School of City & Regional Planning
College of design.


Ph.D. in City and Regional Planning
Doctoral study in city and regional planning combines research and theory in an applied professional field. We link theory to practice, allowing students to explore the most important issues facing rapidly changing urban areas today.
We build socially, economically, and environmentally resilient communities through interdisciplinary study and research. Our doctoral students consistently graduate to top academic and other professional careers. We welcome your interest and inquiries.
Meet Us to Learn More!
Design your very own Open House experience by selecting the online and on-campus events that align best with your interests, questions, and availability. We have drafted a menu that allows you to engage with program directors, faculty, current students, and alumni, learn interactively about our programs, get insights into the application process and funding opportunities, and get a taste of our lecture series, signature events, and courses. All of our events allow for your unique individual questions to be answered. Click the link below to RSVP.
Extending the Horizon of Planning
Each year, the Ph.D. program seeks applicants with research interests that correspond closely to those of our faculty. Our faculty engage in research and teaching across the diverse spectrum of planning, including economic and community development, housing, land use, environment, transportation, planning theory, collaborative governance, and urban design.
Some of the cutting-edge issues they focus on include climate change, urban analytics, economic resilience, megaregions, disaster planning, and healthy cities. The three to five new Ph.D. students that we admit annually work closely with their faculty advisors to develop a course of study that will extend the horizons of knowledge available in our profession.
Besides their major area of focus in planning, students identify a minor area outside of planning to augment their intellectual foundation. Students are able to take courses in other degree programs at Georgia Tech, as well as at other research universities in Atlanta, including Emory University and Georgia State University.
If you apply to our program, we will want to know what motivates you to make the significant commitment to pursue a Ph.D. in the field of planning, as well as why you see Georgia Tech as an appropriate home to fulfill that commitment.
Program Requirements
The doctoral program has three main components: the coursework (which includes the program core, a major field, and a minor field); the comprehensive exams; and the dissertation.
The program of study requires two years of residency minimum (no fewer than four semesters enrolled for at least six credit hours each, excluding summer) devoted to coursework and other preparation for advancement to candidacy. Successful students demonstrate mastery in these areas and are prepared to pursue upper-level careers in government, business, research, and academia. Full details can be found in the Ph.D. Program Handbook .
Coursework involves a specialized program of study designed by the student and faculty focusing on a major field within city and regional planning, and on a minor field outside the College of Design.
Students complete at least 46 credit hours in their major field, minor field, and the Ph.D. program core requirements, and in various elective courses.
Students complete a minimum of 15 semester-hours of study in their major field, a minimum of 9 hours in their minor field, and a minimum of 19 hours in the program core.
Descriptions of courses offered in city and regional planning and other programs in the College of Design can be found in the Institute’s course catalog .
Major Fields
Upon admission, each Ph.D. student chooses a major area of study. Any change to the major requires review and approval by the Ph.D. faculty.
To meet the major requirement, students must have satisfactory performance (B or better letter grade) in courses composing not fewer than 15 credit hours. The student’s Advisory Committee may require other courses within the College or other units within the University System of Georgia consistent with the student’s expressed interest in her selected field of concentration.
The composition of chosen courses should provide a full background and preparation in both the substance of the field of study, and appropriate methods of inquiry and analysis.
Examples of majors pursued by doctoral students in the School of City and Regional Planning include:
- Urban climate change management
- Built environment and transportation planning
- Equity and social justice planning
Minor Fields
Students choose a minor to demonstrate competence and inquiry in an area of study related to, but outside of, the School of City and Regional Planning.
To meet the minor requirement, students must have satisfactory performance (defined as a B or better letter grade) in courses composing not fewer than 9 credit hours.
Examples of minors outside the School of City and Regional Planning include:
- Regional economics
- Public health
- Water resources management
Program Core
The core course requirement provides students with a basic knowledge of planning theory, regional theory, and research design and methods.
The Ph.D. seminars acquaint students with questions, methods, and paradigms of research and with the modes of scholarship and pedagogy associated with the city and regional planning field.
Requirements include:
- Advanced Planning Theory (three credit hours)
- Advanced Urban and Regional Development Theory (three credit hours)
- Quantitative Research Design and Methods (three credit hours)
- Qualitative Research Design and Methods (three credit hours)
- Ph.D. Foundations Seminar (one credit hour)
- Ph.D. Planning Seminar (one credit hour each year)
Comprehensive Examination
Once students have completed their coursework, with the exception of on-going attendance in Seminar in Advanced Research Design and Methods, they are ready to take the comprehensive examinations.
Students are tested in five areas: the student’s major and minor fields, and three core area exams in planning theory, regional economic theory, and research design and methods. Core comprehensive exams can be waived by earning a letter grade of ‘A’ in a core course.
The examination process includes both written and oral testing of a student’s mastery of the subjects. Upon successful completion, the student moves on to the dissertation phase of the program.
Dissertation
The doctoral dissertation is a written piece of original scholarship that represents a significant new perspective or contribution in the candidate’s chosen field of study. The dissertation must be relevant to the field of planning, and either an addition to the fundamental knowledge base in the field of study or a new and better interpretation of facts already known. It must demonstrate that the candidate possesses powers of original thought, talent for research, understanding of theory and methodology, and ability to organize and present findings.

Application for Admission Details
All application materials are submitted using the Georgia Tech Graduate Studies and Admissions Online System. We will begin review of applications for admissions on January 16, 2025 . In most cases, students are accepted for and enter the program in the Fall semester.
Applicants admitted to the PhD Program normally will have completed the requirements for the Master of City and Regional Planning (MCRP), or a related Masters degree program. Students from allied fields are also encouraged to apply. In exceptional cases, students with a Bachelors degree only may be accepted directly into the PhD Program but will be required to complete the Masters in City and Regional Planning degree before advancing to candidacy for the PhD degree. PhD students are eligible for an accelerated MCRP curriculum, as outlined in the Ph.D. Program Handbook
Application materials:
Application Forms
Application Fee.
Georgia Tech offers application fee waivers to qualifying applicants. Comprehensive information on whether you qualify for the Institute-sponsored application fee waiver program and how to request one if you do is available here . The School of City and Regional Planning is additionally offering a limited number of department-sponsored application fee waivers to applicants who do not fall in the waiver categories described ; If paying the application fee poses an undue financial burden to you and you do not qualify for an Institute-sponsored fee waiver, you may apply to be considered for a SCaRP departmental application fee waiver by completing this form before December 1st.
Three Letters of Recommendation
Examples of previous research and written works
Official transcripts from all previously attended institutions of higher learning
Statement of Purpose
Describe what you have done to prepare yourself for study in a PhD Program.
Why have you chosen to apply to the PhD program in City and Regional Planning at Georgia Institute of Technology?
What area of planning research is of particular interest to you? How might you explore this interest as a doctoral student at Georgia Tech?
Detail your academic and research goals and career plans.
Personal Biography Form
Graduate Record Examination (GRE) scores is required for admission of this program, with a minimum score of 150 (Verbal), 150 (Quantitative), and 4.0 (Analytical Writing). GRE waivers could be granted under special circumstances.
Proof of English proficiency for applicants whose first language is not English: Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL). TOEFL scores of 620/261/102 or higher for the test (paper, computer, and internet tests respectively) are expected. Other evidence of English proficiency, such as provided in writing samples or oral interviews, may also be considered in determining language proficiency. Applicants having completed a Bachelors or Masters degree at a US University are not required to submit TOEFL scores. OR International English Language Testing System (IELTS) with a minimum score of 7.5. For complete outline of the English proficiency requirement and ways to get exemptions from testing, please see https://grad.gatech.edu/english-proficiency
Cost, Funding and Financial Aid
The SCaRP PhD program typically makes fully funded offers for the first four years of the program. Students receive a tuition waiver, discounted health insurance and monthly stipend while working 15-20 hours per week as graduate research assistants, as co-op students with local partners, as TAs or instructors for our graduate and undergraduate offerings. The College of Design 2024-2025 monthly stipend rates are:
- $2,302 working at 15 hours per week
- $2,770 working at 20 hours per week
The institution guidelines for stipends can be found here: Stipends for Graduate Assistantships | Policy Library .
Recent Doctoral Student Work

Student Work: AeroATL Greenway Path
Xiaofan liang, ph.d..
This dissertation introduces an exploratory framework about network duality, delving into the nuanced yet often contradictory dynamics of urban networks. This framework argues that connectivity is a multifaceted urban phenomenon embedded in network infrastructure that can induce duality, such as connecting one population while excluding the other, exhibiting influence in one system yet causing inequality in another, or co-existing with other infrastructure in some places but not others. Mitigating this duality is important for an inclusive and equitable network society. The critical inquiries are two-fold. First, what types of connectivity are prioritized or supported by urban infrastructure, for whom, at where, and at what cost? Second, what are some strategies (e.g., approaches, toolbox, and practices) that planners can use to mitigate the harmful effects of network infrastructure duality (e.g., exclusion and inequality), especially on marginalized communities?

Towards a Politics of Human Flourishing
Meaghan mcsorley, ph.d..
The purpose of this dissertation is to explore how planners can contribute to human flourishing. In the first chapter, a theoretical framework for community-level thriving is developed. The theory-building work of the first chapter bolsters several streams of planning thought by asserting that
interpersonal skills are themselves a critical method for planners to promote flourishing. The second chapter takes stock of practice around interpersonal skills by analyzing publications from the American Planning Association. Importantly, there appears to be an assumption that planners are gaining interpersonal skills during their education. The final chapter covers an exploratory, mixed methods intervention study to identify creative means of improving interpersonal skills during planning education. Ultimately, this research offers planning practitioners a framework to support community visioning conversation; identifies new pathways for scholarly research around interpersonal skills; and explores novel pedagogical methods to support students in gaining important interpersonal skills.
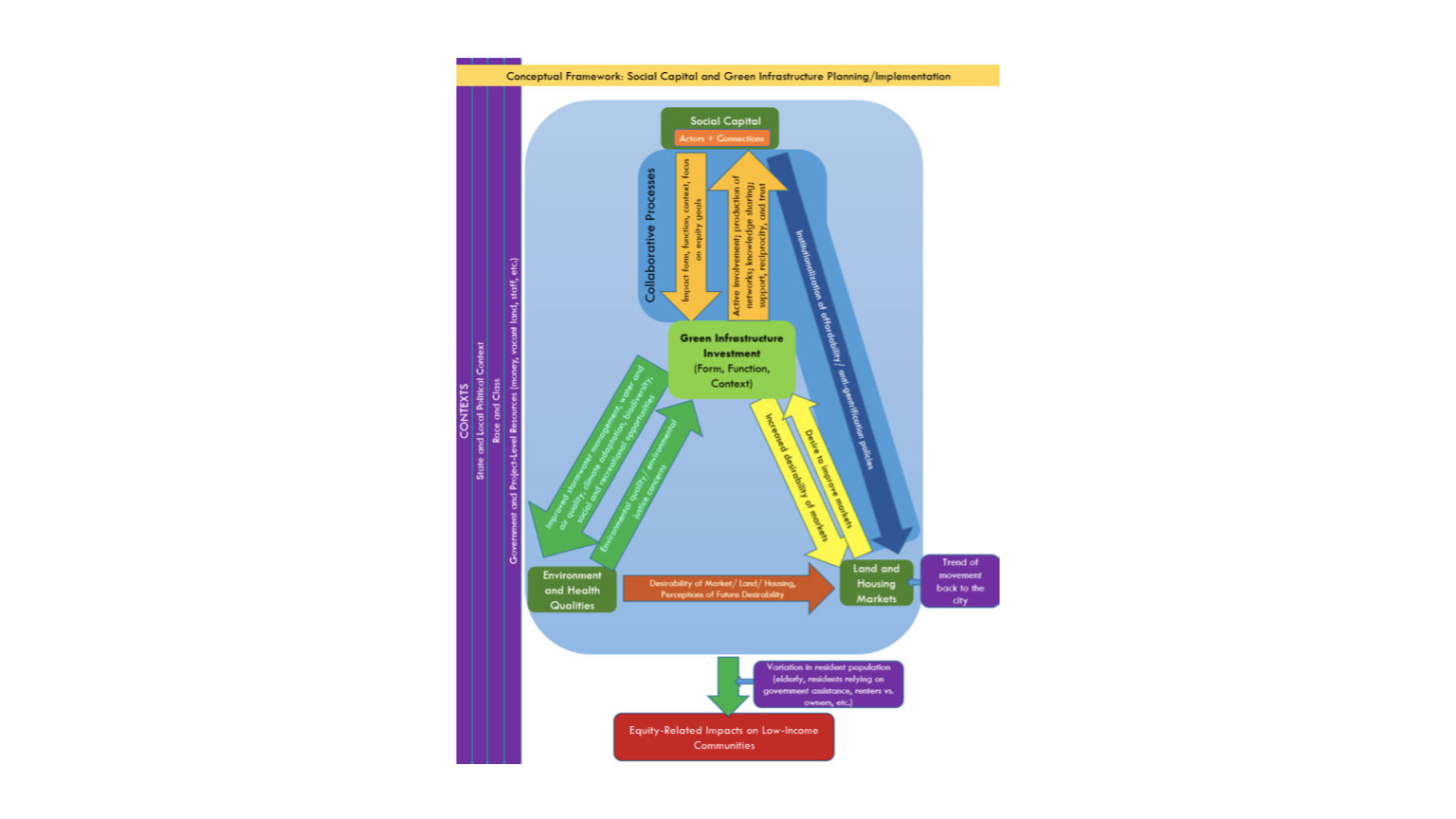
Student Work: Green Infrastructure
Jessica fisch.
Planners, policymakers, and elected officials increasingly view investments in green infrastructure, parks and other green development as opportunities for spurring economic growth, increasing environmental quality, and providing social and recreational amenities in urban areas. However, research has indicated that these projects do not adequately address equity concerns, such as access for low-income and marginalized groups, housing affordability, and displacement of existing residents. Consequently, green infrastructure projects can lead to ‘environmental gentrification.’
This dissertation work finds that green infrastructure planning may reinforce social capital, which in turn shapes green infrastructure projects and planning processes with regard to addressing housing affordability and community benefits concerns. It further finds that social capital has served as a catalyst for advocacy and the development of organizations, policies, and programs focused on housing affordability and workforce development.
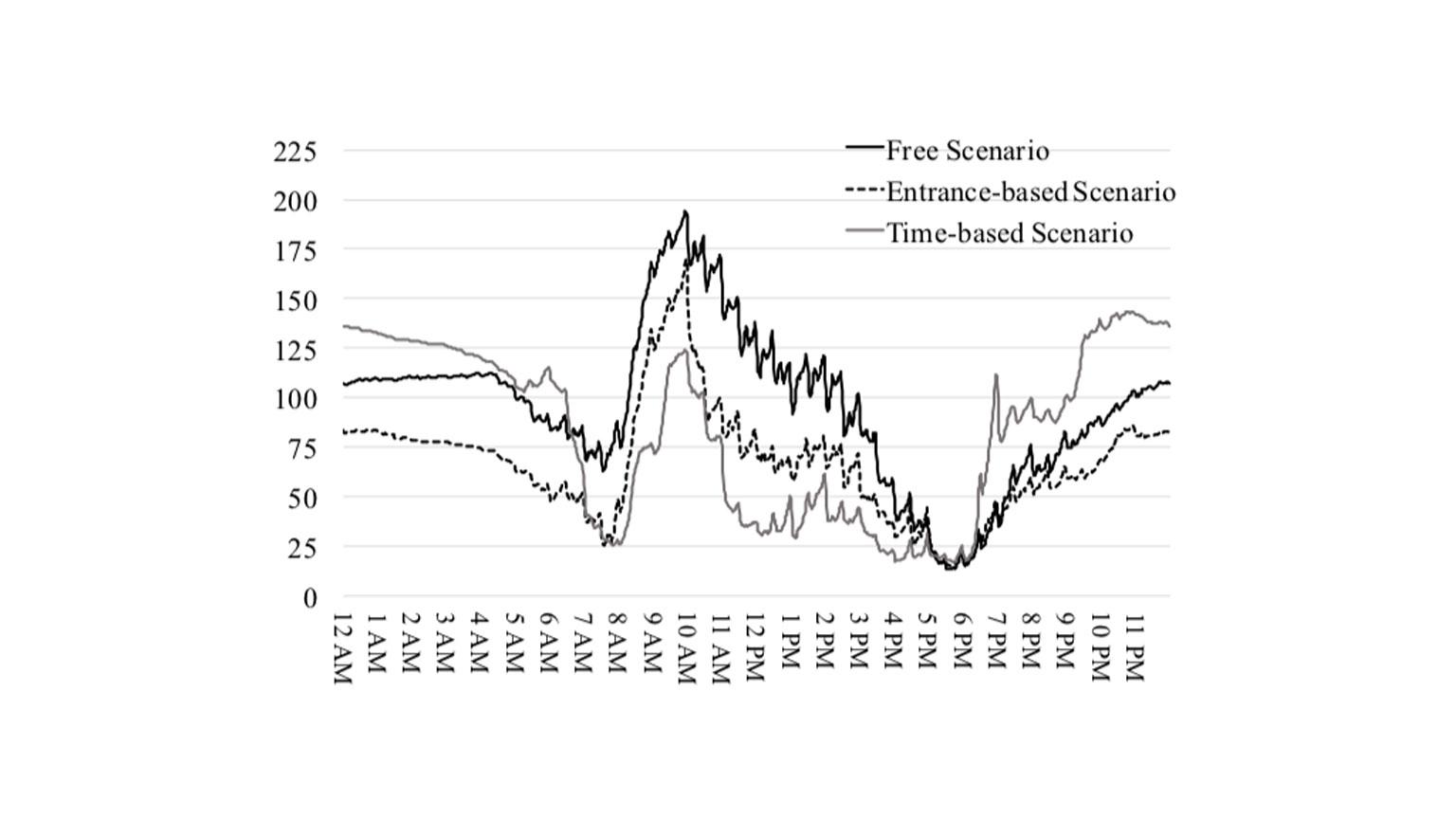
Student Work: Shared Autonomous Vehicles
Wenwen zhang.
We are on the cusp of a new era in mobility given that the enabling technologies for autonomous vehicles (AVs) are almost ready for deployment. This promising technology together with the sharing economy will enable a new travel mode – Shared Autonomous Vehicles (SAVs), a taxi service without drivers.
Recent studies have explored the feasibility, affordability, environmental benefits, and parking demand of the system in hypothetical grid-base cities. Despite these rapidly proliferating studies, it remains unclear how this affordable and environmentally friendly travel mode will influence residential and commercial location choices and potentially transform urban form. How much parking will we need and where will it be located when the SAV system is a popular mode of travel?
In this graphic, we see how the demand for parking fluctuates in response to three pricing scenarios: free parking, a flat rate, and a time-variable rate. The results of this dissertation work suggest the SAV system can reduce over 90% of parking demand for households who participate into the system and give up their private vehicles, potentially freeing substantial acreage of urban land for other critical needs.
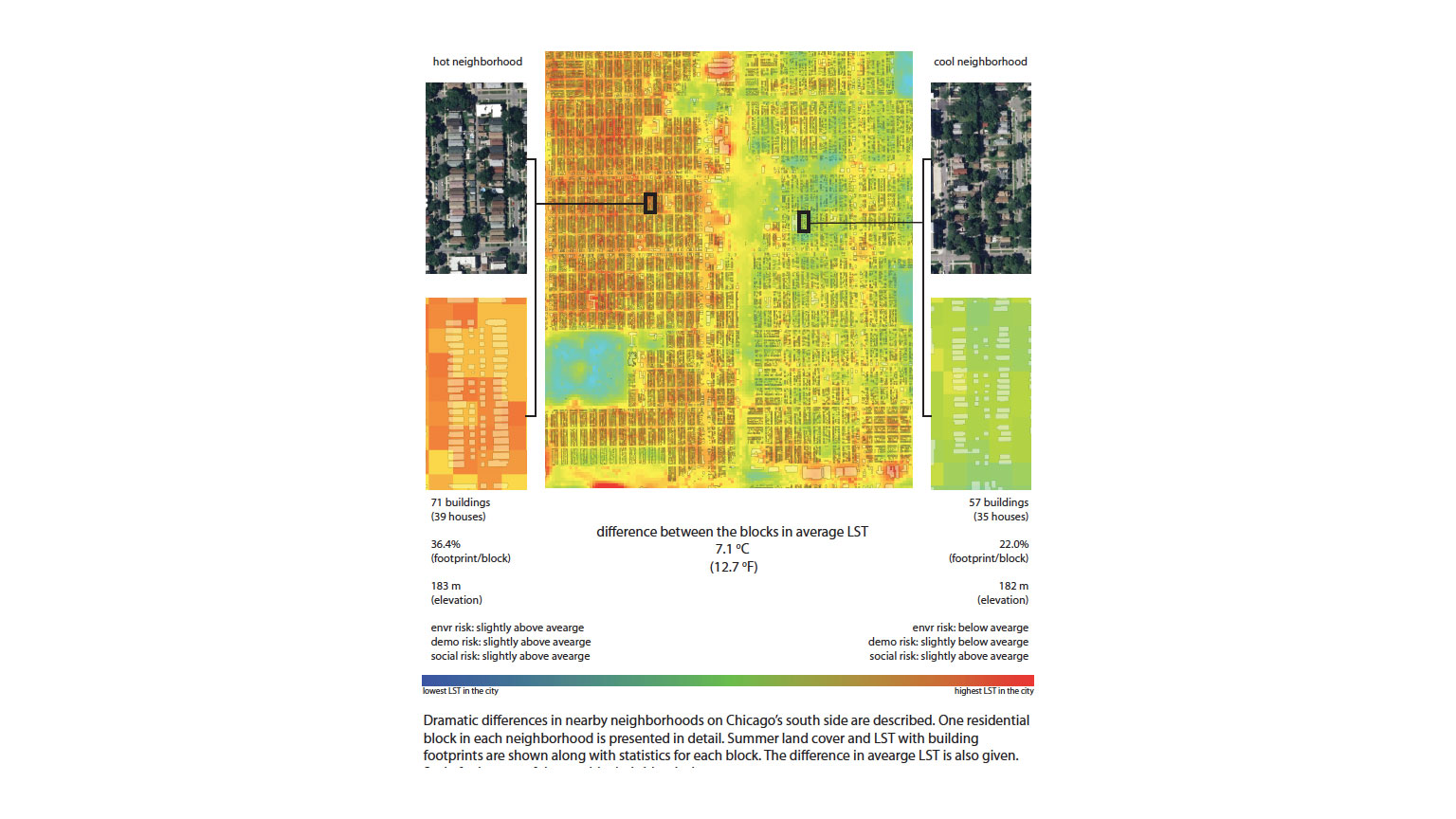
Student Work: Local Environment and Extreme Heat
Jason vargo, 2012.
This dissertation explores interactions between global trends in climate change with local influences tied to urban land covers. First, it examines temperatures during an extended period of extreme heat and asks whether changes in land surface temperatures during a heat wave are consistent in space and time across all land cover types.
Second, the influences of land covers on temperatures are considered for normal and extreme summer weather to find out which characteristics of the built environment most influence temperatures during periods of extreme heat.
Finally, the distribution of extreme heat health risks within cities are described and examined for spatial patterns. As illustrated in this graphic, the physical design of city blocks can yield very different patterns of heat exposure in cities, with direct implications for human health. The results of this dissertation are assisting cities in their development of climate change adaptation plans focused on rising levels of heat exposure.

Meet the Ph.D. Program Director
Elora raymond.
Elora Lee Raymond is an urban planner and Assistant Professor in the School of City and Regional Planning in the College of Design at Georgia Tech. She is interested in the financialization of housing and property in land, displacement and dispossession through housing systems, housing and disasters, housing justice, race, segregation, and the transnational Pacific Islander community.
We know the relationship between a Doctoral Student and their advisor is crucial to getting the most out of their degree. We are here to make the most out of your PhD education. We encourage those interested in the Ph.D. program to reach out to Elora Raymond with questions about pursuing a Ph.D. at Georgia Tech.
Want to Know More?
Get answers about our programs, join our email list, sign up for an information session.
