- Paragraph Generator
- Cover Letter
- Authorization Letter
- Application Letter
- Letter of Intent
- Letter of Recommendation
- Business Plan
- Incident Report
- Reference Letter
- Minutes of Meeting
- Letter of Resignation
- Excuse Letter
- Research Proposal
- Job Application
- Acknowledgement
- Employment Letter
- Promissory Note
- Business Proposal
- Statement of Purpose
- Offer Letter
- Deed of Sale
- Letter of Interest
- Power of Attorney
- Solicitation Letter

Agriculture Business Plan
Agriculture business plan format, agriculture business plan samples, what is an agriculture business plan, benefits of agriculture business plan, tips on agriculture business plan, how to write an agriculture business plan, what is the use of an agriculture business plan, is there a great income in an agriculture business, how often should an agriculture business plan be updated, how does market research impact an agriculture business plan, how can technology enhance an agriculture business plan, what makes an executive summary effective in a business plan, is a mission statement necessary for an agriculture business plan, why is sustainability important in an agriculture business plan.

1. Executive Summary
- Introduction: Briefly introduce the business, mission, vision, and goals.
- Business Idea: Highlight the specific agricultural products or services offered.
- Target Market: Summarize the market analysis and the intended customer base.
- Financial Overview: Present an outline of projected income, expenses, and profitability.
2. Company Overview
- Business Name and Structure: Mention the name and legal structure (e.g., sole proprietorship, partnership).
- Location: Provide details of the business location (e.g., farm, office, etc.).
- Business History: If applicable, include background information about the farm or company.
- Mission Statement: State the mission that guides the business.
- Vision Statement: Define the long-term vision for the agriculture business.
3. Industry and Market Analysis
- Agricultural Trends: Analyze current trends in the agriculture sector.
- Target Market: Describe the demographics and needs of the target customers.
- Market Size and Growth: Provide an estimate of the market size and potential for growth.
- Competitor Analysis: List key competitors, their strengths and weaknesses, and your competitive advantage.
- Regulatory Considerations: Note any agriculture-specific regulations or requirements.
4. Products and Services
- Product Line: Describe the agricultural products or services offered (e.g., crops, livestock, organic produce).
- Production Process: Explain how products will be grown, harvested, or produced.
- Unique Selling Proposition (USP): Highlight what makes your products/services different (e.g., organic farming, eco-friendly methods).
5. Marketing and Sales Strategy
- Marketing Plan: Detail strategies for promoting products (e.g., digital marketing, farmer’s markets, partnerships).
- Pricing Strategy: Define how products will be priced (e.g., cost-based, value-based pricing).
- Distribution Channels: Outline the channels used to reach customers (e.g., wholesalers, direct-to-consumer).
- Sales Plan: Include projected sales volumes and strategies for reaching sales goals.
6. Operations Plan
- Production Plan: Detail how crops or livestock will be cultivated, cared for, and harvested.
- Suppliers and Inputs: List suppliers of seeds, fertilizers, equipment, etc.
- Equipment and Machinery: Describe the equipment and machinery needed for operations.
- Facilities: Explain the physical setup of the farm, processing units, or other facilities.
- Staffing Plan: Outline the roles, responsibilities, and number of employees required.
7. Management and Organization
- Management Team: Provide bios and roles of key management personnel.
- Organizational Structure: Display the organizational hierarchy of the business.
- Advisory Board (if any): Mention any advisors or experts consulted for business guidance.
8. Financial Plan
- Startup Costs: List all costs for starting the business (e.g., land, equipment, seeds).
- Projected Income Statement: Present revenue, expenses, and profits for the first 3-5 years.
- Cash Flow Projection: Include cash flow forecasts for 3-5 years.
- Balance Sheet: Offer a projected balance sheet for 3-5 years.
- Break-Even Analysis: Calculate when the business is expected to break even.
- Funding Requirements: State the amount of funding required and its intended use.
9. Risk Analysis
- SWOT Analysis: Detail the business’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- Risk Management Plan: Describe measures to mitigate potential risks (e.g., crop failure, market fluctuations).
10. Appendix
- Supporting Documents: Include any supporting documents, like market research data, licenses, contracts, etc.
- Visuals: Add diagrams of farm layout, production plans, or organizational charts if necessary.

Agriculture Business Financial Plan

Agriculture Consulting Business Plan

Agriculture Services Business Plan

Regenerative Agriculture Business Plan

Agriculture Farm Business Plan

Farm Business Plan

Organic Farm Business Plan
Draft Farm Business Plan

Small Farm Business Plan

Simple Farm Business Plan

Vegetable Farm Business Plan

Agri-Business Plan

Farm Business Succession Plan

Sample Agriculture Business Plan

Hop Farming Business Plan

Farm Tour Business Plan

Partnership Business Plan for Farm

Farm Business Planning Model

Community Farm Business Plan

Urban Farm Business Plan

Agriculture Farms Business Plan

Organic Farm & Agriculture Business Plan

Sustainable Agriculture Farm Business Plan

Agriculture and Forestry Business Plan

Value Added Agriculture Business Plan

Agriculture Sector Business Plan

Elements of Agriculture Business Plan

New Farmers Business Plan

Agricultural Producers Business Plan

Agricultural and Business Management Business Plan

Beginning Farmer Business Plan

Agricultural Co-operatives Business Plan

Agricultural Business Plan Example

Standard Agricultural Business Plan

Agricultural Entrepreneurs Business Plan
Agricultural Sales 3 Year Business Plan

Agricultural Innovation Business Plan Request Proposal

Agricultural Business Digital Marketing Plan

Precision Agricultural Business Plan

Food Hub Business Plan

Produce Farm Business Plan

Agriculture Business Initiative Plan

Pilot Framers Business Plan

Agricultural Enterprise Business Plan

Sample Sustainable Agriculture Farm Business Plan

Step 1: Develop an Executive Summary
Step 2: define goals and objectives, step 3: craft an engaging introduction, step 4: present a mission statement, step 5: highlight your company history, share this post on your network, you may also like these articles, action plan.

An action plan is a detailed strategy that outlines the steps required to achieve specific goals or objectives within a set timeframe. It serves as a roadmap, guiding individuals,…
Clothing Business Plan

Starting a clothing business requires strategic planning, and a well-structured business plan serves as a roadmap to success. It outlines key elements such as market analysis, product offerings, operational…
browse by categories
- Questionnaire
- Description
- Reconciliation
- Certificate
- Spreadsheet
Information
- privacy policy
- Terms & Conditions
An official website of the United States government Here’s how you know
- Translated Resources |
- Service Centers |
- Local Dashboard
Farmers.gov is not optimized for this browser. Please use the latest versions of Chrome, Edge, or Safari for the best experience. Dismiss
Find your state/county's agriculture data and USDA resources on your farmers.gov Local Dashboard !
How to Start a Farm: Plan Your Operation
Think about your operation from the ground up and start planning for your business. A good farm business plan is your roadmap to start-up, profitability, and growth, and provides the foundation for your conversation with USDA about how our programs can complement your operation.
Keep reading about planning your business below, get an overview of the beginning farmer's journey , or jump to a different section of the farmer's journey.
On This Page
Why you need a farm business plan.
A comprehensive business plan is an important first step for any size business, no matter how simple or complex. You should create a strong business plan because it:
- Will help you get organized . It will help you to remember all of the details and make sure you are taking all of the necessary steps.
- Will act as your guide . It will help you to think carefully about why you want to farm or ranch and what you want to achieve in the future. Over time, you can look back at your business plan and determine whether you are achieving your goals.
- Is required to get a loan . In order to get an FSA loan, a guarantee on a loan made by a commercial lender, or a land contract, you need to create a detailed business plan . Lenders look closely at business plans to determine if you can afford to repay the loan.
How USDA Can Help
Whether you need a good get-started guide, have a plan that you would like to verify, or have a plan you’re looking to update for your next growth phase, USDA can help connect you to resources to help your decisions.
Your state's beginning farmer and rancher coordinator can connect you to local resources in your community to help you establish a successful business plan. Reach out to your state's coordinator for one-on-one technical assistance and guidance. They can also connect you with organizations that specifically serve beginning farmers and ranchers.
It is important to know that no single solution fits everyone, and you should research, seek guidance, and make the best decision for your operation according to your own individual priorities.
Build a Farm Business Plan
There are many different styles of business plans. Some are written documents; others may be a set of worksheets that you complete. No matter what format you choose, several key aspects of your operation are important to consider.
Use the guidelines below to draft your business plan. Answering these kinds of questions in detail will help you create and develop your final business plan. Once you have a business plan for your operation, prepare for your visit to a USDA service center. During your visit, we can help you with the necessary steps to register your business and get access to key USDA programs.
Business History
Are you starting a new farm or ranch, or are you already in business? If you are already in business:
- What products do you produce?
- What is the size of your operation?
- What agricultural production and financial management training or experience do you, your family members, or your business partners have?
- How long have you been in business?
Mission, Vision, and Goals
This is your business. Defining your mission, vision and goals is crucial to the success of your business. These questions will help provide a basis for developing other aspects of your business plan.
- What values are important to you and the operation as a whole?
- What short- and long-term goals do you have for your operation?
- How do you plan to start, expand, or change your operation?
- What plans do you have to make your operation efficient or more profitable ?
- What type of farm or ranch model (conventional, sustainable, organic, or alternative agricultural practices) do you plan to use?
Organization and Management
Starting your own business is no small feat. You will need to determine how your business will be structured and organized, and who will manage (or help manage) your business. You will need to be able to convey this to others who are involved as well.
- What is the legal structure of your business? Will it be a sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation, trust, limited liability company, or other type of entity?
- What help will you need in operating and managing your farm or ranch?
- What other resources, such as a mentor or community-based organization , do you plan to use?
Marketing is a valuable tool for businesses. It can help your businesses increase brand awareness, engagement and sales. It is important to narrow down your target audience and think about what you are providing that others cannot.
- What are you going to produce ?
- Who is your target consumer ?
- Is there demand for what you are planning to produce?
- What is the cost of production?
- How much will you sell it for and when do you expect to see profit ?
- How will you get your product to consumers ? What are the transportation costs and requirements?
- How will you market your products?
- Do you know the relevant federal, state, and local food safety regulations? What licensing do you need for your operation?
Today there are many types of land, tools, and resources to choose from. You will need to think about what you currently have and what you will need to obtain to achieve your goals.
- What resources do you have or will you need for your business?
- Do you already have access to farmland ? If not, do you plan to lease, rent, or purchase land?
- What equipment do you need?
- Is the equipment and real estate that you own or rent adequate to conduct your operation? If not, how do you plan to address those needs?
- Will you be implementing any conservation practices to sustain your operation?
- What types of workers will you need to operate the farm?
- What additional resources do you need?
Now that you have an idea of what you are going to provide and what you will need to run your operation you will need to consider the finances of your operation.
- How will you finance the business?
- What are your current assets (property or investments you own) and liabilities (debts, loans, or payments you owe)?
- Will the income you generate be sufficient to pay your operating expenses, living expenses, and loan payments?
- What other sources of income are available to supplement your business income?
- What business expenses will you incur?
- What family living expenses do you pay?
- What are some potential risks or challenges you foresee for your operation? How will you manage those risks?
- How will you measure the success of your business?
Farm Business Plan Worksheets
The Farm Business Plan Balance Sheet can help gather information for the financial and operational aspects of your plan.
Form FSA-2037 is a template that gathers information on your assets and liabilities like farm equipment, vehicles and existing loans.
- FSA-2037 - Farm Business Plan - Balance Sheet
- FSA-2037 Instructions
Planning for Conservation and Risk Management
Another key tool is a conservation plan, which determines how you want to improve the health of your land. A conservation plan can help you lay out your plan to address resource needs, costs and schedules.
USDA’s Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS) staff are available at your local USDA Service Center to help you develop a conservation plan for your land based on your goals. NRCS staff can also help you explore conservation programs and initiatives, such as the Environmental Quality Incentives Program (EQIP) .
Conservation in Agriculture
Crop insurance, whole farm revenue protection and other resources can help you prepare for unforeseen challenges like natural disasters.
Disaster Recovery

Special Considerations
Special considerations for businesses.
There are different types of farm businesses each with their own unique considerations. Determine what applies to your operation.
- Organic Farming has unique considerations. Learn about organic agriculture , organic certification , and the Organic Certification Cost Share Program to see if an organic business is an option for you. NRCS also has resources for organic producers and offers assistance to develop a conservation plan.
- Urban Farming has special opportunities and restrictions. Learn how USDA can help farmers in urban spaces .
- Value-Added Products . The Agricultural Marketing Resource Center (AgMRC) is a national virtual resource center for value-added agricultural groups.
- Cooperative. If you are interested in starting a cooperative, USDA’s Rural Development Agency (RD) has helpful resources to help you begin .
Special Considerations for Individuals
Historically Underserved Farmers and Ranchers: We offer help for the unique concerns of producers who meet the USDA definition of "historically underserved," which includes farmers who are:
- socially disadvantaged
- limited resource
- military veterans
Women: Learn about specific incentives, priorities, and set asides for women in agriculture within USDA programs.
Heirs' Property Landowners: If you inherited land without a clear title or documented legal ownership, learn how USDA can help Heirs’ Property Landowners gain access to a variety of programs and services
Business Planning
Creating a good business plan takes time and effort. The following are some key resources for planning your business.
- Farm Answers from the University of Minnesota features a library of how-to resources and guidance, a directory of beginning farmer training programs, and other sources of information in agriculture. The library includes business planning guides such as a Guide to Developing a Business Plan for Farms and Rural Businesses and an Example Business Plan .
- The Small Business Administration (SBA) offers information about starting, managing, and transitioning a business.
SCORE is a nonprofit organization with a network of volunteers who have experience in running and managing businesses. The Score Mentorship Program partners with USDA to provide:
- Free, local support and resources, including business planning help, financial guidance, growth strategies.
- Mentorship through one-on-one business coaching -- in-person, online, and by phone.
- Training from subject matter experts with agribusiness experience.
- Online resources and step-by-step outlines for business strategies.
- Learn more about the program through the Score FAQ .
Training Opportunities
Attend field days, workshops, courses, or formal education programs to build necessary skills to ensure you can successfully produce your selected farm products and/or services. Many local and regional agricultural organizations, including USDA and Cooperative Extension, offer training to beginning farmers.
- Cooperative Extension offices address common issues faced by agricultural producers, and conduct workshops and educational events for the agricultural community.
- extension.org is an online community for the Cooperative Extension program where you can find publications and ask experts for advice.
Now that you have a basic plan for your farm operation, prepare for your visit to a USDA service center.
2. Visit Your USDA Service Center
How to Start a Farm with USDA
Get an overview of the beginning farmer's journey or jump to a specific page below.
Find Your Local Service Center
USDA Service Centers are locations where you can connect with Farm Service Agency, Natural Resources Conservation Service, or Rural Development employees for your business needs. Enter your state and county below to find your local service center and agency offices. If this locator does not work in your browser, please visit offices.usda.gov.
Learn more about our Urban Service Centers . Visit the Risk Management Agency website to find a regional or compliance office or to find an insurance agent near you.

Agriculture Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky

Agriculture Business Plan
Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 500 entrepreneurs and farm owners create business plans to start and grow their agricultural companies.
If you’re unfamiliar with creating an agriculture or farm business plan, you may think creating one will be a time-consuming and frustrating process. For most entrepreneurs it is, but for you, it won’t be since we’re here to help. We have the experience, resources, and knowledge to help you create a good business plan.
In this article, you will learn some background information on why business planning is important. Then, you will learn how to write an agriculture business plan step-by-step so you can create your plan today.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here >
What is an Agriculture Business Plan?
A business plan provides a snapshot of your agricultural business as it stands today, and lays out your growth plan for the next five years. It is a valuable tool that explains your business goals and your strategies for reaching them. It also includes market research to support your plans.
Why You Need a Business Plan for an Agriculture Business
If you’re looking to start an agricultural business or grow your existing agricultural company, you need a business plan. A business plan will help you raise funding, if needed, and plan out the growth of your farm to improve your chances of success. Your agricultural business plan is a living document that should be updated annually as your company grows and changes.
Sources of Funding for Agricultural Businesses
With regard to funding, the main sources of funding for an agricultural business are personal savings, credit cards, bank loans, and angel investors. When it comes to bank loans, banks will want to review a comprehensive business plan and gain confidence that you will be able to repay your loan and interest. To acquire this confidence, the loan officer will not only want to ensure that your financials are reasonable, but they will also want to see a professional plan. Such a plan will give them the confidence that you can successfully and professionally operate a business. Personal savings and bank loans are the most common funding paths for agricultural companies.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
How to Write a Business Plan for an Agricultural Business
If you want to start an agricultural business or expand your current one, you need a business plan. A good farm business plan should include 10 sections as follows:
Executive Summary
Company overview, industry analysis, customer analysis, competitive analysis, marketing plan, operations plan, management team, financial plan.
Your executive summary provides an introduction to your business plan, but it is normally the last section you write because it provides a summary of each key section of your plan. The goal of your executive summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the kind of farm business you are running and the status. For example, are you a startup, do you have an agricultural business that you would like to grow, or do you have a farming operation that you would like to sell? Next, provide an overview of each of the subsequent sections of your plan.
- Give a brief overview of the agricultural industry.
- Discuss the type of farm you are operating.
- Detail your direct competitors. Give an overview of your target customers.
- Provide a snapshot of your marketing strategy. Identify the key members of your team.
- Offer an overview of your financial plan.
In your company overview, you will detail the type of agricultural production you are operating.
For example, you might specialize in one of the following types of agricultural businesses:
- Animal feed manufacturing : the production and sale of food formulas for farm animals.
- Agrichemical and seed manufacturing : the production and sale of agrichemicals (e.g., fertilizers, pesticides, and fungicides) and seeds to farmers that support the growth of their crops.
- Agricultural engineering : development, testing, and implementation of new agriculture tools and machinery to improve the process for farmers.
- Biofuel manufacturing : the production of energy from biomass.
- Crop production : the process of growing and harvesting a variety of crops such as fruits, vegetables, and grains.
In addition, the company overview needs to provide information about the business history.
Include answers to questions such as:
- When and why did you start the business?
- What milestones have you achieved to date? Milestones could include reaching X number of harvests per year, the number of customers served, or reaching $X amount in revenue.
- Your legal business Are you incorporated as an S-Corp? An LLC? A sole proprietorship? Explain your legal structure here.
In your industry or market analysis, you need to provide an overview of the agricultural industry. While this may seem unnecessary, it serves multiple purposes.
First, researching the agricultural industry educates you. It helps you understand the market in which you are operating.
Secondly, market research can improve your marketing strategy, particularly if your analysis identifies industry trends.
The third reason is to prove to readers that you are an expert in your industry. By conducting the research and presenting it in your plan, you achieve just that.
The following questions should be answered in this section:
- How big is the agricultural industry (in dollars)?
- Is the market declining or increasing?
- Who are the key competitors in the market?
- Who are the key suppliers in the market?
- What trends are affecting the industry?
- What is the industry’s growth forecast over the next 5 – 10 years?
- What is the relevant market size? That is, how big is the potential target market for your agricultural business? You can extrapolate such a figure by assessing the size of the market in the entire country and then applying that figure to your local population.
The customer analysis section must detail the customers you serve and/or expect to serve.
The following are examples of customer segments: individuals, schools, families, and corporations.
As you can imagine, the customer segment(s) you choose will have a great impact on the type of agricultural business you operate. Clearly, schools would respond to different marketing promotions than corporations, for example.
Try to break out your target market into segments in terms of their demographic and psychographic profiles. With regards to demographics, including a discussion of the ages, genders, locations, and income levels of the potential customers you seek to serve.
Psychographic profiles explain the wants and needs of your target audience. The more you can recognize and define these needs, the better you will do in attracting and retaining your customers.
Finish Your Agriculture Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template , you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Your competitive analysis should identify the indirect and direct competitors your business faces and then focus on the latter.
Direct competitors are other farms and agricultural producers.
Indirect competitors are other options that customers have to purchase from that aren’t directly competing with your product or service. This includes other types of farmers, wholesalers, and distributors.
For each such competitor, provide an overview of their business and document their strengths and weaknesses. Unless you once worked at your competitors’ businesses, it will be impossible to know everything about them. But you should be able to find out key things about them such as:
- What types of customers do they serve?
- What type of agricultural business are they?
- What is their pricing (premium, low, etc.)?
- What are they good at?
- What are their weaknesses?
With regards to the last two questions, think about your answers from the customers’ perspective. And don’t be afraid to ask your competitors’ customers what they like most and least about them.
The final part of your competitive analysis section is to document your areas of competitive advantage. For example:
- Will you make it easier for your customers to engage with you?
- Will you offer products or services that your competition doesn’t?
- Will you provide better customer service?
- Will you offer better pricing?
Think about ways you will outperform your competition and document them in this section of your plan.
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P’s: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For an agriculture business, your marketing strategy should include the following:
Product : In the product section, you should reiterate the type of agricultural company that you documented in your company overview. Then, detail the specific products or services you will be offering. For example, will you produce fruit, soy, or vegetable products?
Price : Document the prices you will offer and how they compare to your competitors. Essentially in the product and price sub-sections of your plan, you are presenting the products and/or services you offer and their prices.
Place : Place refers to the site of your agricultural company. Document where your company is situated and mention how the site will impact your success. For example, is your agricultural business located on a small or large farm near your customer base? And, will you operate one or multiple locations? Discuss how your site might be the ideal location for your customers.
Promotions : The final part is where you will document how you will drive potential customers to your location(s). The following are some promotional methods you might consider:
- Advertise in local papers, radio stations and/or magazines
- Reach out to websites
- Distribute flyers
- Attend farmers markets
- Engage in email marketing
- Advertise on social media platforms
- Improve the SEO (search engine optimization) on your website for targeted keywords
While the earlier sections of your business plan explained your goals, your operations plan describes how you will meet them. Your operations plan should have two distinct sections as follows.
Everyday short-term processes include all of the tasks involved in running your farm business, including scheduling employees, tracking inventory, accepting orders and payments, and meeting with customers.
Long-term goals are the milestones you hope to achieve. These could include the dates when you expect to reach your Xth harvest, or when you hope to generate $X in revenue. It could also be when you expect to expand your farm business to a new region.
To demonstrate your potential to succeed, a strong management team is essential. Highlight your key players’ backgrounds, emphasizing those skills and experiences that prove their ability to grow a company.
Ideally, you and/or your team members have direct experience in managing agricultural businesses. If so, highlight this experience and expertise. But also highlight any experience that you think will help your business succeed.
If your team is lacking, consider assembling an advisory board. An advisory board would include 2 to 8 individuals who would act as mentors to your business. They would help answer questions and provide strategic guidance. If needed, look for advisory board members with experience in managing an agriculture business, or owning their own farm.
Your financial plan should include your 5-year financial statement broken out both monthly or quarterly for the first year and then annually. Your financial statements include your income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statements.
Income Statement
An income statement is more commonly called a Profit and Loss statement or P&L. It shows your revenue and then subtracts your costs to show whether you turned a profit or not.
In developing your income statement, you need to devise assumptions. For example, how many pounds of each crop do you plan to yield each season? And what is your sales strategy to grow by 2% or 10% per year? As you can imagine, your choice of assumptions will greatly impact the financial forecasts for your business. As much as possible, conduct research to try to root your assumptions in reality.
Balance Sheets
Balance sheets show your assets and liabilities. While balance sheets can include much information, try to simplify them to the key items you need to know about. For instance, if you spend $50,000 on building out your farm business, this will not give you immediate profits. Rather it is an asset that will hopefully help you generate profits for years to come. Likewise, if a lender writes you a check for $50,000, you don’t need to pay it back immediately. Rather, that is a liability you will pay back over time.
Cash Flow Statement
Your cash flow statement will help determine how much money you need to start or grow your business, and ensure you never run out of money. What most entrepreneurs and business owners don’t realize is that you can turn a profit but run out of money and go bankrupt.
When creating your Income Statement and Balance Sheets be sure to include several of the key costs needed in starting or growing a farm business:
- Cost of farm equipment and supplies
- Operating expenses
- Payroll or salaries paid to staff
- Business insurance
- Other start-up costs (if you’re a new business) like legal expenses, permits, computer software, and equipment
Attach your full financial projections in the appendix of your plan along with any supporting documents that make your plan more compelling. For example, you might include your farm’s location lease or a list of agricultural equipment and machinery used on your farm.
Free Business Plan Template for a Farm or Agriculture Business
You can download our farm business plan PDF template here.
Agriculture Business Plan Summary
Putting together a business plan for your agriculture business will improve your company’s chances of success. The process of developing your plan will help you better understand your target market, your competition, and your customers. You will also gain a marketing plan to better attract and serve customers, an operations plan to focus your efforts, and financial projections that give you goals to strive for and keep your company focused.
Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template allows you to quickly and easily write your business plan.
Additional Resources for Starting an Agriculture Business
- How To Start a Farm
- Sample Farm Business Plan
- Starting a New Agricultural Business
- Small and Mid-Sized Farmer Resources
- Starting a Sustainable Agriculture Business
- Beginning Farmers and Ranchers Loans
- Business Resources for Those Starting to Farm or for an Existing Farm
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success.
See how Growthink’s business plan professional services can help you create a winning business.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

Farm Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Farm Business Plan
Whether you’re starting a small organic farm or planning a large-scale agricultural operation, this sample farm business plan, created by the seasoned professionals at PlanBuildr.com, is the perfect place to start. With over 20 years of experience helping entrepreneurs grow their ideas into thriving businesses, our team knows exactly what it takes to turn your farming aspirations into a reality.
Below are links to each section of a small farm business plan template. It can be used to create a vegetable farm business plan, fruit farm business plan, agriculture farm business plans or many other types of rural businesses.
Sample Business Plan For Farms & Agricultural Businesses
Below is a farm business plan example to help you create each section of your own farm business plan:
Executive Summary
Business overview.
Veggie Good Vegetable Farm is a certified organic vegetable farm located in Northfield, Vermont. It is owned by Joe and Amanda Green, a local couple who have made it their lifelong goal to own and operate a vegetable farm. Joe and Amanda perfectly complement each other, as Joe is experienced and knowledgeable in operating a farm and Amanda has made her career as an accounting, tax, and finance professional. Joe will oversee all operations of the vegetable farm and Amanda will manage the farm’s accounting, accounts payable, tax payments, licenses and permits, as well as all marketing functions.
Veggie Good Vegetable Farm will offer the freshest, organic, and responsibly sourced and farmed vegetables using the most technologically advanced farming equipment. Veggie Good will be the only Vermont farm utilizing these techniques and Joe and Amanda will market this to their advantage. The advanced technological practices ensure less waste for the soil and environment, and it will produce a more robust and fresh vegetable.
Veggie Good Vegetable Farm will sell their products by offering Community Supported Agriculture (CSA) membership subscriptions, where a customer can pay a monthly subscription to receive a weekly vegetable box. We will also participate in local farmers markets to receive maximum exposure from the Northfield community. Lastly, Veggie Good will target local restaurants to offer wholesale pricing for it to receive their vegetables and be able to offer their local produce on the restaurant’s menu.
Product Offering
The following are the products that Veggie Good Vegetable Farm will provide:
- Specialty greens
Customer Focus
Veggie Good Vegetable Farm will target all residents of Northfield, Vermont. We will also target local restaurants to offer wholesale pricing to, and consumers of local farmers markets.
Management Team
Veggie Good Vegetable Farm will be owned and operated by Joe and Amanda Green. The team has over 15 years of experience working at farms and researching professional and effective farming techniques.
Joe Green has had a 15 year career working at a local dairy farm as a farm operator. During his tenure with the dairy farm, he has worked in all aspects of operating the farm and became the lead farmer for the owner. Joe has amassed a wealth of knowledge in the operation and business of a farm and is ready to put his knowledge to work with his own vegetable farm.
Amanda Green has worked as an accountant for over 10 years at a local CPA firm. She is extremely knowledgeable and certified in all accounting functions, tax regulations, licensing, and permitting. Amanda is also knowledgeable with marketing efforts, website design, and social media management. Her organization, skills, and business competence will ensure the success and profitability of Veggie Good Vegetable Farm.
Success Factors
Veggie Good Vegetable Farm will be able to achieve success by offering the following competitive advantages:
- Friendly, knowledgeable, and highly qualified team of farmers who share the same sustainability and environmentally-friendly mindset of its customers.
- Certified organic vegetable farm that utilizes the latest technology in horticulture and farming practices.
- Cost-effective CSA membership pricing and the ability to customize subscription vegetable boxes.
Financial Highlights
Veggie Good Vegetable Farm is seeking $300,000 in debt financing to launch its vegetable farm. The funding will be dedicated towards securing 10 acres of farmland and purchasing farm equipment and supplies. Funding will also be dedicated towards three months of overhead costs to include payroll of the staff, rent, and marketing costs for the website development, and working capital. The breakout of the funding is below:
- Farmland and facility build-out: $100,000
- Farm equipment, supplies, and materials: $100,000
- Three months of overhead expenses (payroll, rent, utilities): $75,000
- Marketing costs: $10,000
- Working capital: $15,000
The following graph below outlines the pro forma financial projections for Veggie Good Vegetable Farm.
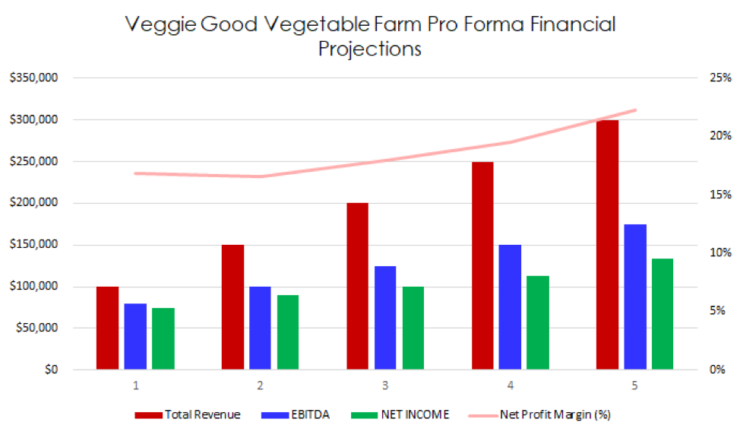
Company Overview
Who is veggie good vegetable farm.
Veggie Good Vegetable Farm is a newly-established organic vegetable farm owned and operated by Joe and Amanda Green. Joe and Amanda will be leasing 10 acres of farmland in Northfield, Vermont to begin and establish their vegetable farming business. The farm will grow beets, carrots, turnips, peppers, specialty greens, and tomatoes. Their goal is to be able to provide weekly vegetable subscription boxes by selling memberships and also sell their vegetables wholesale to nearby restaurants and cafeterias.
Veggie Good Vegetable Farm will utilize the latest technological farming equipment in order to ensure quality, taste, and responsible farming practices. Joe and Amanda see this as a marketing advantage as their competition do not currently utilize the latest technological standards.
Veggie Good Vegetable Farm History
Veggie Good Vegetable Farm is the startup venture of Joe and Amanda Green, a local Vermont couple who has spent years studying agriculture and farming techniques. Joe has worked at a nearby dairy farm for over 15 years and Amanda has worked as an accountant at a local CPA firm for 10 years. Joe and Amanda are graduates of the University of Vermont where Joe received his Bachelor’s Degree in Farm Business Management and Amanda received her Bachelor’s Degree in Accounting. Now that both have spent years in farming and learning how to run a farm business, they are ready to make their dream of owning and operating a successful farm into reality.
Since incorporation, Veggie Good Vegetable Farm has achieved the following milestones:
- Located and signed a lease for 10 acres of farmland in Northfield, Vermont.
- Researched and developed a plan to purchase the appropriate fertility and agricultural equipment, capital investments required, researched market potential, and laid out a 5-10 year plan.
- Began recruiting staff to work at the farm.
- Developed a comprehensive membership program that it will begin marketing to the local community.

Veggie Good Vegetable Farm Products
The following will be the products Veggie Good Vegetable Farm will provide:
Industry Analysis
With vegetable consumption expected to expand 25.0% to reach US Department of Agriculture (USDA)-recommended levels, the industry is expected to reach $20 billion in the next five years.
This, along with increasing health awareness, could lead to a surge in demand for vegetable farmers. Also, amid steady demand from wholesalers and full-service single-location restaurants, the price of vegetables is expected to increase an annualized 0.5% over the five year period. Steady demand and expected product price appreciation, coupled with the value industry exports increasing during the period, are expected to drive industry revenue.
Further, the USDA projects total US vegetable and melon output to rise over the next five years. Improvements in yield and dedicated acreage will likely drive this increase; larger farms are increasingly using genetically modified seeds and farming machinery to increase yields per acre. Steady demand, high vegetable prices and increased productivity are expected to help drive industry revenue growth over the next five years.
Customer Analysis
Demographic profile of target market.
Veggie Good Vegetable Farm will target all residents and households that live in Northfield, Vermont. They will also target local restaurants and schools to sell their vegetables wholesale to.
The precise demographics for Northfield, Vermont are:
Customer Segmentation
Veggie Good Vegetable Farm will primarily target the following customer profiles:
- Residents of Northfield, Vermont
- Locally owned restaurants who could order their vegetable produce from Veggie Good
- Local schools who serve daily breakfasts and/or lunches to its students
Competitive Analysis
Direct and indirect competitors.
Veggie Good Vegetable Farm will face competition from other companies with similar business profiles. A description of each competitor company is below.
Mighty Food Farm
Mighty Food Farm is a certified organic vegetable farm located in Shaftsbury, Vermont. They have been in business for 15 years and are able to provide their customers with fresh vegetables year-round. Mighty Food Farm offers a CSA program where there is a mutual partnership between the farmer and the community of supporters who buy shares of the farm’s harvest each year. The CSA shares are typically paid for in the late winter and early spring. The CSA for Mighty Food Farm is 50-60% of the farms annual revenue. The Mighty Food Farm’s CSA program allows members to choose what is in their box every week. Mighty Food offers flowers, strawberries, peas, beans, potatoes, parsnips, eggplants, squash, cabbage, kale, tomatoes, carrots, cauliflowers, etc. Customers are also able to purchase from Mighty Food Farm at the local farmers markets in town. Businesses are also able to purchase from Mighty Food Farm through their wholesale program.
Berry Creek Farm
Berry Creek Farm is a 158-acre organic family farm in Vermont that has been in business for over 28 years. Owned by Gerard and Rosemary Croizet, they have made it their mission to pursue sustainable organic agricultural enterprises linking local food to the community. Berry Creek Farm will provide agricultural educational opportunities, a living for farmers, and ensure the viability of the farming operation for the next generation. Berry Creek Farm offers strawberries, vegetables, honey, CSA shares, beeswax candles, beef, jams, cut flowers, annuals, herbs, perennials, hanging flower baskets, patio tomatoes, and vegetable plants. Not all of their products are certified organic. Berry Creek Farm also carries a number of products from other producers. They also offer two different CSA programs; one where the customer can choose to pick up a prepared box of produce each week, or they can choose to use their share to purchase items whenever the customer likes at their farm during the hours of operation.
Root 5 Farm
Root 5 Farm is a certified organic vegetable farm located on 38 acres in Fairlee, Vermont along the Connecticut River. Owned by Benner Dana and Danielle Allen, the fertile river bottom soils provide a rich environment for growing over 100 different types of vegetables. The farm has been certified organic by Vermont Organic Farmers (VOF) since 2006. They utilize growing practices that use a holistic approach to soil fertility, pest control, and plant and animal health. They build their soil through crop rotation, cover cropping, and minimal tillage. Root 5 Farm sells their products through local farmers markets, CSA memberships, local restaurants, and local coop food stores. Their CSA membership offers weekly vegetable box deliveries May through December. Members can choose between three different sizes of boxes, three season options, 11 upper valley pick up sites, add on products from other local farms, and a pay as you go subscription.
Competitive Advantage
Veggie Good Vegetable Farm will be able to offer the following advantages over their competition:
Marketing Plan
Brand & value proposition.
Veggie Good Vegetable Farm will offer the unique value proposition to its clientele:
- Friendly and knowledgeable farming staff that believes in sustainability and environmentally-friendly farming practices.
- Certified organic fresh vegetables sourced from the most technological farming practices.
Promotions Strategy
The promotions strategy for Veggie Good Vegetable Farm is as follows:
CSA Memberships
Veggie Good Vegetable Farm will focus on selling memberships to the community for vegetable box subscriptions. By obtaining a handful of CSA memberships, the revenue obtained will be able to financially support the farm’s financial requirements.
Farmers Markets
Veggie Good Vegetable Farm will attend all local farmers markets in Northfield, Vermont. By participating in the farmers markets, Veggie Good will receive exposure to the population of Northfield who are most likely to participate in their CSA membership program.
Website/SEO Marketing
Veggie Good Vegetable Farm will develop and maintain a professionally-designed website to list their products, CSA membership information, and information regarding their advanced technological farming practices. The website will also list their contact information and address so that visitors to the site know where to find them. Amanda Green will also manage Veggie Good’s website presence with SEO marketing tactics so that anytime someone types in the Google or Bing search engine “organic Vermont vegetable farm” or “vegetable farm near me”, Veggie Good Vegetable Farm will be listed at the top of the search results.
Social Media
Veggie Good Vegetable Farm will also maintain a strong social media presence through Facebook and Instagram. Amanda Green will frequently post appetizing pictures of their fruits and the CSA membership program.
Wholesale to Restaurants
Veggie Good Vegetable Farm will also target local restaurants to offer wholesale pricing to the establishment. Veggie Good will treat it as a partnership where each business could advertise on behalf of the other.
The pricing of Veggie Good Vegetable Farm will be moderate and on par with competitors, so customers feel they receive value when purchasing their products.
Operations Plan
The following will be the operations plan for Veggie Good Vegetable Farm.
Operation Functions:
- Joe Green – Owner and Head Farmer who will manage crops, supplies, equipment, and staff.
- Amanda Green – Owner and Farm Accountant who will oversee all accounting, finance, tax, and payroll functions. Amanda will also manage marketing efforts, CSA membership dues and collections, and farm licenses and permits.
- Joe and Amanda will employ a staff of four employees to start with to assist Joe with all farming duties.
Milestones:
Veggie Good Vegetable Farm will have the following milestones complete in the next six months.
5/1/202X – Finalize contract to lease 10 acres of farmland
5/15/202X – Purchase farm equipment and supplies
6/1/202X – Begin planting seeds for future vegetable crops
6/15/202X – Start hiring staff to assist in farming duties
6/22/202X – Begin marketing program to begin to get the word out of Veggie Good’s CSA membership program
7/1/202X – Begin approaching local restaurants to offer and sell their vegetables at wholesale price
9/1/202X – Begin participating in farmers markets with the first batch of crops that have harvested; also sell CSA memberships at farmers markets.
Veggie Good Vegetable Farm will be owned and operated by Joe and Amanda Dunn, a local Vermont couple who have made it their lifelong goal of eventually owning and operating a vegetable farm. They have spent the last fifteen years studying farming practices and responsible farming practices. They have attended workshops and seminars of the latest technology advancements available in farming equipment and practices and have received certifications of how to operate the equipment.
Joe Green received a Bachelor’s degree from the University of Vermont in farm business management. After graduation, he found employment at a local dairy farm and has apprenticed under the owners and managers of the farm. Joe has spent the last fifteen years studying the operations of a farm. Because Joe is widely respected at the dairy farm, the owners are wanting to partner with Veggie Good and offer some of the vegetable products to their frequent customers.
Amanda Green received a Bachelor’s degree from the University of Vermont in Accounting and has spent the last ten years working as an accountant at a local CPA firm. Amanda is well versed in tax accounting, accounts payable, and profit and loss statements. She is the perfect complement to Joe, as she will handle all administrative, accounting, and marketing duties. Amanda has researched extensively how to manage a farm and make it profitable. She, along with Joe, are ready to embark on their own vegetable farm.
Financial Plan
Key revenue & costs.
The revenue drivers for Veggie Good Vegetable Farm are the CSA membership subscriptions, sales from the farmers markets, and revenue obtained from selling vegetables to local restaurants at the wholesale price.
The cost drivers will be the overhead costs required in order to staff the team of four support farmers, farming equipment, supplies, seeds, tools, boxes, and packaging goods. Other expenses will be the payroll cost, rent for the leased farmland, utilities, and marketing materials.
Funding Requirements and Use of Funds
Veggie Good Vegetable Farm is seeking $300,000 in debt financing to launch its vegetable farm. The funding will be dedicated towards securing the 10 acres of farmland and purchasing farm equipment and supplies. Funding will also be dedicated towards three months of overhead costs to include payroll of the staff, rent, and marketing costs for the website development, and working capital. The breakout of the funding is below:
Key Assumptions
The following outlines the key assumptions required in order to achieve the revenue and cost numbers in the financials and in order to pay off the startup business loan.
- Number of Initial CSA Membership Subscriptions Per Month: 25
- Average Fees per Month: $50,000
- Farmland Lease per Year: $300,000
Financial Projections
Income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement, farm business plan faqs, what is a farm business plan.
A farm business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your farm business. Among other things, a good agriculture farm business plan outlines your business concept, identifies your target audience , presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections.
You can easily complete your farm business plan using our Farm Business Plan Template here .
What Are the Main Types of Farms?
There are many types of farms. Some have commercial farms that produce crops and agricultural products for sale. Others have cooperative farms owned by people who pool their resources together and share profits among themselves. There are also vegetable farms, dairy, micro, organic, poultry, subsistence, or urban farms.
What Are the Main Sources of Revenues and Expenses for a Farm?
The primary source of revenue for a farm is the sale of its farmed goods such as rice, corn, milk, beef, chicken, depending on the kind of farm a business is.
Some key expenses for a farm are labor expenses, production costs like irrigation, fertilizer, water, and machinery maintenance.
How Do You Get Funding for Your Agriculture Business?
Farm business plans often receive funding from bank loans. Financing is also typically available from grants offered by local and state governments. Personal savings, credit card financing and angel investors are other funding options. This is true for starting any agricultural business.
What are the Steps To Start a Farm Business?
Starting a farming business can be an exciting endeavor. Having a clear roadmap of the steps to start a business will help you stay focused on your goals and get started faster.
- Develop An Agricultural Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed agriculture business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include potential market size and target customers, the services or products you will offer, pricing strategies and a detailed financial forecast. It should also include your business goals and mission statement. You can quickly complete your farm business plan using our Farm Business Plan Template here .
- Choose Your Legal Structure - It's important to select an appropriate legal entity for your farm business. This could be a limited liability company (LLC), corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks, so it’s important to do research and choose wisely so that your farm business is in compliance with local laws.
- Register Your Agriculture Business - Once you have chosen a legal structure, the next step is to register your farm business with the government or state where you’re operating from. This includes obtaining licenses and permits as required by federal, state, and local laws.
- Identify Financing Options - It’s likely that you’ll need some capital to start your farm business, so take some time to identify what financing options are available such as bank loans, investor funding, grants, or crowdfunding platforms.
- Choose a Business Location - Whether you plan on operating out of a physical location or not, you should always have an idea of where you’ll be based should it become necessary in the future as well as what kind of space would be suitable for your operations.
- Hire Employees - There are several ways to find qualified employees including job boards like LinkedIn or Indeed as well as hiring agencies if needed – depending on what type of employees you need it might also be more effective to reach out directly through networking events.
- Acquire Necessary Farm Equipment & Supplies - In order to start your agricultural business, you'll need to purchase all of the necessary equipment and supplies to run a successful operation.
- Market & Promote Your Business - Once you have all the necessary pieces in place, it’s time to start promoting and marketing your farm business. This includes creating a website, utilizing social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter, and having an effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy. You should also consider traditional marketing techniques such as radio or print advertising.
Learn more about how to start a successful farm business and agribusiness planning:
- How to Start a Farm Business
Where Can I Get a Farm Business Plan PDF?
You can download our free farm business plan template PDF here . This is a good farm business plan template you can use in PDF format.

Farm Business Plan

Most entrepreneurs are terrified of planning. But this can be a different scenario for you. A farming business can be more successful if you will develop a farm business plan . Not only will you set the steps that you need to follow to achieve your goals, but you can also become more prepared with the risks. More so, your strategic plans will help you develop a mission statement that will guide you through. So, are you ready for this? Below,we provide you a farm business plan examples that you can look into as a guide.
20+ Farm Business Plan Examples
1. farm business plan template.

- Google Docs
Size: A4 & US
2. Animal Farm Business Plan Template

3. Agriculture Business Plan Template

4. Dairy Farm Business Plan Template

Size: A4, US
5. Vegetable Farming Business Plan Example

6. Farm Business Plan Template Example

- Apple Pages
Size: 21 KB
7. Farm Business Plan Template

Size: US, A4
8. Partnership Business Plan for Farm Management Example

Size: 619 KB
9. Farm Business Planning Model Example

10. Community Farm Business Plan Example

11. Small Farm Business Planning Example

Size: 782 KB
12. Agricultural Business Plan Guidelines Example

13. Organic Farm Business Plan Example

Size: 369 KB
14. Farm business Succession Plan Example

Size: 3007 KB
15. Dairy Farm Business Plan Example

16. Farm Partnership Business Plan Example

17. Farm Business Planning Example

Size: 736 KB
18. Simple Farm Business Plan Example

19. Agri-Business Plan for a Farm Example

Size: 270 KB
20. Agricultural Farm Business Plan Example
Size: 515 KB
21. Farm Business Plan Example

Size: 153 KB
What Is a Farm Business Plan?
A farm business plan is an excellent organizational and business material that you can use for a variety of purposes. All you must do is to be familiar with business plan guidelines and the basics of farm business management so you can already identify the specific business plan document that you need.
Importance of a Farm Business Plan
Have you ever been to a hotel where you can see each process’s organization from the welcoming of guests up to their check-out procedures? One of the planning documents that provide a contribution to that organization is a hotel operational business plan . This can be compared to the usage of a farm business plan if you want to ensure that the operations of your farm business are laid out properly. According to a gathered analysis published by Noble Research Institute, the advantages of a farm business plan includes an easy application to loans. It can also promote solidarity within the farm business’s stakeholders. This is relatively substantial, especially for every small business in the agricultural industry.
How To Create a Farm Business Plan
Creating your farm business plan can be easier if you will refer to helpful agriculture business plan examples. But aside from the items mentioned above, there are still some items that can make it more efficient for you to develop an outstanding, complete, and organized farm business plan . Some of these tips and guidelines are all listed below.
1. Begin with a Realistic Plan
To begin with, always start by visualizing your ideas. After that, you can now proceed with outlining your goals and objectives. Remember to make it as realistic as possible. Come up with measurable and obtainable plans. This should include proposals , marketing , and budget . Truly, there is no easy business. So, plan long-term, and everything else will follow.
2. Provide an Executive Summary
Next, you have to learn how to write an executive summary for your business plan. Especially for farm business startups, an executive summary is one of the parts of the farm business plan that will be first seen by your target audience. Make it as appealing and as presentable as possible so you can already get positive responses and impressions. But remember, don’t make it too long and invite confusion from readers. Make it precise as much as possible.
3. Set an Action Plan
What could be the necessary steps to do in achieving your goals? Here, you have to outline your action plans . It should be relevant to your objectives. Therefore, they must align. You can also set a schedule to follow. This helps you cope with your daily tasks while keeping it on time. Another thing to remember is to make it attainable for everyone in the organization.
4. Present the Values and Benefits
make sure that your farm business plan can present your business values. It should be a reflection of your identity, brand, mission statement , and image as a business. These characteristics can set you apart from your competition. It can promote memory retention, which is an excellent way for you to remain relevant and memorable in the marketplace where the farm business belongs.
5. Proofread the Plan
Don’t propose it right away. But make sure that you check your content from the cover page down to the last pages. Is your budget for the business plan considerable? Can your members achieve success in no time? It is essential to check it first before using it for actual scenarios. This helps you come up with an excellent report later on.
FAQ’s
How much is a typical business plan.
The price of a business plan depends on the agency that creates it. But in most cases, it reaches up to $15,000 for a complete plan.
Is a business plan necessary?
A business plan is a necessity if you take a look at the bigger picture when it comes to finances and projects. This helps you accomplish more than what you imagine for your business.
What are the two primary elements of a business plan?
Among the various elements of a business plan, the executive summary and market analysis are standard.
Again, feeling overwhelmed with everything that you need to consider when developing a farm business plan is normal. However, you should make sure that you will not be carried away so you can focus on the items that can help you give the farm business a boost in productivity, efficiency, sales, visibility, and leads. Be mindful of how you will develop farm planning strategies. Also, see how an effective one can improve your farm business’s overall operations . So, get ready with your document and follow the list of steps above.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Create a study plan for final exams in high school
Develop a project timeline for a middle school science fair.
🌍 Upmetrics is now available in
- Sample Business Plans
- Agriculture, Farm & Food Production
Farming Business Plan
Agriculture is the one industry that consistently does well, irrespective matter the economic conditions of the world. So, for a stable income and career farming business is a great option.
Are you looking to start writing a business plan for your farming business? Creating a business plan is essential to starting, growing, and securing funding for your business. We have prepared a farming business plan template for you to help in start writing yours.

Free Business Plan Template
Download our Free Farming Business Plan Template now and pave the way to success. Let’s turn your vision into an actionable strategy!
- Fill in the blanks – Outline
- Financial Tables
How to Write a Farming Business Plan?
Writing a farming business plan is a crucial step toward the success of your business. Here are the key steps to consider when writing a business plan:
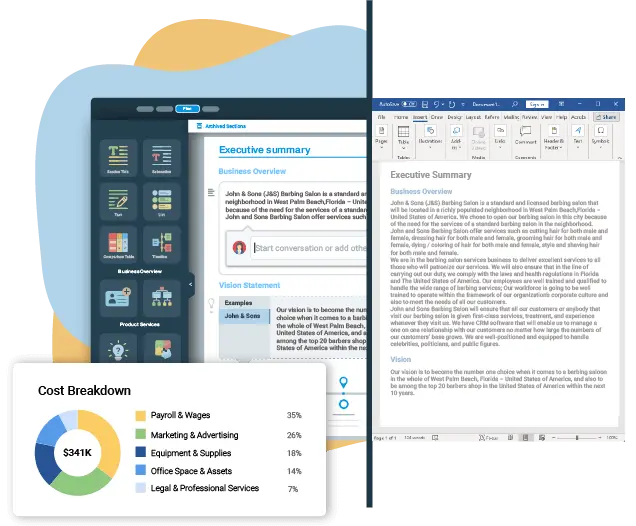
1. Executive Summary
An executive summary is the first section of the business plan intended to provide an overview of the whole business plan. Generally, it is written after the entire business plan is ready. Here are some components to add to your summary:
- Start with a brief introduction: Start your executive summary by introducing your idea behind starting a farming business and explaining what it does. Give a brief overview of the idea that how will your farming business will be different.
- Market opportunity: Describe the target market in brief, and explain the demographics, geographic location, and psychographic attributes of your customer. Explain how your agriculture business meets its needs. Clearly describe the market that your business will serve.
- Mention your services: Describe in detail the products and crops your agriculture farm produces. Also, incorporate all the details about the tools and equipment you will use keeping quality in mind.
- Management team: Name all the key members of your management team with their duties, responsibilities, and qualifications.
- Financial highlights: Provide a summary of your financial projections for the company’s initial years of operation. Include any capital or investment requirements, startup costs, projected revenues, and profits.
- Call to action: After giving a brief about your business plan, end your summary with a call to action, for example; inviting potential investors or readers to the next meeting if they are interested in your business.
Ensure you keep your executive summary concise and clear, use simple language, and avoid jargon.
Say goodbye to boring templates
Build your business plan faster and easier with AI
Plans starting from $7/month

2. Business Overview
Depending on what details of your business are important, you’ll need different elements in your business overview. Still, there are some foundational elements like business name, legal structure, location, history, and mission statement that every business overview should include:
- The name of your farming business and the type of business you are running or will run: organic farming, agricultural farming, dairy farming, commercial farming, or something else.
- Company structure of your farming business whether it is a proprietorship, LLC, partnership firm, or some other.
- Location of your farm and the reason why you selected that place.
- Mission statement: Add a mission statement that sums up your farming business’s objectives and core principles. This statement needs to be memorable, clear, and brief.
- Business history: Include an outline of the farming business history and how it came to be in its current position. If you can, add some personality and intriguing details, especially if you got any achievements or recognitions till now for your incredible services.
- Future goals: It’s crucial to convey your aspirations and your vision. Include the vision of where you see your agriculture in the near future.
This section should provide an in-depth understanding of your farming business. Also, the business overview section should be engaging and precise.
3. Market Analysis
Market analysis provides a clear understanding of the market in which your farming business will run along with the target market, competitors, and growth opportunities. Your market analysis should contain the following essential components:
- Target market: Identify your target market and define your ideal customer. Know more about your customers and which products they prefer: meat, crops, vegetables, or some other products.
- Market size and growth potential: Provide an overview of the agriculture industry. It will include market size, trends, growth potential, and regulatory considerations.
- Competitive analysis: Identify and analyze all other agricultural farms nearby, including direct and indirect competitors. Evaluate their strengths and weaknesses, and explain how your farm can offer qualitative products.
- Market trends: Analyze current and emerging trends in your industry, such as changes in technology, fertilizers, or customer preference. Explain how your farming business will cope with all the trends.
- Regulatory environment: Describe any regulations or licensing requirements that affect the agricultural farm, such as safety codes, or hiring any agricultural engineer or food safety employee.
Some additional tips for writing the market analysis section of your business plan:
- Use a variety of sources to gather data, including industry reports, market research studies, and surveys.
- Be specific and provide detailed information wherever possible.
- Include charts and graphs to help illustrate your key points.
- Keep your target audience in mind while writing the business plan
4. Products And Services
The product and services section of an agriculture business plan should describe the specific services and products that will be offered to customers. To write this section should include the following:
- List the products you will produce or sell, such as crops, fruits, flowers, livestock, or value-added products like cheese or jams.
- Describe each product: Explain the features of your products, such as their quality, variety, and uniqueness. Also, discuss how your products will be packaged and marketed.
- Emphasize safety and quality: In all descriptions of services and products, emphasize the importance of safety and quality. Explain how your farming business will ensure that all services and products are delivered with the highest standards of safety and efficacy.
Overall, the product and services section of a business plan should be detailed, informative, and customer-focused. By providing a clear and compelling description of your offerings, you can help potential investors and readers understand the value of your business.
5. Operations Plan
When writing the operations plan section, it’s important to consider the various aspects of your business operations. Here are the components to include in an operations plan:
- Operational process: Explain the steps taken to produce your crops or raise your livestock. This can involve planting, fertilizing, watering, harvesting, looking after animals, and other activities.
- Technologies: Make a list of the tools and equipment you’ll need to run your farm, including tractors, harvesters, greenhouses, barns, and processing machinery. Describe your plans for purchasing and maintaining your farming business.
By including these key elements in your operations plan section, you can create a comprehensive plan that outlines how you will run your farming business.
6. Management Team
The management team section provides an overview of the individuals responsible for running the farming business. This section should provide a detailed description of the experience and qualifications of each manager, as well as their responsibilities and roles.
- Key managers: Describe the key members of your management team, their roles, and their responsibilities. It should include the owners, senior management, and any other farm manager, soil and plant scientist, agricultural salesperson, or someone else.
- Organizational structure: Describe the organizational structure of the management team, including reporting lines and how decisions will be made.
- Compensation plan: Describe your compensation plan for the management team and staff, including salaries, bonuses, and other benefits.
- Board of advisors: If you have a board of advisors for your business, then mention them along with their roles and experience.
Describe your company’s key personnel and highlight why your business has the fittest team.
7. Financial Plan
When writing the financial plan section of a business plan, it’s important to provide a comprehensive overview of your financial projections for the first few years of your business.
- Profit & loss statement: Create a projected profit & loss statement that describes the expected revenue, cost of products sold, and operational costs. Your farm’s anticipated net profit or loss should be computed and included.
- Cash flow statement: Estimate your cash inflows and outflows for the first few years of operation. It should include cash receipts from clients, payments to vendors, loan payments, and any other cash inflows and outflows.
- Balance sheet: Prepare a projected balance sheet, which shows the business’s assets, liabilities, and equity.
- Break-even point: Determine the point at which your farming business will break even, or generate enough revenue to cover its operating costs. This will help you understand how much revenue you need to generate to make a profit.
- Financing needs: Estimate how much financing you will need to start and operate your farming business. It should include both short-term and long-term financing needs, such as loans or investment capital.
Remember to be realistic with your financial projections, and to provide supporting evidence for all of your estimates.
8. Appendix
When writing the appendix section, you should include any additional information that supports the main content of your plan. This may include financial statements, market research data, legal documents, and other relevant information.
- Include a table of contents for the appendix section to make it easy for readers to find specific information.
- Include financial statements such as income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. These should be up-to-date and show your financial projections for at least the first three years of your business.
- Provide market research data, such as statistics on the size of the agriculture industry, consumer demographics, and trends in the industry.
- Include any legal documents such as permits, licenses, and contracts.
- Provide any additional documentation related to your business plans, such as marketing materials, product brochures, and operational procedures.
- Use clear headings and labels for each section of the appendix so that readers can easily find the information they need.
Remember, the appendix section of your farming business should only include relevant and important information that supports the main content of your plan.
The Quickest Way to turn a Business Idea into a Business Plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
This farming business plan sample will provide an idea for writing a successful farming business plan, including all the essential components of your business.
After this, if you are still confused about how to write an investment-ready agriculture business plan to impress your audience, then download our farming business plan pdf .
Related Posts
Farmers Market Business Plan
Organic Farm Business Plan
Small Farming Business Plan
400+ Business Plan Template Example
How to make Business Plan Cover Page
Best Business Planning Tools
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do you need a farming business plan.
A business plan is an essential tool for anyone looking to start or run a successful farming business. It helps to get clarity in your business, secures funding, and identifies potential challenges while starting and growing your farming business.
Overall, a well-written plan can help you make informed decisions, which can contribute to the long-term success of your farming business.
How to get funding for your farming business?
There are several ways to get funding for your agriculture business, but one of the most efficient and speedy funding options is self-funding. Other options for funding are!
- Bank loan – You may apply for a loan in government or private banks.
- Small Business Administration (SBA) loan – SBA loans and schemes are available at affordable interest rates, so check the eligibility criteria before applying for it.
- Crowdfunding – The process of supporting a project or business by getting many people to invest in your farming business, usually online.
- Angel investors – Getting funds from angel investors is one of the most sought options for startups.
- Venture capital – Venture capitalists will invest in your business in exchange for a percentage of shares, so this funding option is also viable.
Apart from all these options, there are small business grants available, check for the same in your location and you can apply for it.
Where to find business plan writers for your farming business?
There are many business plan writers available, but no one knows your business and idea better than you, so we recommend you write your farming business plan and outline your vision as you have in your mind.
What is the easiest way to write your agriculture business plan?
A lot of research is necessary for writing a business plan, but you can write your plan most efficiently with the help of any farming business plan example and edit it as per your need. You can also quickly finish your plan in just a few hours or less with the help of our business plan software.
About the Author

Vinay Kevadiya
Vinay Kevadiya is the founder and CEO of Upmetrics, the #1 business planning software. His ultimate goal with Upmetrics is to revolutionize how entrepreneurs create, manage, and execute their business plans. He enjoys sharing his insights on business planning and other relevant topics through his articles and blog posts. Read more

Turn your business idea into a solid business plan
Explore Plan Builder
Plan your business in the shortest time possible
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee

Create a great Business Plan with great price.
- 400+ Business plan templates & examples
- AI Assistance & step by step guidance
- 4.8 Star rating on Trustpilot
Streamline your business planning process with Upmetrics .

Don't bother with copy and paste.
Get this complete sample business plan as a free text document.
Agriculture Farm Business Plan
Start your own agriculture farm business plan
Botanical Bounty
Executive summary executive summary is a brief introduction to your business plan. it describes your business, the problem that it solves, your target market, and financial highlights.">, opportunity.
The health and vitamin industry is growing at a very quick pace. Customers want to have natural and plant alternatives to medication. They are starting to believe the body is a temple. They don’t want to pollute with chemicals. The industry needs botanical plants that are ready to process as well as give to nurseries for the “do it yourselfers”.
Botanical Bounty is working hard to become a leading producer of botanical plants for the natural supplement industry as well as plant nurseries.
Botanical Bounty has three distinct customers: supplement companies, processors of botanicals for supplement companies, and nurseries that resell the plants.
The first two customers purchase the plants for use in their products which they ultimately sell to the end consumer.
The market for natural supplements is quite exciting. Surveys show that over 158 million consumers (over 55% of U.S. population) use dietary supplements. An estimated 115.3 million consumers buy vitamins and minerals for themselves, and 55.8 million purchase them for other members of their family, including children. Consumer surveys consistently find that nearly half of all Americans now use herbs – a statistic that is particularly remarkable when we realize that today’s herbal products industry is just over a quarter century old.`
Competition
Competition takes two forms, farms similar in size and production capacity to Botanical Bounty and megafarms. The similarly sized farms range in size from 5-30 acres. The number of different herbs grown varies from a handful to upwards of 50. The choice of plants grown is based on owner preference as well as location and the ability of the local growing conditions to support the different plants.
It is Botanical Bounty’s mission to become the leading provider of botanical perennials to the health/vitamin industry. This will be accomplished by providing quality plants at fair prices while exceeding customer’s expectations.
Expectations
To finance our growth and full-time production, we need to purchase $35,000 worth of new equipment as long-term assets taking that total up to $53,800. To that end, we are seeking a $100,000 10-year loan. Sales forecasts conservatively indicate that $190,000 revenue will be generated in year two, rising to over 400,000 by year 4.
Financial Highlights by Year
Financing needed.
We need to have a $100,000 10 year loan. We will use our $35,000 of cash from our current operations.
Problem & Solution
Problem worth solving.
There is a growing trend towards plant cures to common diseases or health issues.Consumers care about getting a natural supplement to make them feel better and take care of their body. Because of this the natural market has grown exponentially in the last few years. The market needs high quality botanicals to keep up with demand.
Our Solution
Botanical Bounty has identified three keys that will be instrumental in their success. The first is the implementation of strict financial controls. By having the proper controls, production efficiency will be maximized. The second key will be the never ending pursuit for the industry’s highest concentration levels of botanical ingredients in each plant. The third key is the recognition and implementation of the philosophy that 100% customer satisfaction is required to ensure a profitable business. Profits are a by product of satisfying customers, not the other way around.
Target Market
Market size & segments.
Botanical Bounty has identified three different target market segments:
Supplement Companies This customer group manufactures botanical supplements for their own label products. The companies purchase the plants and extract the active ingredients and transform them into sellable products for their own brand. There are a handful of large companies that operate in this market space. Ten years ago there were many different ones but through consolidation the industry has grown in size but decreased in the number of different players.
Processors These customers purchase the the plants, extract the botanicals and either sell the concentrated botanicals to the end producers or they themselves produce the supplement and sell the final product to other companies for their private label products. In essence they are the subcontractor for the supplement companies. These companies therefore are one layer within the manufacturing system and do not sell to the end consumer. They act as a supplier/processor for the retail brands.
Other Nurseries/Garden Centers This customer group purchases the plants which they in turn sell at retail to the individual end consumer. The typical consumer is a health conscious individual who is interested in either extracting the botanical from the plant immediately or growing the plant in their own garden for future use.
Current Alternatives
As mentioned previously, competition takes two forms, farms similar in size and production capacity to Botanical Bounty and megafarms. The similarly sized farms range in size from 5-30 acres. The number of different herbs grown varies from a handful to upwards of 50. The choice of plants grown is based on owner preference as well as location and the ability of the local growing conditions to support the different plants.
On the other end of spectrum is the megafarm. These farms have a similar range of species cultivated, however they differ greatly in production capacity. These farms are huge, typically not less than 100 acres, peaking at 300 acres. These growers however are few number.
The buying patterns of the different customers are typically based on these variables:
- Availability
- Ability to deliver consistently on long-term contracts
- Significant % of active ingredients
- Consistency
Our Advantages
Botanical Bounty has a dual competitive edge:
Healthy Plants The healthier the plant, the faster it will grow, the more botanicals that can be extracted from it. This means an increase in production efficiency due to a larger percentage of plants that are sellable. Other characteristics of healthy plants which are important on the production side is: lower pest counts, more established root structures, and high biomass.
High Concentration of Active Botanicals This is beneficial to the purchaser because they are buying the plants precisely for the active botanicals. High concentration levels are valuable to Botanical Bounty because they increase the amount of botanicals produced per plant or per acre, increasing the production capacity of a given amount of land, thereby increasing their return on investment and increasing the attractiveness of Botanical Bounty’s plants relative to the competition.
Keys to Success
Our keys to success are:
- Strict financial controls.
- The never ending pursuit of the highest concentration of botanicals in every plant.
- Ensuring that all customer’s needs are met and they are satisfied with the purchased products.
Marketing & Sales
Marketing plan.

Botanical Bounty’s sales strategy efforts will focus on identifying qualified leads and turning them into paying customers. The main sales effort that Botanical Bounty will undertake is the reinforcement of the fact that Botanical Bounty’s plants have the industry’s highest percentage of botanicals. This will be quite appealing to the buyers as this is exactly what they want, more botanicals per plant. In addition to selling the buyers on Botanical Bounty’s competitive edge of potent plants, there will be an emphasis on Botanical Bounty’s ability to perform on long-term contracts.
Botanical Bounty recognizes that the transactions should not be thought of as individual sales, but as long-term relationships. This is a reasonable assumption based on the fact that the customers are in the business of utilizing botanicals, that they will continually have the need for the botanicals, and that it is far less expensive to establish a relationship with one vendor than to continually have to find new vendors that can meet their needs.
Locations & Facilities
Botanical Bounty is a 10 acre farm that concentrates on the growing of botanical medicinals. Botanical Bounty has chosen five plant species that have significant market demand as well being well suited for growth in the Willamette River Valley. Botanical Bounty will feature: Echinacea – an immune system booster; Ginseng – a source of energy; St John’s Wort – for mild depression; Skullcap- for inflammation; and Ginger – a stomach soother.
Milestones & Metrics
Milestones table, key metrics.
Our key metrics are:
- Sales, cost of sales, expenses, profits, and cash.
- Production cost of goods. We need to keep them low.
- Keep current on our competitors botanical concentration and prices.
- Measure the number of emails and phone calls.
- Measure the Facebook Page views and Twitter re-tweets.
- Measure website searches and inquiries.
Ownership & Structure
Botanical Bounty is an Oregon L.L.C. owned by David and Susan Nealon. The L.L.C. business formation has been chosen as a strategic way to shield the Nealons from personal liability.
Company History
Botanical Bounty has been in operation for two years. Initially it was started as a hobby where Susan could use her plant biology skills while covering some of the costs. The Nealon’s were able to achieve this lifestyle due to a windfall that David received as a result of exercised stock options. After the second year, the Nealon’s decided that although they had the money to live on for many years, it would be irresponsible to needlessly spend it so they got serious about the business and made a concerted effort to become profitable.
Botanical Bounty has chosen the Willamette River Valley as an ideal place to grow perennials. Botanical Bounty has 10 acres of land which they use for production. During several of the winter months, production is moved into their green house for propagation. Botanical Bounty employs a drip irrigation system for all of the plants.
Management Team
Botanical Bounty will be lead by the husband and wife team of David and Sue Nealon. David brings a wealth of business and project management skills to the company. While working at Yahoo!, David was responsible for the successful launch and market lead capture of Yahoo!s driving directions section. Utilizing these skills, David will be responsible for the business operations of the farm. Sue, with a background of plant biology will be the driving force of the operation, growing the highest active ingredient content plants in the country. Additionally, because of her wealth of knowledge, she will be the leader of the sales department.
Personnel Table
Financial plan investor-ready personnel plan .">, key assumptions.
Our key assumptions
- Our market and customer base are growing and with them the opportunities for sales.
- The area has wealthy households that can afford to spend money on non essential vitamins.
- Our customers appreciate our dedication to high quality products and price controls.
- We will be able to get the 100,000 dollar loan at 8 percent based on our past success and being able to put our property up as collateral. We are a safe investment. If unplanned expenses pop up we have people interested in investing.
Revenue by Month
Expenses by month, net profit (or loss) by year, use of funds.
We will be using the loan to purchase machines and to expand our farm and our personnel to grow the highest quality botanicals and process them so they can be turned into vitamins or other products that give the customer a natural cure.
Sources of Funds
We are leveraging our business to get an $100,000 10-year loan. We will also be using the cash on hand from our current business.
Projected Profit & Loss
Projected balance sheet, projected cash flow statement.

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The goal of this document is to serve as a sample business plan for an early stage farm business. In this example, the farmers are preparing to finance a new farm purchase. After leasing land and growing their ... (20 acres of which are considered prime agricultural soils). The tillable soils are a mix of statewide Vershire Dummerston and Cabot ...
Agriculture Business Plan Format 1. Executive Summary. Introduction: Briefly introduce the business, mission, vision, and goals. Business Idea: Highlight the specific agricultural products or services offered. Target Market: Summarize the market analysis and the intended customer base. Financial Overview: Present an outline of projected income, expenses, and profitability.
If you're looking for a free, downloadable agriculture sample business plan PDF to help you create a business plan of your own, look no further. Keep in mind that you don't need to find a sample business plan that exactly matches your farm. Whether you're launching a larger agricultural business outside a bustling city or a smaller ...
Farm Business Plan Worksheets. The Farm Business Plan Balance Sheet can help gather information for the financial and operational aspects of your plan. Form FSA-2037 is a template that gathers information on your assets and liabilities like farm equipment, vehicles and existing loans. FSA-2037 - Farm Business Plan - Balance Sheet; FSA-2037 ...
A business plan provides a snapshot of your agricultural business as it stands today, and lays out your growth plan for the next five years. It is a valuable tool that explains your business goals and your strategies for reaching them. It also includes market research to support your plans. Why You Need a Business Plan for an Agriculture Business
Sample Business Plan For Farms & Agricultural Businesses. Below is a farm business plan example to help you create each section of your own farm business plan: Executive Summary Business Overview. Veggie Good Vegetable Farm is a certified organic vegetable farm located in Northfield, Vermont. It is owned by Joe and Amanda Green, a local couple ...
A farming business can be more successful if you will develop a farm business plan. Not only will you set the steps that you need to follow to achieve your goals, but you can also become more prepared with the risks. More so, your strategic plans will help you develop a mission statement that will guide you through.
This farming business plan sample will provide an idea for writing a successful farming business plan, including all the essential components of your business. After this, if you are still confused about how to write an investment-ready agriculture business plan to impress your audience, then download our farming business plan pdf.
business plans available; it is the hope of the authors that this document will put you on your way to prepare a business plan for a successful business. About the Authors Rod Sharp and Jeff Tranel, authors of "Agriculture Business Planning Workbook" are Agriculture
Explore a real-world agriculture farm business plan example and download a free template with this information to start writing your own business plan. Don't bother with copy and paste. Get this complete sample business plan as a free text document. Download for free. Business Planning.