13 thinking tools to boost your problem-solving skills
7 note-taking strategies to improve your study skills.

What is abstract thinking? 10 activities to improve your abstract thinking skills

5 examples of cognitive learning theory (and how you can use them)
0 results found.
- Aegis Alpha SA
- We build in public
Building with passion in
Reset password New user? Sign up
Existing user? Log in
- Number Theory
- Probability
- Everyday Math
- Classical Mechanics
- Electricity and Magnetism
- Computer Science
- Quantitative Finance
Take a guided, problem-solving based approach to learning Logic. These compilations provide unique perspectives and applications you won't find anywhere else.
What's inside
- Introduction
- Puzzles and Riddles
- Multi-Level Thinking
- The Rational Detective
- Syllogisms and Sets
- Logic Machines
- Arithmetic With Logic Gates
- Propositional Logic
- First-Order Logic
Community Wiki
Browse through thousands of Logic wikis written by our community of experts.
- Truth-Tellers and Liars
- Cryptogram - Problem Solving
- Solving Propositional Logic Word Problem
- Mind Reading with Math
- Information Compression
- K-level thinking
- Chess Puzzles
- Arithmetic Puzzles - Operator Search
- Arithmetic Puzzles - Fill in the Blanks
- Elimination Grids
- Grid Puzzles
- Combinatorial Games - Definition
- Combinatorial Games - Winning Positions
- Tic Tac Toe
- Sprague Grundy Theorem
- Chess Puzzles - Reduced Games
- Chess Puzzles - Opening Strategies
- Chess Puzzles - Rook Strategies
- Rook Polynomial
- Game Theory
- Nash Equilibrium
- Zero-Sum Games
- Prisoner's Dilemma
- Braess' Paradox
- Utility Functions
- Cognitive Bias
- Monty Hall Problem
- Birthday Problem
- Two-Envelope Paradox
- Simpson's Paradox
- Berkson's Paradox
- Newcomb's Paradox
- Benford's Law
- Mathematics of Voting
- Survivorship Bias
- Russell's Paradox
- Zeno's Paradox
- Gabriel's Horn
- Truth Tables
- Proof by Contradiction
- Mathematical Logic and Computability
- Mathematical Logic and Computability II (continuation)
- Propositional Logic Using Algebra
- Venn Diagram
- Predicate Logic
Problem Loading...
Note Loading...
Set Loading...

15 Things We Have Learned About Critical Thinking
Here are the key issues to consider in critical thinking..
Posted July 27, 2018
- What Is Cognition?
- Take our Mental Processing Test
- Find a therapist near me
Not long after the publication of my book, Critical Thinking: Conceptual Perspectives and Practical Guidelines , by Cambridge University Press, Psychology Today contacted me and asked me to write a blog on the subject. I never thought I would write a blog, but when presented with the opportunity to keep sharing my thoughts on critical thinking on a regular basis, I thought, why not ? Maybe my writing might help educators, maybe they might help students and maybe they might help people in their day-to-day decision-making . If it can help, then it’s worthwhile.
To recap, critical thinking (CT) is a metacognitive process, consisting of a number of sub-skills and dispositions, that, when applied through purposeful, self-regulatory, reflective judgment, increase the chances of producing a logical solution to a problem or a valid conclusion to an argument (Dwyer, 2017; Dwyer, Hogan & Stewart, 2014).
CT, if anything, has become more necessary , in this age of information bombardment and the new knowledge economy (Dwyer, Hogan & Stewart, 2014). It allows students to gain a better understanding of complex information (Dwyer, Hogan, & Stewart, 2012; 2014; Gambrill, 2006; Halpern, 2014); it allows them to achieve higher grades and become more employable, informed and active citizens (Barton & McCully, 2007; Holmes & Clizbe, 1997; National Academy of Sciences, 2005); it facilitates good decision-making and problem-solving in social and interpersonal contexts (Ku, 2009); and it decreases the effects of cognitive biases and heuristic -based thinking (Facione & Facione, 2001; McGuinness, 2013).
It’s now been just over a year since I started writing ‘Thoughts on Thinking’. As I consider my thinking and look over my writing during this period, I thought it would be worthwhile to collate and summarise some of the broader learning that has appeared in my writings. So, here’s what we’ve learned:
- We all know CT is important, but it may be the case that many educators, as well as students, don’t really know what researchers mean by "critical thinking" and/or simply haven’t researched it themselves.
- Just as many don’t really know what is meant by "critical thinking", there is also the problem of ensuring consistency across how it is defined/conceptualised, trained and measured , which is no easy task.
- Without adequate training in CT, it may be the case that mature students’ perceptions of how they approach CT do not match their actual ability - despite potentially enhanced autonomy, student responsibility and locus of control , it may be that an over- optimistic outlook on the benefits of experience (and its associated heuristic-based, intuitive judgment) takes centre-stage above and beyond actual ability.
- Social media is many things: entertainment, education , networking and much more. It is also, unfortunately, a vehicle for promoting faulty thinking. Being able to recognise persuasion techniques, illogical argumentation and fallacious reasoning , will allow you to better assess arguments presented to you, and help you to present better arguments.
- Values are unique to each and every individual. Though individuals can certainly share values, there is no guarantee that all of an individual’s values overlap with another’s. On the other hand, using the 'virtue' moniker implies that the individual is right based on some kind of ‘moral correctness’. Though there is nothing wrong with an individual presenting ideas and perspectives that they value, it is ill-conceived and dangerous to treat them as global virtues that everyone else should value too.
- CT is domain-g eneral, but explicit CT training is necessary if educators want to see CT improve and flourish across domains.
- A person with a strong willingness to conduct CT has the consistent internal willingness and motivation to engage problems and make decisions by using reflective judgment . Reflective judgment, the recognition of limited knowledge and how this uncertainty can affect decision-making processes, is an important aspect of critical thinking regarding ‘taking a step back’ and thinking about an argument or problem a little bit longer and considering the basis for the reasons and consequences of responding in a particular way.
- There is a need for general, secondary-school training in bias and statistics. We need to teach CT to the coming generations. When not critically thinking, people don’t listen, and fail to be open-minded and reflect upon the information presented to them; they project their opinions and beliefs regardless of whether or not they have evidence to support their claims.
- Be open-minded towards others. You don’t have to respect them (respect is earned, it’s not a right); but be courteous (sure, we may be in disagreement; but, hey, we’re still civilised people).
- A person said what they said, not how you interpret what they said. If you are unclear as to what has been said, ask for clarification. Asking for clarity is not a sign of weakness; it is a sign of successful problem-solving.
- ‘Proof’ is the dirtiest word in critical thinking. Research and science do not prove things, they can only disprove. Be wary when you hear the word ‘prove’ or any of its variants thrown around; but also, be mindful that people feel safer when they are assured and words like ‘proven’ reinforce this feeling of assuredness.
- Creative thinking isn’t really useful or practical in critical thinking, depending on how you conceptualize it. Critical thinking and creative thinking are very different entities if you treat the latter as something similar to lateral thinking or ‘thinking outside the box’. However, if we conceptualize creative thinking as synthesizing information for the purpose of inferring a logical and feasible conclusion or solution, then it becomes complementary to critical thinking. But then, we are not resorting to creativity alone - all other avenues involving critical thinking must be considered. That is, we can think creatively by synthesizing information we have previously thought about critically (i.e. through analysis and evaluation ) for the purpose of inferring a logical and feasible conclusion or solution. Thus, given this caveat, we can infuse our critical thinking with creative thinking, but we must do so with caution.
- Changing people’s minds is not easy ; and it’s even more difficult when the person you’re working with believes they have critically thought about it. It may simply boil down to the person you’re trying to educate and their disposition towards critical thinking, but the person’s emotional investment in their stance also plays a significant role.
- There is no such thing as good or bad CT – you either thought critically or you didn’t. Those who try it in good faith are likely to want to do it ‘properly’; and so, much of whether or not an individual is thinking critically comes down to intellectual humility and intellectual integrity .
- Finally, there are some general tips that people find useful in applying their critical thinking:
- Save your critical thinking for things that matter - things you care about.
- Do it earlier in your day to avoid faulty thinking resulting from decision fatigue.
- Take a step back and think about a problem a little bit longer, considering the basis for the reasons and consequences of responding in a particular way.
- Play Devil’s Advocate in order to overcome bias and 'auto-pilot processing' through truly considering alternatives.
- Leave emotion at the door and remove your beliefs, attitudes, opinions and personal experiences from the equation - all of which are emotionally charged.
Barton, K., & McCully, A. (2007). Teaching controversial issues where controversial issues really matter. Teaching History, 127, 13–19.
Dwyer, C.P. (2017). Critical thinking: Conceptual perspectives and practical guidelines. UK: Cambridge University Press.
Dwyer, C. P., Hogan, M. J., & Stewart, I. (2012). An evaluation of argument mapping as a method of enhancing critical thinking performance in e-learningenvironments. Metacognition and Learning, 7, 219–244.
Dwyer, C.P., Hogan, M.J. & Stewart, I. (2014). An integrated critical thinking framework for the 21st century. Thinking Skills & Creativity, 12, 43-52.
Eigenauer, J.D. (2017). Don’t reinvent the critical thinking wheel: What scholarly literature tells us about critical thinking instruction. Innovation Abstracts, 39, 2.
Facione, P. A., & Facione, N. C. (2001). Analyzing explanations for seemingly irrational choices: Linking argument analysis and cognitive science. International Journal of Applied Philosophy, 15(2), 267–286.
Gambrill, E. (2006). Evidence-based practice and policy: Choices ahead. Research on Social Work Practice, 16(3), 338–357.
Halpern, D.F. (2014). Though and knowledge. UK: Psychology Press.
Holmes, J., & Clizbe, E. (1997). Facing the 21st century. Business Education Forum, 52(1), 33–35.
Ku, K. Y. L. (2009). Assessing students’ critical thinking performance: Urging for measurements using multi-response format. Thinking Skills and Creativity,4(1), 70–76.
McGuinness, C. (2013). Teaching thinking: Learning how to think. Presented at the Psychological Society of Ireland and British Psychological Association’s Public Lecture Series. Galway, Ireland, 6th March.
National Academy of Sciences. (2005). National Academy of Engineering Institute of Medicine Rising above the gathering storm: Energising and employingAmerica for a brighter economic future. Committee on prospering in the global economy for the 21st century. Washington, DC.

Christopher Dwyer, Ph.D., is a lecturer at the Technological University of the Shannon in Athlone, Ireland.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

When we fall prey to perfectionism, we think we’re honorably aspiring to be our very best, but often we’re really just setting ourselves up for failure, as perfection is impossible and its pursuit inevitably backfires.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
- Book a Demo
Are you looking to enhance your or your team’s problem-solving abilities? Engaging in activities specifically designed to stimulate your and your team’s critical thinking skills can be an excellent way to sharpen your problem-solving prowess. Whether you enjoy puzzles, brain teasers, or interactive challenges, these activities provide an opportunity to overcome obstacles and think creatively.
By immersing yourself in problem-solving activities, you can develop valuable strategies, improve your decision-making abilities, and boost your overall problem-solving IQ.
One key aspect of successful problem-solving is ensuring clear and effective communication, such as when teams use critical tools available online. For example, testing emails for deliverability and using an email spam checker to avoid spam filters can improve team efficiency. Try Maileroo’s free mail tester to validate your email campaigns effectively. Get ready to unlock your full potential and tackle any challenge that comes your way with these exciting activities for problem-solving.
In this article, we will explore activities for problem-solving that can help enhance your team’s problem-solving skills, allowing you to approach challenges with confidence and creativity.
What Are Problem Solving Activities?
Problem-solving activities or problem-solving exercises are interactive games requiring critical thinking to solve puzzles. They enhance teamwork & critical thinking. Examples include building towers, navigating simulated challenges, and fostering creativity and communication.
For instance, imagine a team working together to construct the tallest tower using limited materials. They strategize, communicate ideas, and problem-solve to create the best structure, promoting collaboration and inventive thinking among team members.
Some widely practiced problem-solving activities include:
- A Shrinking Vessel: Teams must fit into a shrinking space, testing their cooperation and adaptability.
- Marshmallow Spaghetti Tower: Participants build a tower using marshmallows and spaghetti, promoting creative engineering.
- Egg Drop: Protecting an egg from a fall challenges problem-solving skills.
- Desert Island Survival: Teams simulate survival scenarios, encouraging creative solutions.
- Rolling Dice: A simple yet effective game involving chance and decision-making.
- Build a Tower: Constructing a stable tower with limited resources fosters teamwork and innovation, etc.
13 Easy Activities For Problem-Solving Ideas to Enhance Team Collaboration
Team building activities offer a great opportunity to test problem-solving abilities and promote effective collaboration within a group to problem solving group activities. By engaging in these activities, teams can break the monotony of the workplace and create a more inclusive and welcoming environment.
Here are nine easy-to-implement activities that can bring substantial change to your team culture and overall workplace dynamics.
#1. Crossword Puzzles
Objective: To enhance problem-solving skills, vocabulary, and cognitive abilities through engaging crossword puzzles.
Estimated Time: 15-20 Minutes
Materials Needed:
- Crossword puzzle sheets
- Pens or pencils
- Distribute crossword puzzle sheets and pens/pencils to each participant.
- Explain the rules of crossword puzzles and the goal of completing as many clues as possible within the given time.
- Participants individually or in pairs work on solving the crossword puzzle by filling in the correct words.
- Encourage critical thinking, word association, and collaborative discussions for solving challenging clues.
- At the end of the time limit, review the answers and discuss any interesting or challenging clues as a group.
- Enhanced Problem-Solving: Participants engage in critical thinking while deciphering clues, promoting effective problem-solving skills.
- Vocabulary Expansion: Exposure to new words and phrases within the crossword improves vocabulary and comprehension.
- Cognitive Stimulation: The mental exercise of solving the puzzle stimulates the brain, enhancing cognitive abilities.
- Team Collaboration: If done in pairs, participants practice collaboration and communication to solve clues together.
- Achievement and Motivation: Successfully completing the crossword brings a sense of accomplishment and motivates individuals to explore more puzzles.
Tips for Facilitators:
- Provide varying levels of crossword puzzles to accommodate different skill levels.
- Encourage participants to share strategies for solving challenging clues.
- Emphasize the fun and educational aspects of the activity to keep participants engaged.
#2. A Shrinking Vessel

Estimated Time: 10-15 Minutes
- Materials Needed: A rope and a ball of yarn
- Prepare the Setting: Lay a rope on the floor in a shape that allows all team members to stand comfortably inside it. For larger teams, multiple ropes can be used, dividing them into smaller groups.
- Enter the Circle: Have all team members stand inside the rope, ensuring that nobody steps outside its boundaries.
- Shrinking the Circle: Begin gradually shrinking the rope’s size, reducing the available space inside the circle.
- Adapt and Maintain Balance: As the circle shrinks, team members must make subtle adjustments to maintain their positions and balance within the shrinking area.
- The Challenge: The objective for the team is to collectively brainstorm and find innovative ways to keep every team member inside the circle without anyone stepping outside.
- Collaboration and Communication: The activity promotes teamwork and open communication as participants strategize to stay within the shrinking circle.
- Adaptability: Team members learn to adapt swiftly to changing circumstances, fostering agility and flexibility.
- Creative Problem-Solving: The challenge encourages inventive thinking and brainstorming to find unique solutions.
- Trust Building: By relying on each other’s actions, participants build trust and cohesion among team members.
- Time-Efficient: The short duration makes it an ideal icebreaker or energizer during meetings or workshops.
- Observe and Facilitate: Monitor the team’s dynamics and offer guidance to encourage equal participation and effective problem-solving.
- Encourage Verbalization: Prompt participants to voice their ideas and collaborate vocally, aiding in real-time adjustments.
- Debrief Thoughtfully: Engage the team in a discussion afterward, reflecting on strategies employed and lessons learned.
- Emphasize Adaptability: Highlight the transferable skill of adaptability and its significance in both professional and personal contexts.
#3. Human Knots
- Objective: Improving Collaboration & enhancing Communication Skills
Estimated Time: 15-20 minutes
- Materials: None required
Procedure:
- Organize your team into a compact circle. For more sizable teams, subdivide them into smaller clusters, with each cluster forming its own circle.
- Direct each individual to grasp the hands of two other people in the circle, with the exception of those positioned directly adjacent to them. This action will result in the formation of a complex “human knot” within the circle.
- Present the challenge to the group: to unravel themselves from this entanglement while maintaining their hold on each other’s hands. If preferred, you can establish a specific time limit.
- Observe the team members collaborating to unravel the knot, witnessing their collective effort to devise solutions and free themselves from the intricate puzzle.
- Team Cohesion: The activity encourages team members to interact closely, promoting bonding and understanding among participants.
- Effective Communication: Participants practice clear and concise communication as they coordinate movements to untangle the knot.
- Problem-Solving: The challenge stimulates creative thinking and problem-solving skills as individuals work collectively to find the optimal path for untangling.
- Adaptability: Participants learn to adapt their actions based on the evolving dynamics of the human knot, fostering adaptability.
- Trust Building: As individuals rely on each other to navigate the intricate knot, trust and cooperation naturally develop.
- Set a Positive Tone: Create an inclusive and supportive atmosphere, emphasizing that the focus is on collaboration rather than competition.
- Encourage Verbalization: Urge participants to articulate their intentions and listen to others’ suggestions, promoting effective teamwork.
- Observe Group Dynamics: Monitor interactions and step in if needed to ensure everyone is actively engaged and included.
- Reflect and Share: Conclude the activity with a debriefing session, allowing participants to share their experiences, strategies, and key takeaways.
- Vary Grouping: Change group compositions for subsequent rounds to enhance interactions among different team members.
#4. Egg Drop

Helps With: Decision Making, Collaboration
- A carton of eggs
- Construction materials (balloons, rubber bands, straws, tape, plastic wrap, etc.)
- A suitable location for the activity
- Assign each team a single egg and random construction materials.
- Teams must create a carrier to protect the egg from breaking.
- Drop the carriers one by one and increase the height if necessary to determine the most durable carrier.
- The winning team is the one with the carrier that survives the highest drop.
- Decision Making: Participants engage in critical decision-making processes as they select construction materials and determine carrier designs.
- Collaboration: The activity necessitates collaboration and coordination among team members to construct an effective carrier.
- Problem-Solving: Teams apply creative problem-solving skills to devise innovative methods for safeguarding the egg.
- Risk Management: Participants learn to assess potential risks and consequences while making design choices to prevent egg breakage.
- Celebrating Success: The victorious team experiences a sense of accomplishment, boosting morale and promoting a positive team spirit.
- Provide Diverse Materials: Offer a wide range of construction materials to stimulate creativity and allow teams to explore various design options.
- Set Safety Guidelines: Prioritize safety by specifying a safe drop height and ensuring participants follow safety protocols during construction.
- Encourage Brainstorming: Prompt teams to brainstorm multiple carrier ideas before finalizing their designs, fostering diverse perspectives.
- Facilitate Reflection: After the activity, lead a discussion where teams share their design strategies, challenges faced, and lessons learned.
- Highlight Collaboration: Emphasize the significance of teamwork in achieving success, acknowledging effective communication and cooperation.
As a teamwork activity, Egg Drop can help team members solve problems through collaboration and communication.
Each team can design and customize their own balloons and can display their team logo, slogan, or elements related to team culture through custom balloons . Awards can also be set up, such as the most creative balloon design, the strongest frangipani structure, etc., to increase the motivation for competition and participation.
After the activity, team sharing and feedback can be conducted to allow everyone to share their learning experience and feelings about teamwork.
This combination allows team members to experience the importance of teamwork in creativity and practice, and strengthen team cohesion by completing challenges and sharing experiences.
#5. Marshmallow Spaghetti Tower
Helps With: Collaboration
Estimated Time: 20-30 Minutes
Materials Needed (per team):
- Raw spaghetti: 20 sticks
- Marshmallow: 1
- String: 1 yard
- Masking tape: 1 roll
- Tower Construction: Instruct teams to collaborate and utilize the provided materials to construct the tallest tower possible within a designated time frame.
- Marshmallow Support: Emphasize that the tower must be capable of standing independently and supporting a marshmallow at its highest point.
- Prototype and Iterate: Encourage teams to engage in prototyping and iteration, testing different design approaches and refining their tower structures.
- T eamwork and Communication: Promote effective teamwork and communication as team members coordinate their efforts to build a stable and tall tower.
- Evaluation Criteria: Evaluate each tower based on its height, stability, and the successful placement of the marshmallow at the top.
- Collaboration: Participants collaborate closely, sharing ideas and working together to design and construct the tower.
- Innovative Thinking: The activity encourages innovative thinking as teams experiment with different strategies to build a stable tower.
- Time Management: Teams practice time management skills as they work within a specified time limit to complete the task.
- Problem-Solving: Participants engage in creative problem-solving to address challenges such as balancing the marshmallow and constructing a sturdy tower.
- Adaptability: Teams adapt their approaches based on trial and error, learning from each iteration to improve their tower designs.
- Set Clear Guidelines: Clearly explain the materials, objectives, and evaluation criteria to ensure teams understand the task.
- Foster Creativity: Encourage teams to think outside the box and explore unconventional methods for constructing their towers.
- Emphasize Collaboration: Highlight the importance of effective communication and teamwork to accomplish the task successfully.
- Time Management: Remind teams of the time limit and encourage them to allocate their time wisely between planning and construction.
- Reflect and Share: Facilitate a discussion after the activity, allowing teams to share their design choices, challenges faced, and lessons learned.

Objective: To engage participants in the strategic and analytical world of Sudoku, enhancing logical thinking and problem-solving abilities.
Estimated Time: 20-25 Minutes
- Sudoku puzzle sheets
- Pencils with erasers
- Distribute Sudoku puzzle sheets and pencils to each participant.
- Familiarize participants with the rules and mechanics of Sudoku puzzles.
- Explain the goal: to fill in the empty cells with numbers from 1 to 9 while adhering to the rules of no repetition in rows, columns, or subgrids.
- Encourage participants to analyze the puzzle’s layout, identify potential numbers, and strategically fill in cells.
- Emphasize the importance of logical deduction and step-by-step approach in solving the puzzle.
- Provide hints or guidance if needed, ensuring participants remain engaged and challenged.
- Logical Thinking: Sudoku challenges participants’ logical and deductive reasoning, fostering analytical skills.
- Problem-Solving: The intricate interplay of numbers and constraints hones problem-solving abilities.
- Focus and Patience: Participants practice patience and attention to detail while gradually unveiling the solution.
- Pattern Recognition: Identifying number patterns and possibilities contributes to enhanced pattern recognition skills.
- Personal Achievement: Successfully completing a Sudoku puzzle provides a sense of accomplishment and boosts confidence.
- Offer varying levels of Sudoku puzzles to cater to different skill levels.
- Encourage participants to share strategies and techniques for solving specific challenges.
- Highlight the mental workout Sudoku provides and its transferable skills to real-life problem-solving.

Helps With: Communication, Problem-solving, & Management
- A lockable room
- 5-10 puzzles or clues
- Hide the key and a set of clues around the room.
- Lock the room and provide team members with a specific time limit to find the key and escape.
- Instruct the team to work together, solving the puzzles and deciphering the clues to locate the key.
- Encourage efficient communication and effective problem-solving under time pressure.
- Communication Skills: Participants enhance their communication abilities by sharing observations, ideas, and findings to collectively solve puzzles.
- Problem-solving Proficiency: The activity challenges teams to think critically, apply logical reasoning, and collaboratively tackle intricate challenges.
- Team Management: The experience promotes effective team management as members assign tasks, prioritize efforts, and coordinate actions.
- Time Management: The imposed time limit sharpens time management skills as teams strategize and allocate time wisely.
- Adaptability: Teams learn to adapt and adjust strategies based on progress, evolving clues, and time constraints.
- Clear Introduction: Provide a concise overview of the activity, emphasizing the importance of communication, problem-solving, and time management.
- Diverse Challenges: Offer a mix of puzzles and clues to engage various problem-solving skills, catering to different team strengths.
- Supportive Role: Act as a facilitator, offering subtle guidance if needed while allowing teams to independently explore and solve challenges.
- Debriefing Session: Organize a debriefing session afterward to discuss the experience, highlight successful strategies, and identify areas for improvement.
- Encourage Reflection: Encourage participants to reflect on their teamwork, communication effectiveness, and problem-solving approach.
#8. Frostbite for Group Problem Solving Activities
Helps With: Decision Making, Trust, Leadership
- An electric fan
- Construction materials (toothpicks, cardstock, rubber bands, sticky notes, etc.)
- Divide the team into groups of 4-5 people, each with a designated leader.
- Blindfold team members and prohibit leaders from using their hands.
- Provide teams with construction materials and challenge them to build a tent within 30 minutes.
- Test the tents using the fan to see which can withstand high winds.
- Decision-Making Proficiency: Participants are exposed to critical decision-making situations under constraints, allowing them to practice effective and efficient decision-making.
- Trust Development: Blindfolding team members and relying on the designated leaders fosters trust and collaboration among team members.
- Leadership Skills: Designated leaders navigate the challenge without hands-on involvement, enhancing their leadership and communication skills.
- Creative Problem Solving: Teams employ creative thinking and resourcefulness to construct stable tents with limited sensory input.
- Team Cohesion: The shared task and unique constraints promote team cohesion and mutual understanding.
- Role of the Facilitator: Act as an observer, allowing teams to navigate the challenge with minimal intervention. Offer assistance only when necessary.
- Clarity in Instructions: Provide clear instructions regarding blindfolding, leader restrictions, and time limits to ensure a consistent experience.
- Debriefing Session: After the activity, conduct a debriefing session to discuss team dynamics, leadership approaches, and decision-making strategies.
- Encourage Communication: Emphasize the importance of effective communication within teams to ensure smooth coordination and successful tent construction.
- Acknowledge Creativity: Celebrate creative solutions and innovative approaches exhibited by teams during the tent-building process.
#9. Dumbest Idea First

Helps With: Critical Thinking & Creative Problem Solving Activity
Estimated Time: 15-20 Minutes
Materials Needed: A piece of paper, pen, and pencil
- Problem Presentation: Introduce a specific problem to the team, either a real-world challenge or a hypothetical scenario that requires a solution.
- Brainstorming Dumb Ideas: Instruct team members to quickly generate and jot down the most unconventional and seemingly “dumb” ideas they can think of to address the problem.
- Idea Sharing: Encourage each participant to share their generated ideas with the group, fostering a relaxed and open atmosphere for creative expression.
- Viability Assessment: As a team, review and evaluate each idea, considering potential benefits and drawbacks. Emphasize the goal of identifying unconventional approaches.
- Selecting Promising Solutions: Identify which seemingly “dumb” ideas could hold hidden potential or innovative insights. Discuss how these ideas could be adapted into workable solutions.
- Divergent Thinking: Participants engage in divergent thinking, pushing beyond conventional boundaries to explore unconventional solutions.
- Creative Exploration: The activity sparks creative exploration by encouraging participants to let go of inhibitions and embrace imaginative thinking.
- Critical Analysis: Through evaluating each idea, participants practice critical analysis and learn to identify unique angles and aspects of potential solutions.
- Open Communication: The lighthearted approach of sharing “dumb” ideas fosters open communication, reducing fear of judgment and promoting active participation.
- Solution Adaptation: Identifying elements of seemingly “dumb” ideas that have merit encourages participants to adapt and refine their approaches creatively.
- Safe Environment: Foster a safe and non-judgmental environment where participants feel comfortable sharing unconventional ideas.
- Time Management: Set clear time limits for idea generation and sharing to maintain the activity’s energetic pace.
- Encourage Wild Ideas: Emphasize that the goal is to explore the unconventional, urging participants to push the boundaries of creativity.
- Facilitator Participation: Participate in idea generation to demonstrate an open-minded approach and encourage involvement.
- Debriefing Discussion: After the activity, facilitate a discussion on how seemingly “dumb” ideas can inspire innovative solutions and stimulate fresh thinking.
This activity encourages out-of-the-box thinking and creative problem-solving. It allows teams to explore unconventional ideas that may lead to unexpected, yet effective, solutions.
#10: Legoman
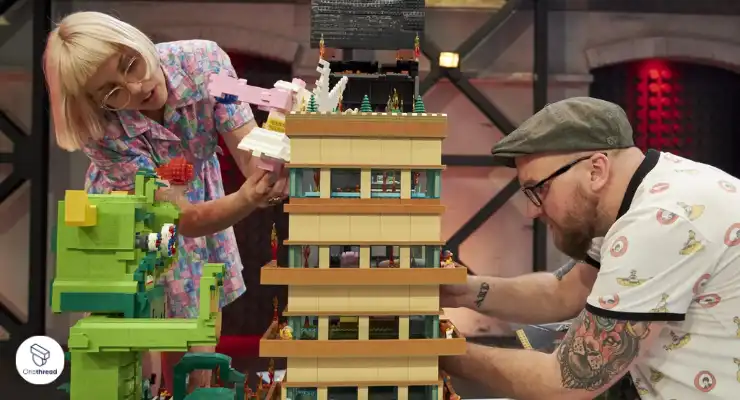

Helps With: Foster teamwork, communication, and creativity through a collaborative Lego-building activity.
Estimated Time: 20-30 minutes
- Lego bricks
- Lego instruction manuals
Procedure :
- Divide participants into small teams of 3-5 members.
- Provide each team with an equal set of Lego bricks and a Lego instruction manual.
- Explain that the goal is for teams to work together to construct the Lego model shown in the manual.
- Set a time limit for the building activity based on model complexity.
- Allow teams to self-organize, build, and collaborate to complete the model within the time limit.
- Evaluate each team’s final model compared to the manual’s original design.
- Enhanced Communication: Participants must communicate clearly and listen actively to collaborate effectively.
- Strengthened Teamwork: Combining efforts toward a shared goal promotes camaraderie and team cohesion.
- Creative Problem-Solving: Teams must creatively problem-solve if pieces are missing or instructions unclear.
- Planning and Resource Allocation: Following instructions fosters planning skills and efficient use of resources.
- Sense of Achievement: Completing a challenging build provides a sense of collective accomplishment.
- Encourage Participation: Urge quieter members to contribute ideas and take an active role.
- Highlight Teamwork: Emphasize how cooperation and task coordination are key to success.
- Ensure Equal Engagement: Monitor group dynamics to ensure all members are engaged.
- Allow Creativity: Permit modifications if teams lack exact pieces or wish to get creative.
- Focus on Enjoyment: Create a lively atmosphere so the activity remains energizing and fun.
#11: Minefield
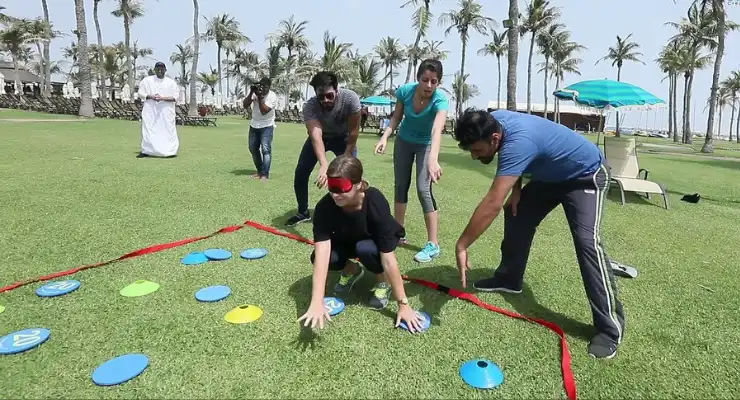

Helps With: Trust, Communication, Patience
Materials Needed: Open space, blindfolds
- Mark a “minefield” on the ground using ropes, cones, or tape. Add toy mines or paper cups.
- Pair up participants and blindfold one partner.
- Position blindfolded partners at the start of the minefield. Direct seeing partners to verbally guide them through to the other side without hitting “mines.”
- Partners switch roles once finished and repeat.
- Time partnerships and provide prizes for the fastest safe crossing.
- Trust Building: Blindfolded partners must trust their partner’s instructions.
- Effective Communication: Giving clear, specific directions is essential for navigating the minefield.
- Active Listening: Partners must listen closely and follow directions precisely.
- Patience & Support: The exercise requires patience and encouraging guidance between partners.
- Team Coordination: Partners must work in sync, coordinating movements and communication.
- Test Boundaries: Ensure the minefield’s size accommodates safe movement and communication.
- Monitor Interactions: Watch for dominant guidance and ensure both partners participate fully.
- Time Strategically: Adjust time limits based on the minefield size and difficulty.
- Add Obstacles: Introduce additional non-mine objects to increase challenge and communication needs.
- Foster Discussion: Debrief afterward to discuss communication approaches and trust-building takeaways.
#12: Reverse Pyramid
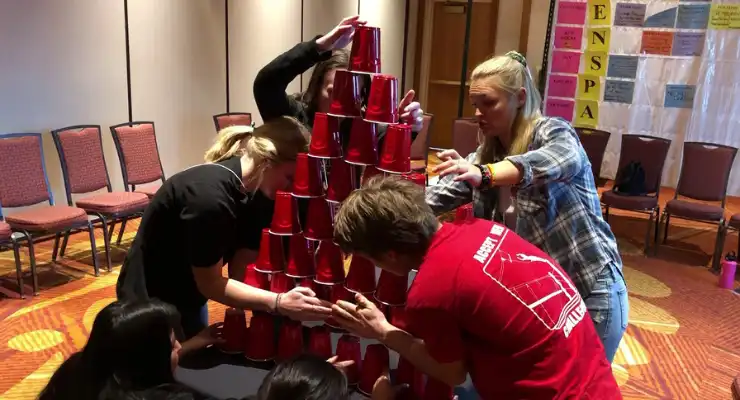

Helps With: Teamwork, Communication, Creativity
Materials Needed: 36 cups per group, tables
- Form small groups of 5-7 participants.
- Provide each group with a stack of 36 cups and a designated building area.
- Explain the objective: Build the tallest pyramid starting with just one cup on top.
- Place the first cup on the table, and anyone in the group can add two cups beneath it to form the second row.
- From this point, only the bottom row can be lifted to add the next row underneath.
- Cups in the pyramid can only be touched or supported by index fingers.
- If the structure falls, start over from one cup.
- Offer more cups if a group uses all provided.
- Allow 15 minutes for building.
Teamwork: Collaborate to construct the pyramid.
Communication: Discuss and execute the building strategy.
Creativity: Find innovative ways to build a tall, stable pyramid.
Clarify Expectations: Emphasize the definition of a pyramid with each row having one less cup.
Encourage Perseverance: Motivate groups to continue despite challenges.
Promote Consensus: Encourage groups to work together and help each other.
Reflect on Failure: Use collapses as a metaphor for overcoming obstacles and improving.
Consider Competitions: Modify the activity for competitive teams and scoring.
#13: Stranded
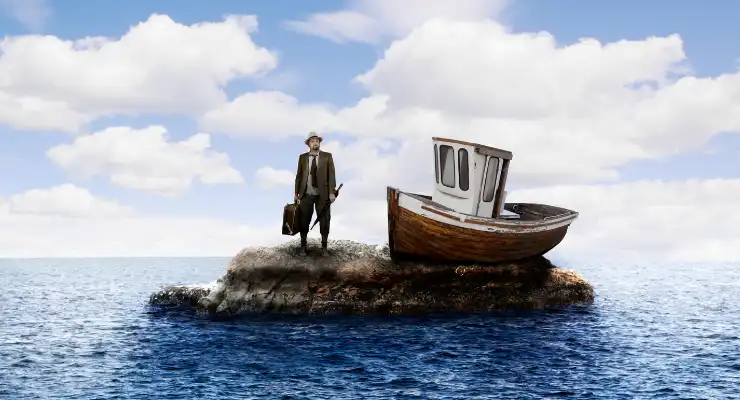

Helps With: Decision-making, Prioritization, Teamwork
Materials Needed: List of salvaged items, paper, pens
- Present a scenario where teams are stranded and must prioritize items salvaged from a plane crash.
- Provide teams with the same list of ~15 salvaged items.
- Instruct teams to agree on an item ranking with #1 being the most important for survival.
- Teams share and compare their prioritized lists. Identify differences in approach.
- Discuss what factors influenced decisions and how teams worked together to agree on priorities.
- Critical Thinking: Weighing item importance requires analytical thinking and discussion.
- Team Decision-Making: Coming to a consensus fosters team decision-making capabilities.
- Prioritization Skills: Ranking items strengthen prioritization and justification abilities.
- Perspective-Taking: Understanding different prioritizations builds perspective-taking skills.
- Team Cohesion: Collaborating toward a shared goal brings teams closer together.
- Encourage Discussion: Urge teams to discuss all ideas rather than allow single members to dominate.
- Be Engaged: Circulate to listen in on team discussions and pose thought-provoking questions.
- Add Complexity: Introduce scenarios with additional constraints to expand critical thinking.
- Highlight Disagreements: When priorities differ, facilitate constructive discussions on influencing factors.
- Recognize Collaboration: Acknowledge teams that demonstrate exceptional teamwork and communication.
Now let’s look at some common types of problem-solving activities.
Types of Problem-Solving Activities
The most common types of problem-solving activities/exercises are:
- Creative problem-solving activities
- Group problem-solving activities
- Individual problem-solving activities
- Fun problem-solving activities, etc.
In the next segments, we’ll be discussing these types of problem-solving activities in detail. So, keep reading!
Creative Problem-Solving Activities
Creative problem solving (CPS) means using creativity to find new solutions. It involves thinking creatively at first and then evaluating ideas later. For example, think of it like brainstorming fun game ideas, discussing them, and then picking the best one to play.
Some of the most common creative problem-solving activities include:
- Legoman: Building creative structures with LEGO.
- Escape: Solving puzzles to escape a room.
- Frostbite: Finding solutions in challenging situations.
- Minefield: Navigating a field of obstacles.
Group Problem-Solving Activities
Group problem-solving activities are challenges that make teams work together to solve puzzles or overcome obstacles. They enhance teamwork and critical thinking.
For instance, think of a puzzle-solving game where a group must find hidden clues to escape a locked room.
Here are the most common group problem-solving activities you can try in groups:
- A Shrinking Vessel
- Marshmallow Spaghetti Tower
- Cardboard Boat Building Challenge
- Clue Murder Mystery
- Escape Room: Jewel Heist
- Escape Room: Virtual Team Building
- Scavenger Hunt
- Dumbest Idea First
Individual Problem-Solving Activities
As the name suggests, individual problem-solving activities are the tasks that you need to play alone to boost your critical thinking ability. They help you solve problems and stay calm while facing challenges in real life. Like puzzles, they make your brain sharper. Imagine it’s like training your brain muscles to handle tricky situations.
Here are some of the most common individual problem-solving activities:
- Puzzles (jigsaw, crossword, sudoku, etc.)
- Brain teasers
- Logic problems
- Optical illusions
- “Escape room” style games
Fun Problem-Solving Activities
Fun problem-solving activities are enjoyable games that sharpen your critical thinking skills while having a blast. Think of activities like the Legoman challenge, escape rooms, or rolling dice games – they make problem-solving exciting and engaging!
And to be frank, all of the mentioned problem-solving activities are fun if you know how to play and enjoy them as all of them are game-like activities.
Team Problems You Can Address Through Problem Solving Activities
Fun problem-solving activities serve as dynamic tools to address a range of challenges that teams often encounter. These engaging activities foster an environment of collaboration, creativity, and critical thinking, enabling teams to tackle various problems head-on. Here are some common team problems that can be effectively addressed through these activities:
- Communication Breakdowns:
Activities like “Escape,” “A Shrinking Vessel,” and “Human Knots” emphasize the importance of clear and effective communication. They require teams to work together, exchange ideas, and devise strategies to accomplish a shared goal. By engaging in these activities, team members learn to communicate more efficiently, enhancing overall team communication in real-world situations.
- Lack of Trust and Cohesion:
Problem-solving activities promote trust and cohesiveness within teams. For instance, “Frostbite” and “Marshmallow Spaghetti Tower” require teams to collaborate closely, trust each other’s ideas, and rely on each member’s strengths. These activities build a sense of unity and trust, which can translate into improved teamwork and collaboration.
- Innovative Thinking:
“Dumbest Idea First” and “Egg Drop” encourage teams to think outside the box and explore unconventional solutions. These activities challenge teams to be creative and innovative in their problem-solving approaches, fostering a culture of thinking beyond traditional boundaries when faced with complex issues.
- Decision-Making Challenges:
Activities like “Onethread” facilitate group decision-making by providing a platform for open discussions and collaborative choices. Problem-solving activities require teams to make decisions collectively, teaching them to weigh options, consider different viewpoints, and arrive at informed conclusions—a skill that is transferable to real-world decision-making scenarios.
- Leadership and Role Clarification:
Activities such as “Frostbite” and “Egg Drop” designate team leaders and roles within groups. This provides an opportunity for team members to practice leadership, delegation, and role-specific tasks. By experiencing leadership dynamics in a controlled setting, teams can improve their leadership skills and better understand their roles in actual projects.
- Problem-Solving Strategies:
All of the problem-solving activities involve the application of different strategies. Teams learn to analyze problems, break them down into manageable components, and develop systematic approaches for resolution. These strategies can be adapted to real-world challenges, enabling teams to approach complex issues with confidence.
- Team Morale and Engagement:
Participating in engaging and enjoyable activities boosts team morale and engagement. These activities provide a break from routine tasks, energize team members, and create a positive and fun atmosphere. Elevated team morale can lead to increased motivation and productivity.
The incentives of event prizes can further stimulate the enthusiasm and participation of team members. The choice of prizes is crucial, as it can directly affect the attractiveness and participation of the event. Among them, Medals are essential prizes.
Medals are symbols of honor awarded to winners and represent the value and achievement of an event.
Medals also have a motivational effect, they encourage team members to pursue higher achievements and progress.
Medals are artistic and aesthetic. They are usually designed by designers according to different occasions and themes and have high collection value.
By incorporating these fun problem-solving activities, teams can address a variety of challenges, foster skill development, and build a more cohesive and effective working environment. As teams learn to collaborate, communicate, innovate, and make decisions collectively, they are better equipped to overcome obstacles and achieve shared goals.
The Benefits of Problem Solving Activities for Your Team
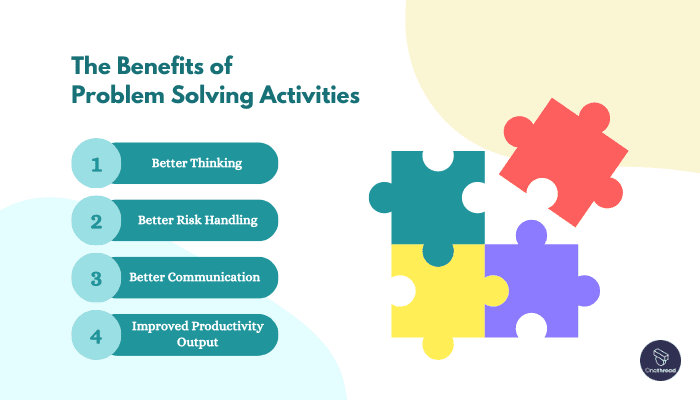
#1 Better Thinking
Problem-solving activities bring out the best in team members by encouraging them to contribute their unique ideas. This stimulates better thinking as team managers evaluate different solutions and choose the most suitable ones.
For example, a remote team struggling with communication benefited from quick thinking and the sharing of ideas, leading to the adoption of various communication modes for improved collaboration.
#2 Better Risk Handling
Team building problem solving activities condition individuals to handle risks more effectively. By engaging in challenging situations and finding solutions, team members develop the ability to respond better to stressful circumstances.
#3 Better Communication
Regular communication among team members is crucial for efficient problem-solving. Engaging in problem-solving activities fosters cooperation and communication within the team, resulting in better understanding and collaboration. Using tools like OneThread can further enhance team communication and accountability.
#4 Improved Productivity Output
When teams work cohesively, overall productivity improves, leading to enhanced profit margins for the company or organization. Involving managers and team members in problem-solving activities can positively impact the company’s growth and profitability.
How Onethread Enhances the Effect of Problem Solving Activities
Problem-solving activities within teams thrive on collaborative efforts and shared perspectives. Onethread emerges as a potent facilitator, enabling teams to collectively tackle challenges and harness diverse viewpoints with precision. Here’s a comprehensive view of how Onethread amplifies team collaboration in problem-solving initiatives:
Open Channels for Discussion:
Onethread’s real-time messaging feature serves as a dedicated hub for open and seamless discussions. Teams can engage in brainstorming sessions, share insightful observations, and propose innovative solutions within a flexible environment. Asynchronous communication empowers members to contribute their insights at their convenience, fostering comprehensive problem analysis with ample deliberation.
Centralized Sharing of Resources:
Effective problem-solving often hinges on access to pertinent resources. Onethread’s document sharing functionality ensures that critical information, references, and research findings are centralized and readily accessible. This eradicates the need for cumbersome email attachments and enables team members to collaborate with precise and up-to-date data.
Efficient Task Allocation and Monitoring:
Problem-solving journeys comprise a series of tasks and actions. Onethread’s task management capability streamlines the delegation of specific responsibilities to team members. Assign tasks related to research, data analysis, or solution implementation and monitor progress in real time. This cultivates a sense of accountability and guarantees comprehensive coverage of every facet of the problem-solving process.
Facilitated Collaborative Decision-Making: Navigating intricate problems often demands collective decision-making. Onethread’s collaborative ecosystem empowers teams to deliberate over potential solutions, assess pros and cons, and make well-informed choices. Transparent discussions ensure that decisions are comprehensively comprehended and supported by the entire team.
Seamless Documentation and Insights Sharing:
As the problem-solving journey unfolds, the accumulation of insights and conclusions becomes pivotal. Onethread’s collaborative document editing feature empowers teams to document their discoveries, chronicle the steps undertaken, and showcase successful solutions. This shared repository of documentation serves as a valuable resource for future reference and continuous learning.
With Onethread orchestrating the backdrop, team collaboration during problem-solving activities transforms into a harmonious fusion of insights, ideas, and actionable steps.
What are the 5 problem-solving skills?
The top 5 problem-solving skills in 2023 are critical thinking, creativity, emotional intelligence, adaptability, and data literacy. Most employers seek these skills in their workforce.
What are the steps of problem-solving?
Problem-solving steps are as follows: 1. Define the problem clearly. 2. Analyze the issue in detail. 3. Generate potential solutions. 4. Evaluate these options. 5. Choose the best solution. 6. Put the chosen solution into action. 7. Measure the outcomes to assess effectiveness and improvements made. These sequential steps assist in efficient and effective problem resolution.

How do you teach problem-solving skills?
Teaching problem-solving involves modelling effective methods within a context, helping students grasp the problem, dedicating ample time, asking guiding questions, and giving suggestions. Connect errors to misconceptions to enhance understanding, fostering a straightforward approach to building problem-solving skills.
So here is all about “activities for problem solving”.No matter which activity you choose, engaging in problem-solving activities not only provides entertainment but also helps enhance cognitive abilities such as critical thinking, decision making, and creativity. So why not make problem solving a regular part of your routine?
Take some time each day or week to engage in these activities and watch as your problem-solving skills grow stronger. Plus, it’s an enjoyable way to pass the time and challenge yourself mentally.
So go ahead, grab a puzzle or gather some friends for a game night – get ready to have fun while sharpening your problem-solving skills!
Let's Get Started with Onethread
Onethread empowers you to plan, organise, and track projects with ease, ensuring you meet deadlines, allocate resources efficiently, and keep progress transparent.
By subscribing you agree to our Privacy Policy .
Giving modern marketing teams superpowers with short links that stand out.
- Live Product Demo
© Copyright 2023 Onethread, Inc

- Search Search Search …
- Search Search …
Lateral Thinking Exercises: Enhance Creativity and Problem Solving Skills

Lateral thinking exercises are designed to challenge conventional patterns of thought and inspire creative problem-solving. These exercises encourage individuals to consider novel perspectives and explore unconventional solutions to seemingly complex problems. By engaging in lateral thinking exercises, one can tap into the power of thinking outside the box and develop the ability to approach challenges with a fresh, innovative mindset.
The concept of lateral thinking was coined by Edward De Bono in 1973 and has since gained popularity as a key component of creative and critical thinking methods. Applying lateral thinking techniques allows individuals to break free of habitual thought patterns and uncover previously unconsidered possibilities. This approach is valuable not only for personal development but also for driving innovation and progress in various fields, including business, science, and technology.
Key Takeaways
- Lateral thinking exercises foster creativity and innovation by challenging conventional thought patterns.
- Techniques used in lateral thinking help individuals break free from habitual thinking and discover new possibilities.
- The concept of lateral thinking is applicable across various fields, promoting innovation and problem-solving.
Understanding Lateral Thinking
Lateral thinking, a term developed by Edward de Bono in 1973, is an approach to problem-solving that aims to generate creative solutions instead of the most straightforward ones. It is sometimes referred to as horizontal thinking or divergent thinking, in contrast to vertical thinking, which follows a more linear and logical path. The key to lateral thinking is exploring alternative perspectives, embracing change, and often causing disruption to traditional ways of thinking.
An essential aspect of lateral thinking is its flexibility and adaptability, enabling individuals to tackle problems from unique or unexpected points of view. It encourages the generation of multiple alternatives and innovative solutions, allowing for a better understanding of complex situations. Practitioners of lateral thinking understand that the most obvious solution may not always be the best one, and they strive to examine all the possibilities.
In contrast, vertical thinking is about following established patterns and sequences, typically relying on logic, past experience, and existing knowledge. Although vertical thinking can be effective in many situations, it may not be the most suitable approach when dealing with complex, dynamic, or novel problems. Lateral thinking complements vertical thinking by challenging assumptions, offering fresh angles, and ultimately leading to more innovative solutions.
The application of lateral thinking can bring significant changes and disruption to traditional methods and beliefs. By identifying and exploring alternatives, lateral thinkers can uncover novel ways to address challenges or capitalize on opportunities, potentially transforming industries, organizations, or beliefs.
Using lateral thinking exercises, such as the famous “one egg left in the carton” puzzle, can help individuals sharpen their creative skills and nurture an innovative mindset. The ability to think laterally can be invaluable in various personal and professional contexts, enabling people to solve problems effectively, adapt to changing circumstances, and leverage their ingenuity to make a difference.
The Art and Science of Lateral Thinking
Lateral thinking is a creative approach to problem-solving that combines art, creativity, and logic to yield innovative and unexpected solutions. Developed by psychologist Edward de Bono in the 1970s, lateral thinking encourages a shift in perspective to break free from conventional reasoning methods.
Unlike critical thinking , which relies heavily on logic, analysis, and direct reasoning, lateral thinking adopts a more indirect approach. This allows individuals to explore a wider range of possibilities, encouraging creativity and out-of-the-box thinking . By fostering an open-minded environment, lateral thinking techniques can lead to unique and effective solutions.
One key aspect of lateral thinking is its emphasis on being aware of the thought process itself. By understanding how the mind processes information, individuals can learn to identify and resist established patterns, paving the way for innovation. This awareness is crucial in enabling individuals to push the boundaries of traditional reasoning.
A cornerstone of lateral thinking is the use of random stimulation to spark new ideas and thought patterns. This tool drives creativity, often leading to surprising and impactful insights. Random stimulation can take various forms, from introducing unrelated elements to a problem to brainstorming without restrictions to letting the subconscious mind work on a problem during moments of relaxation.
In summary, lateral thinking is a versatile and dynamic method that thrives at the intersection of art, creativity, and logic. Its core principles, namely an emphasis on awareness, random stimulation, and the cultivation of a creative and open-minded environment, empower individuals to break away from limiting thought patterns and explore new frontiers in problem-solving. By employing lateral thinking techniques, innovative and often unexpected solutions can be discovered.
Lateral Thinking Techniques
Six thinking hats.
The Six Thinking Hats method, developed by Edward de Bono, is an effective technique for enhancing lateral thinking. This approach encourages individuals to view problems from multiple perspectives by wearing six metaphorical “hats,” each representing a distinct way of thinking. By temporarily adopting these different mental states, individuals can explore alternative solutions, identify potential challenges, and ultimately foster innovation.
Mind Mapping
Another popular lateral thinking technique is Mind Mapping . Mind mapping involves visually organizing information, often through the use of diagrams or charts. To create a mind map, one starts with a central idea or problem and branches out to related concepts, themes, or possible solutions. This technique helps clarify complex issues, uncover hidden connections, and stimulate new ways of thinking. Additionally, mind maps can be an effective tool for collaborative problem-solving, as they provide a clear, visual representation of ideas that can be easily shared and discussed.
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a well-known lateral thinking technique that encourages the generation of numerous ideas in a short amount of time. Brainstorming sessions typically involve a group of individuals working together to find creative solutions to a given problem or challenge. Participants are encouraged to share their thoughts freely, without judgment or criticism, in order to foster an open atmosphere for exploration and innovation. After a brainstorming session, ideas can be evaluated, refined, and prioritized, leading to a more effective problem-solving process.
Lateral Thinking in Problem Solving
Lateral thinking is an essential skill for tackling complex problems and finding innovative solutions. This cognitive process involves looking at problems from different perspectives, breaking free from conventional thinking patterns, and considering alternative solutions to reach a desired outcome.
In problem-solving scenarios, lateral thinking helps individuals to think beyond their learned methods and biases. By incorporating a range of techniques, one can stimulate their mind to explore unchartered territories and generate unique ideas. Some of these techniques include brainstorming, mind mapping, and analyzing assumptions.
Problems come in various shapes and sizes, and conventional problem-solving approaches may not always be effective. Lateral thinking can be especially helpful when confronted with seemingly unsolvable problems or when conventional methods have exhausted their potential.
One way to enhance lateral thinking skills is through engaging in brain teasers and puzzles. These exercises often require individuals to discard their preconceived notions and adopt new ways of contemplating problems. Lateral thinking puzzles are a fun and engaging way to challenge the mind and expand creativity.
When applied to real-life scenarios, lateral thinking can lead to innovative solutions that may not have been considered otherwise. By encouraging an environment of open-mindedness and curiosity, both individuals and organizations can benefit from the creative problem-solving opportunities that arise from lateral thinking .
Incorporating Lateral Thinking in Various Fields
In advertising.
Lateral thinking in the advertising industry is essential for marketers to develop creative and innovative campaigns capable of capturing the attention of consumers. By challenging the status quo and looking for alternative perspectives, marketers can create memorable ads that differentiate their brand from the competition. This approach enables businesses to adapt to the ever-changing environment, make better use of resources, and achieve a higher return on investment.
Examples of lateral thinking in advertising include:
- Storytelling : Presenting a product through an engaging narrative to create an emotional connection with the audience.
- Disruptive visuals : Using unexpected visual elements to grab attention and provoke curiosity about the product or service.
The media industry can also benefit from incorporating lateral thinking techniques by encouraging the exploration of new ideas and underrepresented stories. Journalists, producers, and content creators can apply horizontal thinking strategies to spark conversations, challenge common assumptions, and provide fresh perspectives on current issues. A willingness to think outside the box in media helps establish an open, diverse environment that can drive change and foster innovative solutions.
For example, consider the following applications:
- Investigative journalism : Detectives and journalists may use lateral thinking to uncover new leads and connections in complicated cases.
- Scriptwriting : Writers can create captivating narratives that break from conventional tropes and explore unique scenarios.
In Workplace
Lateral thinking in the workplace is valuable for promoting a more dynamic and collaborative environment. Employees who are encouraged to think creatively are more likely to come up with innovative solutions to problems, spot new opportunities, and approach challenges with a fresh perspective. This can lead to improved productivity, increased job satisfaction, and a more agile and adaptable organization.
Ways to implement lateral thinking in the workplace:
- Brainstorming : Regularly engage in brainstorming sessions, emphasizing free thinking and open-ended discussions.
- Training : Provide training on lateral thinking techniques and encourage employees to apply them within their roles.
In Leadership
Incorporating lateral thinking in leadership practices can have a profound impact on a company’s overall success. Leaders who embrace horizontal thinking often cultivate an open-minded and inclusive culture, empowering team members to take risks, iterate, and learn from failures. This mindset fosters creativity and innovation, ultimately giving the organization a competitive advantage in various industries.
Effective applications of lateral thinking in leadership include:
- Strategic planning : Questioning assumptions, looking for alternative ways to achieve objectives, and embracing uncertainty as a way to innovate.
- Encouraging diverse perspectives : Actively seeking input from individuals with different backgrounds and experiences to generate a wider range of ideas and solutions.
Lateral Thinking and Artificial Intelligence
Lateral thinking is a skill that can help solve problems creatively, generate new ideas, and challenge assumptions. It involves looking at issues from various perspectives, often considering unconventional and non-linear approaches. In this context, the integration of lateral thinking into artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to lead to innovative and more adaptable AI solutions.
AI systems have traditionally focused on logical and analytical problem-solving, which can sometimes struggle with finding creative or unconventional solutions. By incorporating lateral thinking techniques into AI algorithms, AI systems can potentially overcome some of these limitations. This approach can enable AI systems to tackle problems that require outside-the-box thinking , adaptability, and a more human-like understanding of complex situations.
Some researchers are working on developing AI systems with lateral thinking capabilities. One approach involves using random stimulation, where AI algorithms are fed random inputs to encourage them to explore unique solution paths. Another technique includes implementing alternative and altered perspectives, allowing AI to challenge its own assumptions and consider a broader range of possibilities.
Developing AI models with lateral thinking abilities can have numerous applications across various industries and domains. For example, in product design, an AI system with lateral thinking capabilities might discover innovative and previously unconsidered design solutions. In medicine, AI-powered lateral thinking could lead to novel treatments or diagnostic techniques that significantly improve patient outcomes.
Ultimately, incorporating lateral thinking into AI has the potential to make AI systems more adaptable, creative, and capable of tackling complex problems. As research in this area progresses, we can expect to see AI systems that not only think more like humans but also potentially surpass human capabilities in terms of problem-solving and innovation.
Benefits of Lateral Thinking
Lateral thinking offers numerous benefits to individuals and organizations, as it promotes a creative approach to problem-solving. By considering alternatives and embracing disruption, lateral thinking helps foster imagination and innovation.
One of the key advantages of lateral thinking is its ability to break the status quo and promote flexibility in thought processes. This approach allows for the identification of unconventional solutions that may not be immediately obvious. Exploring different perspectives leads to a more comprehensive understanding of complex challenges and encourages the development of unique solutions.
Furthermore, lateral thinking enhances self-awareness and allows individuals to become more attuned to their thought patterns and decision-making processes. This heightened self-awareness leads to better self-management and can improve leadership skills. By understanding and embracing a range of diverse ideas, leaders can make better-informed decisions in the face of uncertainty.
In addition to fostering a creative mindset, lateral thinking helps to strengthen teamwork and collaboration. By incorporating diverse perspectives and encouraging the sharing of ideas, teams can develop a more holistic understanding of challenges they face. A deepened sense of empathy and respect for the unique contributions of each member can lead to more innovative solutions.
Overall, the practice of lateral thinking contributes to the development of individuals and organizations by opening up new avenues for problem-solving, promoting a flexible and adaptable mindset, enhancing self-awareness, and strengthening leadership and collaboration.
Lateral Thinking Exercises and Examples
Lateral thinking exercises challenge the traditional thought patterns and stimulate the mind to find creative solutions. These exercises, puzzles, and brain teasers rely on unconventional thinking, breaking free from linear, step-by-step logic.
One example of a lateral thinking exercise is the random objects technique. In this method, individuals are provided with a random stimulus, such as a word or object, and then encouraged to make connections between that object and the issue they want to resolve. By forcing oneself to consider unrelated items, the brain may discover novel solutions.
Another type of exercise involves challenging assumptions. To practice this, create a list of assumptions around a particular problem, and then deliberately contradict them. With these new perspectives, it becomes easier to see alternative solutions that may have been missed before. For instance, in the classic “nine dots” puzzle, participants are asked to connect all nine dots using four straight lines without lifting the pencil from the paper. Many individuals assume the lines must remain within the grid, but the solution requires going outside the grid’s boundaries.
Provocative operation is another lateral thinking technique focused on generating unique ideas. This method introduces absurd statements or wild ideas, which are intentionally illogical or unrealistic. The goal is to find the hidden value in these provocations and derive innovative ideas from them. For example, imagine a car that runs on water instead of gasoline. This notion might inspire ideas for alternative fuel sources.
Finally, the concept of “backwards planning” can also be applied in lateral thinking exercises. In this method, we start at the desired outcome and work our way back to the current situation. By reversing the linear thinking process, we can identify new pathways to reach the objective, which might not have been obvious when working forwards.
In conclusion, practicing lateral thinking exercises using techniques such as random objects, challenging assumptions, provocative operation, and backwards planning can be valuable in developing creative solutions to complex problems. By engaging in these exercises, individuals can break free from traditional thought patterns and find innovative ways to approach challenges.
You may also like

Can Lateral Thinking Be Taught?
We spend much of our lives solving problems, but while many of the solutions to those problems are purely logical, there is […]

Linear Thinking vs Lateral Thinking
Every single day we use a number of mental models to help us navigate our increasingly complex world. Some of these […]

Lateral Thinking vs Creative Thinking: Understanding Different Problem-Solving Approaches
Lateral thinking and creative thinking are often used interchangeably, signaling a departure from conventional logic to generate innovative solutions and ideas. Lateral […]

Lateral Thinking for Management
Lateral thinking has the potential to totally transform businesses from top to bottom, especially when the charges led by great leaders (and […]
Engaging Critical Thinking Games for Developing Analytical Skills
Annie Walls
In today's fast-paced and complex world, developing analytical skills is essential for success. Analytical skills allow individuals to think critically, solve problems, and make informed decisions. One effective way to enhance analytical skills is through engaging critical thinking games. These games not only provide entertainment but also stimulate the mind and encourage logical reasoning. In this article, we will explore the importance of critical thinking, various engaging critical thinking games, how to incorporate critical thinking in everyday activities, and ways to promote collaborative critical thinking. Here are the key takeaways:
Key Takeaways
- Critical thinking is crucial for developing analytical skills.
- Engaging critical thinking games can enhance analytical thinking.
- Puzzle games, strategy games, logic games, and problem-solving games are effective in developing critical thinking.
- Incorporating critical thinking in everyday activities such as reading, writing, decision making, and analyzing data is important.
- Promoting collaborative critical thinking through group activities, role-playing games, debates, and collaborative problem-solving exercises is beneficial.
The Importance of Critical Thinking
Understanding the role of critical thinking in analytical skills development.
Critical thinking plays a crucial role in the development of analytical skills. It is the ability to objectively analyze and evaluate information, allowing individuals to make informed decisions and solve complex problems. By engaging in critical thinking, individuals can enhance their analytical skills by honing their ability to identify patterns, analyze data, and draw logical conclusions.
To further understand the importance of critical thinking in analytical skills development, let's take a look at a few key points:
- Critical thinking helps individuals develop a systematic approach to problem-solving, enabling them to break down complex issues into manageable parts.
- It encourages individuals to question assumptions and biases, promoting a more objective and unbiased analysis of information.
- Critical thinking fosters creativity and innovation, as it encourages individuals to think outside the box and explore alternative solutions.
Incorporating critical thinking into everyday activities can significantly enhance analytical skills and contribute to personal and professional growth.
Benefits of Developing Analytical Skills through Critical Thinking
Developing analytical skills through critical thinking offers numerous benefits. Improved Problem-Solving: Critical thinking enhances the ability to analyze complex problems and find effective solutions. Enhanced Decision Making : By developing analytical skills, individuals can make informed decisions based on logical reasoning and evidence. Increased Creativity : Critical thinking fosters creativity by encouraging individuals to think outside the box and explore innovative solutions. Effective Communication : Analytical skills developed through critical thinking enable individuals to articulate their thoughts and ideas clearly and persuasively. Better Time Management : Critical thinking helps individuals prioritize tasks and make efficient use of their time.
Engaging Critical Thinking Games
Puzzle games that enhance analytical thinking.
Puzzle games are a great way to enhance analytical thinking skills. These games require players to think critically and strategically in order to solve complex puzzles. By engaging in puzzle games, individuals can improve their problem-solving abilities and develop a logical mindset. Additionally, puzzle games provide an opportunity to exercise creativity and think outside the box. They challenge players to approach problems from different angles and come up with innovative solutions. Overall, puzzle games are an effective tool for developing analytical skills and fostering critical thinking.
Strategy Games for Developing Critical Thinking
Strategy games are an excellent way to develop critical thinking skills. These games require players to analyze different situations, consider various options, and make strategic decisions. By playing strategy games, individuals can enhance their problem-solving abilities and learn how to think critically in complex scenarios. Chess is a classic example of a strategy game that promotes critical thinking. Players must anticipate their opponent's moves, plan their own moves, and strategize to achieve victory. Other strategy games, such as Risk and Settlers of Catan , also provide opportunities for players to develop their analytical skills and make strategic choices.
Logic Games to Stimulate Analytical Skills
Logic games are an excellent way to stimulate analytical skills. These games require players to think critically, analyze information, and make logical deductions. By engaging in logic games, individuals can enhance their problem-solving abilities and develop a systematic approach to decision-making. One popular logic game is Sudoku, which challenges players to fill a grid with numbers based on specific rules. Another example is the game Mastermind, where players must deduce a secret code by using clues provided. These games not only provide entertainment but also help sharpen analytical thinking skills.
Problem-Solving Games that Foster Critical Thinking
Problem-solving games are an excellent way to foster critical thinking skills. These games require players to analyze complex situations, think creatively, and come up with innovative solutions. By engaging in problem-solving games, individuals can develop their analytical skills and enhance their ability to think critically. These games often involve puzzles, riddles, and challenges that require logical reasoning and strategic thinking. They provide a fun and interactive way to practice critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Incorporating Critical Thinking in Everyday Activities
Critical thinking in reading and writing.
Critical thinking plays a crucial role in both reading and writing. When reading, it involves analyzing and evaluating the information presented, questioning the author's arguments, and identifying any biases or logical fallacies. It also requires the ability to make connections between different ideas and draw conclusions based on evidence. In writing, critical thinking helps to organize thoughts, develop coherent arguments, and present information in a logical and persuasive manner. It involves evaluating the credibility of sources, considering alternative perspectives, and anticipating counterarguments. By incorporating critical thinking skills in reading and writing, individuals can enhance their analytical abilities and become more effective communicators.
Critical Thinking in Decision Making
Critical thinking plays a crucial role in decision making. It involves analyzing information, evaluating options, and making informed choices. Effective decision making requires the ability to think critically and consider multiple perspectives. It is important to gather relevant data, assess the credibility of sources, and identify potential biases. Additionally, evaluating the potential outcomes of different decisions can help in making the best choice. Decision making is a skill that can be developed through practice and by incorporating critical thinking strategies.
Critical Thinking in Problem Solving
Problem solving is a crucial skill that requires analytical thinking and creative problem-solving abilities. It involves identifying and analyzing problems, generating potential solutions, evaluating the effectiveness of each solution, and selecting the best course of action. Critical thinking plays a vital role in this process as it helps individuals to think logically, consider different perspectives, and make informed decisions.
To enhance critical thinking in problem solving, individuals can follow a structured approach that includes the following steps:
- Identify the problem : Clearly define the problem and understand its underlying causes.
- Gather information : Collect relevant data and information related to the problem.
- Generate potential solutions : Brainstorm and come up with multiple possible solutions.
- Evaluate the solutions : Analyze the pros and cons of each solution and assess their feasibility.
- Select the best solution : Choose the solution that is most effective and feasible.
By applying critical thinking skills in problem solving, individuals can improve their ability to analyze complex situations, think creatively, and make well-informed decisions.
Critical Thinking in Analyzing Data
Analyzing data requires careful examination and interpretation of information to draw meaningful conclusions. It involves evaluating the reliability and validity of data sources, identifying patterns and trends, and making informed decisions based on the findings. To effectively analyze data, it is important to follow a systematic approach that includes the following steps:
- Data collection : Gather relevant data from reliable sources.
- Data organization : Arrange the data in a structured format for easy analysis.
- Data cleaning : Remove any errors or inconsistencies in the data.
- Data exploration : Explore the data to identify patterns, correlations, and outliers.
- Data analysis : Apply statistical techniques and tools to analyze the data.
- Data interpretation : Interpret the results and draw meaningful conclusions.
Tip: When analyzing data, it is crucial to critically evaluate the quality and relevance of the data sources to ensure accurate and reliable findings.
Promoting Collaborative Critical Thinking
Group activities for critical thinking.
Group activities are an effective way to promote critical thinking skills in a collaborative setting. These activities encourage participants to work together, share ideas, and analyze different perspectives. Here are some examples of group activities that foster critical thinking:
- Brainstorming sessions : In these sessions, participants come together to generate a large number of ideas on a specific topic. This activity encourages creative thinking and helps participants explore different possibilities.
- Case studies : Case studies provide real-life scenarios for participants to analyze and solve. By examining the details of the case, participants develop their analytical skills and learn to apply critical thinking to practical situations.
- Debates : Debates require participants to critically analyze arguments, present evidence, and counter opposing viewpoints. This activity enhances critical thinking by challenging participants to evaluate information and construct persuasive arguments.
- Problem-solving challenges : These challenges present participants with complex problems that require critical thinking to solve. By working together to find solutions, participants develop their analytical skills and learn to think critically under pressure.
Group activities provide a dynamic and engaging environment for developing critical thinking skills. They encourage collaboration, communication, and the exploration of different perspectives, all of which are essential for analytical skills development.
Role-Playing Games to Encourage Analytical Thinking
Role-playing games are a great way to encourage analytical thinking in a fun and interactive way. By assuming different roles and solving problems within a fictional setting, players are challenged to think critically and make strategic decisions. These games often require players to analyze information, consider different perspectives, and come up with creative solutions. They also promote teamwork and communication skills as players work together to achieve common goals. Engaging and immersive , role-playing games provide a unique opportunity for individuals to develop their analytical thinking abilities.
Debates and Discussions for Developing Critical Thinking
Debates and discussions are powerful tools for developing critical thinking skills. They provide opportunities for individuals to analyze different perspectives, evaluate evidence, and construct logical arguments. Through engaging in debates and discussions, participants can enhance their ability to think critically and communicate effectively. These activities also foster active listening and respectful dialogue, encouraging individuals to consider alternative viewpoints and challenge their own assumptions. By engaging in debates and discussions, individuals can develop a deeper understanding of complex issues and strengthen their analytical skills.
Collaborative Problem-Solving Exercises
Collaborative problem-solving exercises are a valuable tool for developing critical thinking skills. These exercises involve working together with others to solve complex problems, allowing individuals to learn from different perspectives and develop creative solutions. By engaging in collaborative problem-solving exercises, participants can enhance their analytical thinking abilities and improve their ability to work effectively in a team.
One effective collaborative problem-solving exercise is the use of case studies. Case studies provide real-world scenarios that require critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Participants can analyze the situation, identify the key issues, and work together to develop strategies and solutions. This exercise not only enhances critical thinking but also promotes teamwork and communication skills.
Another collaborative problem-solving exercise is the use of group projects. Group projects require individuals to work together to achieve a common goal. This exercise encourages participants to think critically, delegate tasks, and collaborate effectively. It also provides an opportunity for individuals to learn from each other's strengths and weaknesses, fostering a supportive and collaborative environment.
In addition to case studies and group projects, collaborative problem-solving exercises can also involve role-playing scenarios. Role-playing allows participants to step into different roles and perspectives, challenging their assumptions and encouraging critical thinking. By engaging in role-playing exercises, individuals can develop empathy, problem-solving skills, and the ability to think critically from multiple viewpoints.
Overall, collaborative problem-solving exercises are an effective way to develop critical thinking skills. They provide opportunities for individuals to work together, learn from each other, and develop creative solutions to complex problems. By incorporating these exercises into educational and professional settings, individuals can enhance their analytical thinking abilities and become more effective problem solvers.
Promoting Collaborative Critical Thinking is essential in today's fast-paced and ever-changing world. As a keynote speaker, James Taylor inspires creative minds to think outside the box and find innovative solutions. With his expertise in business creativity and innovation, James Taylor has become an internationally recognized leader in this field. If you're looking to ignite your team's creativity and foster collaborative critical thinking, visit our website at www.jamestaylor.com and book James Taylor as your keynote speaker today!
In conclusion, engaging critical thinking games are a valuable tool for developing analytical skills. These games provide a fun and interactive way for individuals to practice and enhance their critical thinking abilities. By challenging players to think critically, analyze information, and make informed decisions, these games help to improve problem-solving skills, logical reasoning, and decision-making abilities. Additionally, critical thinking games promote creativity, innovation, and the ability to think outside the box. Overall, incorporating critical thinking games into educational and professional settings can greatly benefit individuals in their personal and professional lives, enabling them to become more effective problem solvers and decision makers.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is critical thinking.
Critical thinking is the ability to analyze and evaluate information, arguments, and ideas in a logical and systematic manner.
Why is critical thinking important?
Critical thinking is important because it helps individuals develop analytical skills, make informed decisions, and solve complex problems effectively.
How does critical thinking contribute to analytical skills development?
Critical thinking enhances analytical skills by encouraging individuals to think critically, analyze information, identify patterns, and draw logical conclusions.
What are the benefits of developing analytical skills through critical thinking?
Developing analytical skills through critical thinking improves problem-solving abilities, enhances decision-making skills, and promotes creativity and innovation.
What are some engaging critical thinking games?
Some engaging critical thinking games include puzzle games, strategy games, logic games, and problem-solving games.
How can critical thinking be incorporated into everyday activities?
Critical thinking can be incorporated into everyday activities such as reading and writing, decision making, problem solving, and analyzing data.

Popular Posts
Corporate workshops in new york city.
Corporate workshops in New York City WATCH VIDEO Check Availability JAMES TAYLOR – Unleashing Team
Robert Hannigan – The Power of Neurodiversity in Innovation, Cybersecurity, GCHQ and Counter-Intelligence #342
Explore key insights on intelligence and decision-making from Professor Sir David Omand’s book, focusing on critical thinking and creativity.
Sam Dixon of Womble Bond Dickinson, The Evolving Role of Lawyers in the AI Era #341
John craske of cms, collaboration between humans and machines in the legal industry #340, jd meier of microsoft, productivity strategies for success #339, sir david omand, author of how spies think – 10 lessons in critical thinking #338.
James is a top motivational keynote speaker who is booked as a creativity and innovation keynote speaker, AI speaker , sustainability speaker and leadership speaker . Recent destinations include: Dubai , Abu Dhabi , Orlando , Las Vegas , keynote speaker London , Barcelona , Bangkok , Miami , Berlin , Riyadh , New York , Zurich , motivational speaker Paris , Singapore and San Francisco
Latest News
- 415.800.3059
- [email protected]
- Media Interviews
- Meeting Planners
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
FIND ME ON SOCIAL
© 2024 James Taylor DBA P3 Music Ltd.

COMMENTS
Exercise #3: Inversion. Inversion is another critical thinking exercise that you can use in any situation. Inversion is sort of like taking on the role of the devil's advocate. In this exercise, adopt the opposite view of whatever issue you're exploring and consider the potential arguments for that side.
Take a guided, problem-solving based approach to learning Logic. These compilations provide unique perspectives and applications you won't find anywhere else.
A person said what they said, not how you interpret what they said. If you are unclear as to what has been said, ask for clarification. Asking for clarity is not a sign of weakness; it is a sign ...
Reflect and Share: Facilitate a discussion after the activity, allowing teams to share their design choices, challenges faced, and lessons learned. #6. Sudoku. Objective: To engage participants in the strategic and analytical world of Sudoku, enhancing logical thinking and problem-solving abilities.
It’s thinking on purpose! Critical thinking involves mindful communication, problem-solving, and a freedom from bias or. About This Workbook. egocentric tendency. You can apply critical thinking to any kind of subject, problem, or situation you choose. The activity pages in the Critical Thinking Workbook are meant to be shared and explored.
Seriously, doing math will vastly improve your ability to reason and think logically. While solving Algebra and Calculus problems can be helpful, your ability to reason will skyrocket when you get into proving theorems. If you're into reading books, a good introduction to logic is Logic Made Easy by D. Bennett.
Lateral thinking is a creative approach to problem-solving that combines art, creativity, and logic to yield innovative and unexpected solutions. Developed by psychologist Edward de Bono in the 1970s, lateral thinking encourages a shift in perspective to break free from conventional reasoning methods. Unlike critical thinking, which relies ...
One effective collaborative problem-solving exercise is the use of case studies. Case studies provide real-world scenarios that require critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Participants can analyze the situation, identify the key issues, and work together to develop strategies and solutions.
Puzzle Solving: Provide the teams with their series of puzzles that involve both problem-solving and trivia elements. Instruct teams to work together to solve each puzzle as efficiently as possible. Time Limit: Set a timer for 20 minutes to add a sense of urgency and encourage teams to manage their time wisely.
Here are a few methods you might consider to develop your logical thinking skills: 1. Spend time on creative hobbies. Creative outlets like drawing, painting, writing and playing music can stimulate the brain and help promote logical thinking. Creative thinking naturally develops problem-solving abilities that can help you become a better ...