

What Is Climate Change?

Climate change is a long-term change in the average weather patterns that have come to define Earth’s local, regional and global climates. These changes have a broad range of observed effects that are synonymous with the term.
Changes observed in Earth’s climate since the mid-20th century are driven by human activities, particularly fossil fuel burning, which increases heat-trapping greenhouse gas levels in Earth’s atmosphere, raising Earth’s average surface temperature. Natural processes, which have been overwhelmed by human activities, can also contribute to climate change, including internal variability (e.g., cyclical ocean patterns like El Niño, La Niña and the Pacific Decadal Oscillation) and external forcings (e.g., volcanic activity, changes in the Sun’s energy output , variations in Earth’s orbit ).
Scientists use observations from the ground, air, and space, along with computer models , to monitor and study past, present, and future climate change. Climate data records provide evidence of climate change key indicators, such as global land and ocean temperature increases; rising sea levels; ice loss at Earth’s poles and in mountain glaciers; frequency and severity changes in extreme weather such as hurricanes, heatwaves, wildfires, droughts, floods, and precipitation; and cloud and vegetation cover changes.
“Climate change” and “global warming” are often used interchangeably but have distinct meanings. Similarly, the terms "weather" and "climate" are sometimes confused, though they refer to events with broadly different spatial- and timescales.
What Is Global Warming?

Global warming is the long-term heating of Earth’s surface observed since the pre-industrial period (between 1850 and 1900) due to human activities, primarily fossil fuel burning, which increases heat-trapping greenhouse gas levels in Earth’s atmosphere. This term is not interchangeable with the term "climate change."
Since the pre-industrial period, human activities are estimated to have increased Earth’s global average temperature by about 1 degree Celsius (1.8 degrees Fahrenheit), a number that is currently increasing by more than 0.2 degrees Celsius (0.36 degrees Fahrenheit) per decade. The current warming trend is unequivocally the result of human activity since the 1950s and is proceeding at an unprecedented rate over millennia.
Weather vs. Climate
“if you don’t like the weather in new england, just wait a few minutes.” - mark twain.
Weather refers to atmospheric conditions that occur locally over short periods of time—from minutes to hours or days. Familiar examples include rain, snow, clouds, winds, floods, or thunderstorms.
Climate, on the other hand, refers to the long-term (usually at least 30 years) regional or even global average of temperature, humidity, and rainfall patterns over seasons, years, or decades.
Find Out More: A Guide to NASA’s Global Climate Change Website
This website provides a high-level overview of some of the known causes, effects and indications of global climate change:
Evidence. Brief descriptions of some of the key scientific observations that our planet is undergoing abrupt climate change.
Causes. A concise discussion of the primary climate change causes on our planet.
Effects. A look at some of the likely future effects of climate change, including U.S. regional effects.
Vital Signs. Graphs and animated time series showing real-time climate change data, including atmospheric carbon dioxide, global temperature, sea ice extent, and ice sheet volume.
Earth Minute. This fun video series explains various Earth science topics, including some climate change topics.
Other NASA Resources
Goddard Scientific Visualization Studio. An extensive collection of animated climate change and Earth science visualizations.
Sea Level Change Portal. NASA's portal for an in-depth look at the science behind sea level change.
NASA’s Earth Observatory. Satellite imagery, feature articles and scientific information about our home planet, with a focus on Earth’s climate and environmental change.
Header image is of Apusiaajik Glacier, and was taken near Kulusuk, Greenland, on Aug. 26, 2018, during NASA's Oceans Melting Greenland (OMG) field operations. Learn more here . Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Discover More Topics From NASA
Explore Earth Science

Earth Science in Action

Earth Science Data
Facts About Earth

Argumentative Essay Writing
Argumentative Essay About Climate Change

Make Your Case: A Guide to Writing an Argumentative Essay on Climate Change
Published on: Mar 2, 2023
Last updated on: Oct 26, 2024

People also read
Argumentative Essay - A Complete Writing Guide
Learn How to Write an Argumentative Essay Outline
Best Argumentative Essay Examples for Your Help
Basic Types of Argument and How to Use Them?
250+ Argumentative Essay Topics For Your Next Paper
Essential Tips and Examples for Writing an Engaging Argumentative Essay about Abortion
Crafting a Winning Argumentative Essay on Social Media
Craft a Winning Argumentative Essay about Mental Health
Strategies for Writing a Winning Argumentative Essay about Technology
Crafting an Unbeatable Argumentative Essay About Gun Control
Win the Debate - Writing An Effective Argumentative Essay About Sports
Ready, Set, Argue: Craft a Convincing Argumentative Essay About Wearing Mask
Crafting a Powerful Argumentative Essay about Global Warming: A Step-by-Step Guide
Share this article
With the issue of climate change making headlines, it’s no surprise that this has become one of the most debated topics in recent years.
But what does it really take to craft an effective argumentative essay about climate change?
Writing an argumentative essay requires a student to thoroughly research and articulate their own opinion on a specific topic.
To write such an essay, you will need to be well-informed regarding global warming. By doing so, your arguments may stand firm backed by both evidence and logic.
In this blog, we will discuss some tips for crafting a factually reliable argumentative essay about climate change!
On This Page On This Page -->
What is an Argumentative Essay about Climate Change?
The main focus will be on trying to prove that global warming is caused by human activities. Your goal should be to convince your readers that human activity is causing climate change.
To achieve this, you will need to use a variety of research methods to collect data on the topic. You need to make an argument as to why climate change needs to be taken more seriously.
Argumentative Essay Outline about Climate Change
An argumentative essay about climate change requires a student to take an opinionated stance on the subject.
The outline of your paper should include the following sections:
Argumentative Essay About Climate Change Introduction
The first step is to introduce the topic and provide an overview of the main points you will cover in the essay.
This should include a brief description of what climate change is. Furthermore, it should include current research on how humans are contributing to global warming.
An example is:

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Thesis Statement For Climate Change Argumentative Essay
The thesis statement should be a clear and concise description of your opinion on the topic. It should be established early in the essay and reiterated throughout.
For example, an argumentative essay about climate change could have a thesis statement such as:
Climate Change Argumentative Essay Conclusion
The conclusion should restate your thesis statement and summarize the main points of the essay.
It should also provide a call to action, encouraging readers to take steps toward addressing climate change.
For example,
How To Write An Argumentative Essay On Climate Change
Writing an argumentative essay about climate change requires a student to take an opinionated stance on the subject.
Following are the steps to follow for writing an argumentative essay about climate change
Do Your Research
The first step is researching the topic and collecting evidence to back up your argument.
You should look at scientific research, articles, and data on climate change as well as current policy solutions.
Pick A Catchy Title
Once you have gathered your evidence, it is time to pick a title for your essay. It should be specific and concise.
Outline Your Essay
After selecting a title, create an outline of the main points you will include in the essay.
This should include an introduction, body paragraphs that provide evidence for your argument, and a conclusion.
Compose Your Essay
Finally, begin writing your essay. Start with an introduction that provides a brief overview of the main points you will cover and includes your thesis statement.
Then move on to the body paragraphs, providing evidence to back up your argument.
Finally, conclude the essay by restating your thesis statement and summarizing the main points.
Proofread and Revise
Once you have finished writing the essay, it is important to proofread and revise your work.
Check for any spelling or grammatical errors, and make sure the argument is clear and logical.
Finally, consider having someone else read over the essay for a fresh perspective.
By following these steps, you can create an effective argumentative essay on climate change. Good luck!
Examples Of Argumentative Essays About Climate Change
Climate Change is real and happening right now. It is one of the most urgent environmental issues that we face today.
Argumentative essays about this topic can help raise awareness that we need to protect our planet.
Argumentative Essay About Climate Change And Global Warming
Persuasive Essay About Climate Change
Argumentative Essay About Climate Change In The Philippines
Argumentative Essay About Climate Change Caused By Humans
Geography Argumentative Essay About Climate Change
Check our extensive blog on argumentative essay examples to ace your next essay!
Good Argumentative Essay Topics About Climate Change
Choosing a great topic is essential to help your readers understand and engage with the issue.
Here are some suggestions:
- Should governments fund projects that will reduce the effects of climate change?
- Is it too late to stop global warming and climate change?
- Are international treaties effective in reducing carbon dioxide emissions?
- What are the economic implications of climate change?
- Should renewable energy be mandated as a priority over traditional fossil fuels?
- How can individuals help reduce their carbon footprint and fight climate change?
- Are regulations on industry enough to reduce global warming and climate change?
- Could geoengineering be used to mitigate climate change?
- What are the social and political effects of global warming and climate change?
- Should companies be held accountable for their contribution to climate change?
Check our comprehensive blog on argumentative essay topics to get more topic ideas!
We hope these topics and resources help you write a great argumentative essay about climate change.
Now that you know how to write an argumentative essay about climate change, it’s time to put your skills to the test.
Overwhelmed with assignments and thinking, "I wish someone could write me an essay "?
Our specialized writing service is here to turn that wish into reality. With a focus on quality, originality, and timely delivery, our team of professionals is committed to crafting essays that align perfectly with your academic goals.
And for those seeking an extra edge, our essay writer , an advanced AI tool, is ready to elevate your writing to new heights.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a good introduction to climate change.
An introduction to a climate change essay can include a short description of why the topic is important and/or relevant.
It can also provide an overview of what will be discussed in the body of the essay.
The introduction should conclude with a clear, focused thesis statement that outlines the main argument in your essay.
What is a good thesis statement for climate change?
A good thesis statement for a climate change essay should state the main point or argument you will make in your essay.
You could argue that “The science behind climate change is irrefutable and must be addressed by governments, businesses, and individuals.”
Cathy A. (Medical school essay, Education)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Need Help With Your Essay?
Also get FREE title page, Turnitin report, unlimited revisions, and more!
Keep reading

OFF ON CUSTOM ESSAYS
Essay Services
- Argumentative Essay Service
- Descriptive Essay Service
- Persuasive Essay Service
- Narrative Essay Service
- Analytical Essay Service
- Expository Essay Service
- Comparison Essay Service
Writing Help
- Term Paper Writing Help
- Research Writing Help
- Thesis Help
- Dissertation Help
- Report Writing Help
- Speech Writing Help
- Assignment Help
Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.

Global Warming Definition, Causes, Effects, Impacts, Solutions
Global Warming is a long-term increase in average global temperature. Read about Global Warming Definition, Causes, Effects, Impact on Climate Change & Solutions for the UPSC exam.

Table of Contents
What is Global Warming?
Global Warming is a long-term increase in average global temperature. It is considered a natural phenomenon but anthropogenic activities on earth, particularly post Industrial Revolution , have led to an increase in the rate of this temperature increase. Reports from the International Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) show that human activities have raised the average global temperature by about 1 degree Celsius since 1850, with most of this warming occurring in the latter half of the 20th century. The fact that 5 of the hottest years ever recorded happened since 2015 shows us how much human activities are hurting the planet.
Global Warming Causes
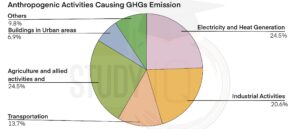
Green House Gases also known as GHGs in the atmosphere trap the solar radiations that are reflected by the earth’s surface. Normally, most of the Earth’s radiation escapes into space. But human activities have increased greenhouse gases (GHGs) in the atmosphere, causing the planet to heat up. Common GHGs include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and water vapor. Each gas has a different warming effect; for instance, methane is 25 times more powerful than carbon dioxide, and nitrous oxide is over 250 times stronger. The top anthropogenic activities that are responsible for the release of GHGs are shown below.
Global Warming and Green House Effect
Both phenomena are related to each other. Green House Gases also known as GHGs in the atmosphere trap the solar radiations that are reflected by the earth’s surface. Under normal circumstances, most of these radiations escape into outer space. However, the release of GHGs by anthropogenic activities has increased their concentration in the atmosphere. This is the primary cause of Global Warming .
Global Warming Effects
Increase in the average temperature of the earth.
According to IPCC reports, human-induced global warming is responsible for nearly 1 degree Celsius temperature rise vis a vis pre-industrial level. Data from NASA suggest that 2016 has been the hottest year on record.
Frequency of Extreme Weather Events is Increasing
Extreme weather events are happening more often around the world. For example, forest fires in California are now a yearly occurrence and are getting more frequent. We’ve also seen heat waves in Antarctica recently, and cyclones in the Bay of Bengal are becoming stronger. Similarly, the frequency of occurrence of El Niño and La Niña has reduced from once in 8–10 years to once in 3–4 years now. More frequent episodes of floods and drought are being recorded every year across the world.
Melting of Ice
According to IPCC, there is 10% less permafrost in North Hemisphere at present compared to the 1900s. Remote sensing data suggest Arctic ice is melting fast. Experts suggest that not only will the sea level rise with the melting of glaciers, but there is also a danger of new bacteria and viruses being released into the environment which has so far been trapped in ice sheets. This may lead to outbreaks of disease and pandemics which are beyond the control of human medical sciences.
Sea Level Rise and Acidification of Ocean
A report published by WMO, suggests that the rate of sea level rise has doubled for the period between 2013 and 2021 compared to the rate for the period between 1993 and 2002. Earth scientists warn that if this continues, many coastal areas where people live could be underwater in the coming years. Rising carbon dioxide levels are also causing oceans to absorb more CO2, leading to ocean acidification. This can be harmful to ocean life, especially coral reefs.
Adverse Impact on Terrestrial Ecosystems of the Earth
It has been recorded that many flora and fauna species are heading northwards in Northern Hemisphere, changes have been observed in the migratory movements of birds across the world. Animals are arriving early at their summer feeding and breeding grounds. Experts say rising temperatures in tropical and subtropical areas could cause new diseases, putting many plants and animals at risk of extinction.
Social and Economic Impact
A rising number of extreme weather events will have an adverse impact on agriculture and fisheries. Rising global temperatures will have a negative impact on the productivity of human beings, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions of the earth. The impact on life and livelihoods of indigenous people across the world will be even more pronounced.

Global Warming Solutions
Global cooperation for reduction of emissions.
We need to take the goal of keeping the global temperature rise within 1.5 degrees Celsius seriously. Global efforts should recognize that all countries have different responsibilities. This means acknowledging past injustices faced by developing countries and giving them a fair chance to grow. Countries must work quickly to reach Net Zero Emissions as soon as possible.
Transition to Cleaner and Greener Forms of Energy
Coal-based power plants should be made more efficient, and the inefficient ones should be closed down. We should promote the use of renewable energy like solar power and explore hydrogen as a fuel. Also, we need to look into nuclear fusion for energy and make nuclear fission safer.
Changes in Agricultural Practices and Land Use
Agriculture based on the use of nitrogenous fertilizers must be replaced with organic farming techniques. We should capture methane gas from farms and animal waste to use as biogas at home. There should be large tree-planting efforts, and city governments need to make sure to include green spaces in their plans.
Improving Transportation System
The rise of electric vehicles is great, but we need better batteries for them. City planners should focus on improving public transportation and design cities to encourage more walking and cycling.
Behavioural Changes
All the above discussions will have no meaning if we as individuals are not sensitive enough. We need to make reducing, reusing and recycling a mantra of our living. It should be our civic duty to save water, and wildlife and raise awareness among others.
Solar Geoengineering
Solar geoengineering, a proposed climate intervention method focus to counteract global warming by reflecting a portion of the sun’s rays back into space. One method involves injecting sulfur dioxide into the upper atmosphere to create reflective particles that can scatter sunlight and cool the Earth. However, solar geoengineering is controversial because it may disrupt weather patterns and create geopolitical risks. Research in this field is ongoing, but it remains a theoretical concept with limited practical implementation.
Can Solar Geoengineering Halt Global Warming?
Solar geoengineering is also called solar radiation management (SRM) is being studied as a way to reduce global warming by reflecting sunlight away from Earth. This could involve injecting substances like sulfur dioxide into the atmosphere to create reflective aerosols. However, its effectiveness and potential side effects raise concerns, and it is still mostly theoretical with little practical use so far.
Global Warming Conclusion
It’s often said that “charity begins at home,” and this idea applies to climate action too. Each person can start by ensuring their home and nearby areas are eco-friendly. When individuals do this it helps make local, national, and global policies more effective.
Global Warming UPSC
Each year, we read about rising global temperatures. Also, catching the headlines is the news related to disasters caused by events like cyclones, forest fires, floods and drought. All these phenomena can be attributed to one single cause which is global warming.
Global Warming is a long-term increase in average global temperature. It is considered a natural phenomenon, but anthropogenic activities on earth, particularly post-Industrial Revolution, have led to an increase in the rate of this temperature increase.
Sharing is caring!
Why is global warming a problem?
Global Warming at present rate can lead to disastrous impacts like rising sea level, out break of new diseases, extreme weather events among others.
What are 3 causes of global warming?
Human induced green house gas emission due to activities like agriculture, industrial emissions, transportation are the top 3 causes of global warming.
What are 5 effects of global warming?
Rising sea level, out break of new diseases, extreme weather events, changes in biodiversity and melting of glaciers are top 5 effects of global warming.
Why global warming is important?
Global warming at its natural rate is important to keep up the temperature of earth within the range that makes it habitable. This makes global warming important.
Can we control global warming?
Number of mitigation measures like shifting to cleaning forms of energy and transportation can be taken to control global warming.
Who help with global warming?
Global Warming is a collective challenge for entire humanity. Citizens, civil societies, governments and businesses must act in unison to address it.
I, Sakshi Gupta, am a content writer to empower students aiming for UPSC, PSC, and other competitive exams. My objective is to provide clear, concise, and informative content that caters to your exam preparation needs. I strive to make my content not only informative but also engaging, keeping you motivated throughout your journey!

Trending Event
- BPSC 70th Answer key 2024
- BPSC 70th Exam Analysis 2024
- BPSC 70th Question Paper 2024
- NDA 1 Notification 2025
- CDS 1 Notification 2025
- UPPSC Prelims Admit Card 2024
- TSPSC Group 2 Hall Ticket 2024
- OPSC OCS Admit Card 2024
Daily Downloads
- UPSC Daily English Current Affairs PDF 2024
- UPSC Daily Hindi Current Affairs PDF 2024

Recent Posts

- UPSC Online Coaching
- UPSC Syllabus 2025
- UPSC Prelims Syllabus 2025
- UPSC Mains Syllabus 2025
- UPSC Exam Pattern 2025
- UPSC Age Limit 2025
- UPSC Calendar 2025
- UPSC Syllabus in Hindi
- UPSC Full Form
- UPPSC Exam 2024
- UPPSC Calendar
- UPPSC Syllabus 2024
- UPPSC Exam Pattern 2024
- UPPSC Application Form 2024
- UPPSC Eligibility Criteria 2024
- UPPSC Salary And Posts
- UPPSC Cut Off
- UPPSC Previous Year Paper
BPSC Exam 2024
- BPSC 70th Notification
- BPSC 69th Exam Analysis
- BPSC Admit Card
- BPSC Syllabus
- BPSC Exam Pattern
- BPSC Cut Off
- BPSC Question Papers
SSC CGL 2024
- SSC CGL Exam 2024
- SSC CGL Syllabus 2024
- SSC CGL Cut off
- SSC CGL Apply Online
- SSC CGL Salary
- SSC CGL Previous Year Question Paper
- SSC CGL Admit Card 2024
- SSC MTS 2024
- SSC MTS Apply Online 2024
- SSC MTS Syllabus 2024
- SSC MTS Salary 2024
- SSC MTS Eligibility Criteria 2024
- SSC MTS Previous Year Paper
SSC Stenographer 2024
- SSC Stenographer Notification 2024
- SSC Stenographer Apply Online 2024
- SSC Stenographer Syllabus 2024
- SSC Stenographer Salary 2024
- SSC Stenographer Eligibility Criteria 2024
SSC GD Constable 2025
- SSC GD Salary 2025
- SSC GD Constable Syllabus 2025
- SSC GD Eligibility Criteria 2025
IMPORTANT EXAMS

- Terms & Conditions
- Return & Refund Policy
- Privacy Policy
What's the difference between global warming and climate change?
Global warming refers only to the Earth’s rising surface temperature, while climate change includes warming and the “side effects” of warming—like melting glaciers, heavier rainstorms, or more frequent drought. Said another way, global warming is one symptom of the much larger problem of human-caused climate change.

Global warming is just one symptom of the much larger problem of climate change. NOAA Climate.gov cartoon by Emily Greenhalgh.
Another distinction between global warming and climate change is that when scientists or public leaders talk about global warming these days, they almost always mean human -caused warming—warming due to the rapid increase in carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases from people burning coal, oil, and gas.
Climate change, on the other hand, can mean human-caused changes or natural ones, such as ice ages. Besides burning fossil fuels, humans can cause climate changes by emitting aerosol pollution—the tiny particles that reflect sunlight and cool the climate— into the atmosphere, or by transforming the Earth's landscape, for instance, from carbon-storing forests to farmland.
A climate change unlike any other
The planet has experienced climate change before: the Earth’s average temperature has fluctuated throughout the planet’s 4.54 billion-year history. The planet has experienced long cold periods ("ice ages") and warm periods ("interglacials") on 100,000-year cycles for at least the last million years.
Previous warming episodes were triggered by small increases in how much sunlight reached Earth’s surface and then amplified by large releases of carbon dioxide from the oceans as they warmed (like the fizz escaping from a warm soda).
Increases and decreases in global temperature during the naturally occurring ice ages of the past 800,000 years, ending with the early twentieth century. NOAA Climate.gov graph by Fiona Martin, based on EPICA Dome C ice core data provided by the Paleoclimatology Program at NOAA’s National Centers for Environmental Information.
Today’s global warming is overwhelmingly due to the increase in heat-trapping gases that humans are adding to the atmosphere by burning fossil fuels. In fact, over the last five decades, natural factors (solar forcing and volcanoes) would actually have led to a slight cooling of Earth’s surface temperature.
Global warming is also different from past warming in its rate. The current increase in global average temperature appears to be occurring much faster than at any point since modern civilization and agriculture developed in the past 11,000 years or so—and probably faster than any interglacial warm periods over the last million years.
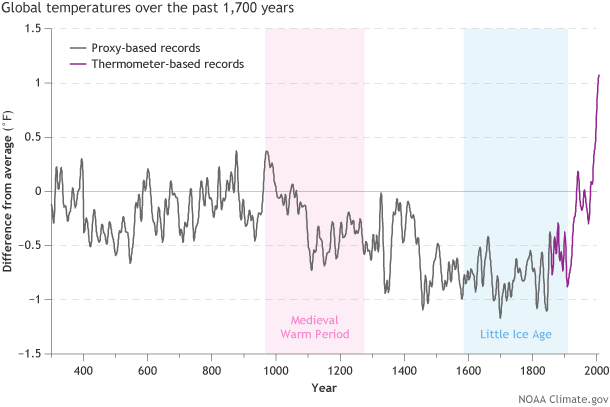
Temperatures over most of the past 2000 years compared to the 1961-1990 average, based on proxy data (tree rings, ice cores, corals) and modern thermometer-based data. Over the past two millenia, climate warmed and cooled, but no previous warming episodes appear to have been as large and abrupt as recent global warming. NOAA Climate.gov graph by Fiona Martin, adapted from Figure 34.5 in the National Climate Assessment, based on data from Mann et al., 2008.
New understanding required new terms
Regardless of whether you say that climate change is all the side effects of global warming, or that global warming is one symptom of human-caused climate change, you’re essentially talking about the same basic phenomenon: the build up of excess heat energy in the Earth system. So why do we have two ways of describing what is basically the same thing?
According to historian Spencer Weart , the use of more than one term to describe different aspects of the same phenomenon tracks the progress of scientists’ understanding of the problem.
As far back as the late 1800s, scientists were hypothesizing that industrialization, driven by the burning of fossil fuels for energy, had the potential to modify the climate. For many decades, though, they weren’t sure whether cooling (due to reflection of sunlight from pollution) or warming (due to greenhouse gases) would dominate.
By the mid-1970s, however, more and more evidence suggested warming would dominate and that it would be unlike any previous, naturally triggered warming episode. The phrase “global warming” emerged to describe that scientific consensus.
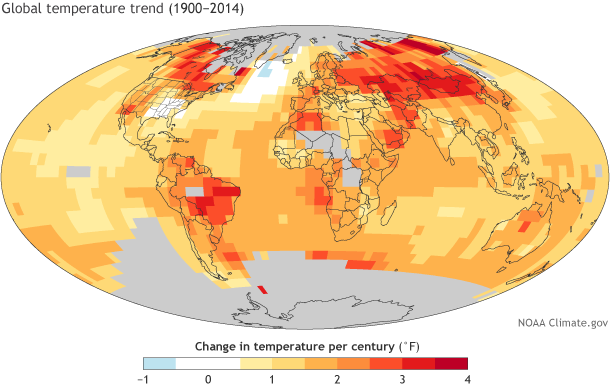
Change in temperature (degrees per century) from 1900-2014. Gray areas indicate where there is insufficient data to detect a long-term trend. NOAA Climate.gov map, based on NOAAGlobalTemp data from NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information.
But over subsequent decades, scientists became more aware that global warming was not the only impact of excess heat absorbed by greenhouse gases. Other changes—sea level rise, intensification of the water cycle, stress on plants and animals—were likely to be far more important to our daily lives and economies. By the 1990s, scientists increasingly used “human-caused climate change” to describe the challenge facing the planet.
The bottom line
Today’s global warming is an unprecedented type of climate change, and it is driving a cascade of side effects in our climate system. It’s these side effects, such as changes in sea level along heavily populated coastlines and the worldwide retreat of mountain glaciers that millions of people depend on for drinking water and agriculture, that are likely to have a much greater impact on society than temperature change alone.
Broecker, W. S. (1975). Climatic Change: Are We on the Brink of a Pronounced Global Warming? Science , 189(4201), 460–463. http://doi.org/10.1126/science.189.4201.460
Climate Data Primer . Climate.gov.
Gillett, N. P., V. K. Arora, G. M. Flato, J. F. Scinocca, and K. von Salzen, 2012: Improved constraints on 21st-century warming derived using 160 years of temperature observations. Geophysical Research Letters, 39, 5, doi:10.1029/2011GL050226. [Available online at http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2011GL050226/pdf ]
Global Warming FAQ . Climate.gov.
How do we know the world has warmed? by J. J. Kennedy, P. W. Thorne, T. C. Peterson, R. A. Ruedy, P. A. Stott, D. E. Parker, S. A. Good, H. A. Titchner, and K. M. Willett, 2010: [in " State of the Climate in 2009 "]. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 91 (7), S79-106.
Huber, M., and R. Knutti, 2012: Anthropogenic and natural warming inferred from changes in Earth’s energy balance. Nature Geoscience, 5, 31-36, doi:10.1038/ngeo1327. [Available online at http://www.nature.com/ngeo/journal/v5/n1/pdf/ngeo1327.pdf ]
Jouzel, J., et al. 2007. EPICA Dome C Ice Core 800KYr Deuterium Data and Temperature Estimates. IGBP PAGES/World Data Center for Paleoclimatology Data Contribution Series # 2007-091. NOAA/NCDC Paleoclimatology Program, Boulder CO, USA.
Mann, M. E., Zhang, Z., Hughes, M. K., Bradley, R. S., Miller, S. K., Rutherford, S., & Ni, F., 2008: Proxy-based reconstructions of hemispheric and global surface temperature variations over the past two millennia. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 105(36), 13252-13257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0805721105.
Melillo, Jerry M., Terese (T.C.) Richmond, and Gary W. Yohe, Eds., 2014: Climate Change Impacts in the United States: The Third National Climate Assessment . U.S. Global Change Research Program, 841 pp. doi:10.7930/J0Z31WJ2. Online at: nca2014.globalchange.gov
National Academy of Sciences, Climate Research Board, Carbon Dioxide and Climate: A Scientific Assessment (Jules Charney, Chair) . (1979). Washington, DC: National Academy of Sciences. [Online (pdf)] http://web.atmos.ucla.edu/~brianpm/download/charney_report.pdf
Walsh, J., D. Wuebbles, K. Hayhoe, J. Kossin, K. Kunkel, G. Stephens, P. Thorne, R. Vose, M. Wehner, J. Willis, D. Anderson, V. Kharin, T. Knutson, F. Landerer, T. Lenton, J. Kennedy, and R. Somerville, 2014: Appendix 4: Frequently Asked Questions. Climate Change Impacts in the United States: The Third National Climate Assessment, J. M. Melillo, Terese (T.C.) Richmond, and G. W. Yohe, Eds., U.S. Global Change Research Program, 790-820. doi:10.7930/J0G15XS3
Weart, S. (2008). Timeline (Milestones). In The Discovery of Global Warming . [Online] American Institute of Physics website.
What's in a Name? Global Warming vs. Climate Change . NASA.
We value your feedback
Help us improve our content
Related Content
News & features, carbon dioxide: earth's hottest topic is just warming up, climate change: atmospheric carbon dioxide, what's the hottest earth's ever been, ocean acidification: the other carbon problem, maps & data, global temperature anomalies - map viewer, climate forcing, global temperature anomalies - graphing tool, teaching climate, toolbox for teaching climate & energy, white house climate education and literacy initiative, the smap/globe partnership: citizen scientists measure soil moisture, climate resilience toolkit, food production, food- and water-related threats.
What Is Climate Change?
Climate change is a long-term change in the average weather patterns that have come to define Earth’s local, regional and global climates. These changes have a broad range of observed effects that are synonymous with the term.
Changes observed in Earth’s climate since the mid-20th century are driven by human activities, particularly fossil fuel burning, which increases heat-trapping greenhouse gas levels in Earth’s atmosphere, raising Earth’s average surface temperature. Natural processes, which have been overwhelmed by human activities, can also contribute to climate change, including internal variability (e.g., cyclical ocean patterns like El Niño, La Niña and the Pacific Decadal Oscillation) and external forcings (e.g., volcanic activity, changes in the Sun’s energy output , variations in Earth’s orbit ).
Scientists use observations from the ground, air, and space, along with computer models , to monitor and study past, present, and future climate change. Climate data records provide evidence of climate change key indicators, such as global land and ocean temperature increases; rising sea levels; ice loss at Earth’s poles and in mountain glaciers; frequency and severity changes in extreme weather such as hurricanes, heatwaves, wildfires, droughts, floods, and precipitation; and cloud and vegetation cover changes.
“Climate change” and “global warming” are often used interchangeably but have distinct meanings. Similarly, the terms "weather" and "climate" are sometimes confused, though they refer to events with broadly different spatial- and timescales.
What Is Global Warming?
Global warming is the long-term heating of Earth’s surface observed since the pre-industrial period (between 1850 and 1900) due to human activities, primarily fossil fuel burning, which increases heat-trapping greenhouse gas levels in Earth’s atmosphere. This term is not interchangeable with the term "climate change."
Since the pre-industrial period, human activities are estimated to have increased Earth’s global average temperature by about 1 degree Celsius (1.8 degrees Fahrenheit), a number that is currently increasing by more than 0.2 degrees Celsius (0.36 degrees Fahrenheit) per decade. The current warming trend is unequivocally the result of human activity since the 1950s and is proceeding at an unprecedented rate over millennia.
Weather vs. Climate
“If you don’t like the weather in New England, just wait a few minutes.” - Mark Twain
Weather refers to atmospheric conditions that occur locally over short periods of time—from minutes to hours or days. Familiar examples include rain, snow, clouds, winds, floods, or thunderstorms.
Climate, on the other hand, refers to the long-term (usually at least 30 years) regional or even global average of temperature, humidity, and rainfall patterns over seasons, years, or decades.
Find Out More: A Guide to NASA’s Global Climate Change Website
This website provides a high-level overview of some of the known causes, effects and indications of global climate change:
Evidence. Brief descriptions of some of the key scientific observations that our planet is undergoing abrupt climate change.
Causes. A concise discussion of the primary climate change causes on our planet.
Effects. A look at some of the likely future effects of climate change, including U.S. regional effects.
Vital Signs. Graphs and animated time series showing real-time climate change data, including atmospheric carbon dioxide, global temperature, sea ice extent, and ice sheet volume.
Earth Minute. This fun video series explains various Earth science topics, including some climate change topics.
Other NASA Resources
Goddard Scientific Visualization Studio. An extensive collection of animated climate change and Earth science visualizations.
Sea Level Change Portal. NASA's portal for an in-depth look at the science behind sea level change.
NASA’s Earth Observatory. Satellite imagery, feature articles and scientific information about our home planet, with a focus on Earth’s climate and environmental change.
Header image is of Apusiaajik Glacier, and was taken near Kulusuk, Greenland, on Aug. 26, 2018, during NASA's Oceans Melting Greenland (OMG) field operations. Learn more here . Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Global warming | Definition, Causes, Effects, Solutions, & Facts ...
The terms "global warming" and "climate change" are sometimes used interchangeably, but "global warming" is only one aspect of climate change. "Global warming" refers to the long-term warming of the planet. Global temperature shows a well-documented rise since the early 20th century and most notably since the late 1970s. Worldwide since 1880, the average surface […]
Climate change is a long-term change in the average weather patterns that have come to define Earth's local, regional and global climates. These changes have a broad range of observed effects that are synonymous with the term. Changes observed in Earth's climate since the mid-20th century are driven by human activities, particularly fossil fuel burning, […]
Climate change is a major issue facing the world today. Over the past century, human activities have caused global temperatures to rise significantly, leading to drastic environmental effects such as increased sea levels, extreme weather events and changes in biodiversity.
Essentially, global warming refers to the gradual increase in the Earth's temperature, leading to climate change. Climate change occurs when pollutants like carbon dioxide accumulate in the atmosphere, trapping sunlight and solar radiation that have bounced off the Earth's surface.
What is Global Warming? Global Warming is a long-term increase in average global temperature. It is considered a natural phenomenon but anthropogenic activities on earth, particularly post Industrial Revolution, have led to an increase in the rate of this temperature increase.Reports from the International Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) show that human activities have raised the average global ...
Climate Explained, a part of Yale Climate Connections, is an essay collection that addresses an array of climate change questions and topics, including why it's cold outside if global warming is real, how we know that humans are responsible for global warming, and the relationship between climate change and national security.
Another distinction between global warming and climate change is that when scientists or public leaders talk about global warming these days, they almost always mean human-caused warming—warming due to the rapid increase in carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases from people burning coal, oil, and gas.. Climate change, on the other hand, can mean human-caused changes or natural ones, such ...
diverse climate change questions, including why it's cold outside if global warming is real, how we know that humans are responsible for global warming, and the relationship between climate change and national security. Image 1. Example Climate Explained essays on the Yale Climate Connections website.
This website provides a high-level overview of some of the known causes, effects and indications of global climate change: Evidence. Brief descriptions of some of the key scientific observations that our planet is undergoing abrupt climate change. Causes. A concise discussion of the primary climate change causes on our planet. Effects.