How to Synthesize Written Information from Multiple Sources
Shona McCombes
Content Manager
B.A., English Literature, University of Glasgow
Shona McCombes is the content manager at Scribbr, Netherlands.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Saul McLeod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul McLeod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
On This Page:
When you write a literature review or essay, you have to go beyond just summarizing the articles you’ve read – you need to synthesize the literature to show how it all fits together (and how your own research fits in).
Synthesizing simply means combining. Instead of summarizing the main points of each source in turn, you put together the ideas and findings of multiple sources in order to make an overall point.
At the most basic level, this involves looking for similarities and differences between your sources. Your synthesis should show the reader where the sources overlap and where they diverge.

Unsynthesized Example
Franz (2008) studied undergraduate online students. He looked at 17 females and 18 males and found that none of them liked APA. According to Franz, the evidence suggested that all students are reluctant to learn citations style. Perez (2010) also studies undergraduate students. She looked at 42 females and 50 males and found that males were significantly more inclined to use citation software ( p < .05). Findings suggest that females might graduate sooner. Goldstein (2012) looked at British undergraduates. Among a sample of 50, all females, all confident in their abilities to cite and were eager to write their dissertations.
Synthesized Example
Studies of undergraduate students reveal conflicting conclusions regarding relationships between advanced scholarly study and citation efficacy. Although Franz (2008) found that no participants enjoyed learning citation style, Goldstein (2012) determined in a larger study that all participants watched felt comfortable citing sources, suggesting that variables among participant and control group populations must be examined more closely. Although Perez (2010) expanded on Franz’s original study with a larger, more diverse sample…
Step 1: Organize your sources
After collecting the relevant literature, you’ve got a lot of information to work through, and no clear idea of how it all fits together.
Before you can start writing, you need to organize your notes in a way that allows you to see the relationships between sources.
One way to begin synthesizing the literature is to put your notes into a table. Depending on your topic and the type of literature you’re dealing with, there are a couple of different ways you can organize this.
Summary table
A summary table collates the key points of each source under consistent headings. This is a good approach if your sources tend to have a similar structure – for instance, if they’re all empirical papers.
Each row in the table lists one source, and each column identifies a specific part of the source. You can decide which headings to include based on what’s most relevant to the literature you’re dealing with.
For example, you might include columns for things like aims, methods, variables, population, sample size, and conclusion.
For each study, you briefly summarize each of these aspects. You can also include columns for your own evaluation and analysis.
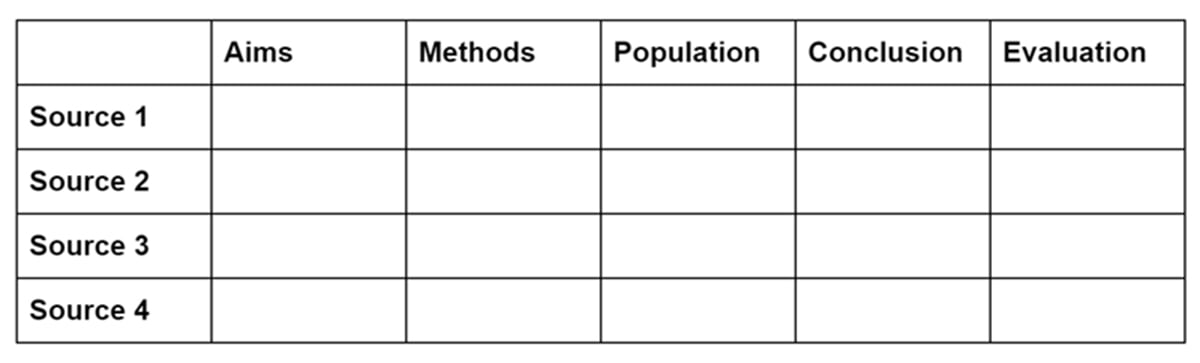
The summary table gives you a quick overview of the key points of each source. This allows you to group sources by relevant similarities, as well as noticing important differences or contradictions in their findings.
Synthesis matrix
A synthesis matrix is useful when your sources are more varied in their purpose and structure – for example, when you’re dealing with books and essays making various different arguments about a topic.
Each column in the table lists one source. Each row is labeled with a specific concept, topic or theme that recurs across all or most of the sources.
Then, for each source, you summarize the main points or arguments related to the theme.
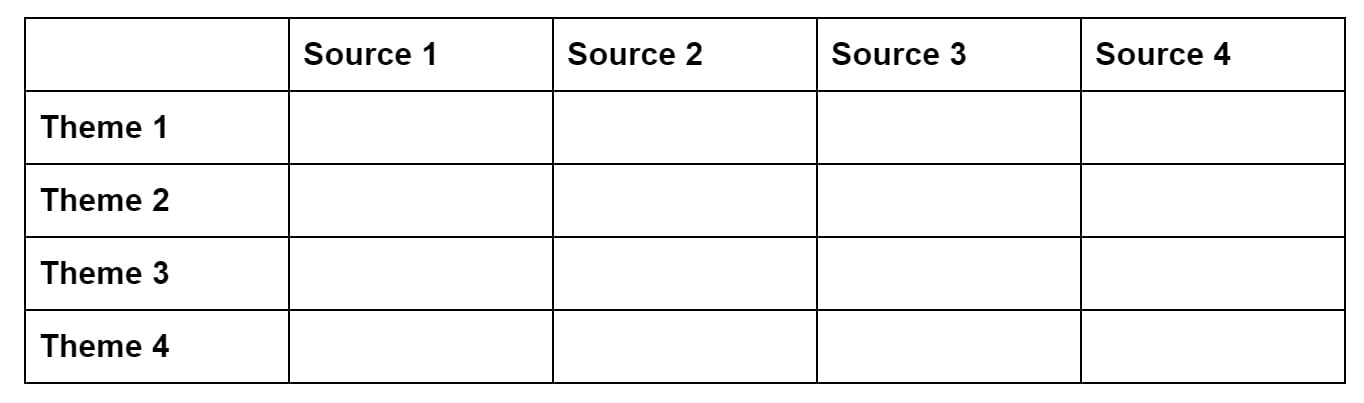
The purposes of the table is to identify the common points that connect the sources, as well as identifying points where they diverge or disagree.
Step 2: Outline your structure
Now you should have a clear overview of the main connections and differences between the sources you’ve read. Next, you need to decide how you’ll group them together and the order in which you’ll discuss them.
For shorter papers, your outline can just identify the focus of each paragraph; for longer papers, you might want to divide it into sections with headings.
There are a few different approaches you can take to help you structure your synthesis.
If your sources cover a broad time period, and you found patterns in how researchers approached the topic over time, you can organize your discussion chronologically .
That doesn’t mean you just summarize each paper in chronological order; instead, you should group articles into time periods and identify what they have in common, as well as signalling important turning points or developments in the literature.
If the literature covers various different topics, you can organize it thematically .
That means that each paragraph or section focuses on a specific theme and explains how that theme is approached in the literature.
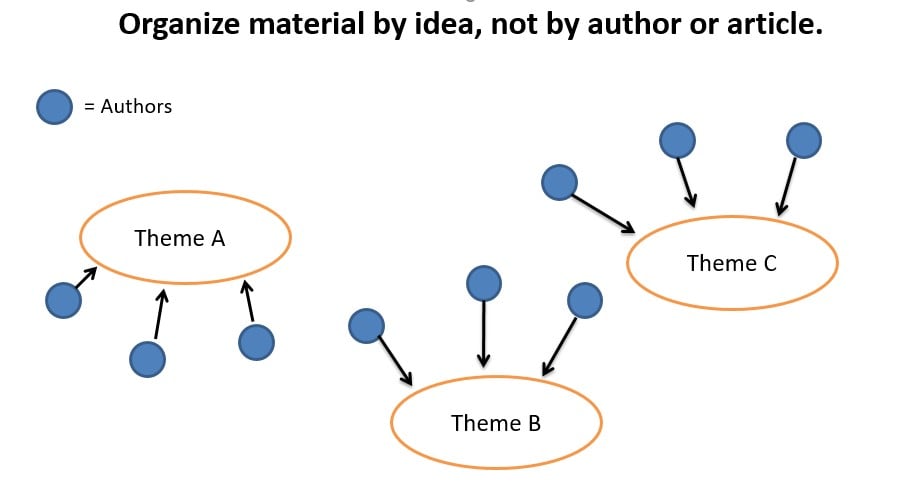
Source Used with Permission: The Chicago School
If you’re drawing on literature from various different fields or they use a wide variety of research methods, you can organize your sources methodologically .
That means grouping together studies based on the type of research they did and discussing the findings that emerged from each method.
If your topic involves a debate between different schools of thought, you can organize it theoretically .
That means comparing the different theories that have been developed and grouping together papers based on the position or perspective they take on the topic, as well as evaluating which arguments are most convincing.
Step 3: Write paragraphs with topic sentences
What sets a synthesis apart from a summary is that it combines various sources. The easiest way to think about this is that each paragraph should discuss a few different sources, and you should be able to condense the overall point of the paragraph into one sentence.
This is called a topic sentence , and it usually appears at the start of the paragraph. The topic sentence signals what the whole paragraph is about; every sentence in the paragraph should be clearly related to it.
A topic sentence can be a simple summary of the paragraph’s content:
“Early research on [x] focused heavily on [y].”
For an effective synthesis, you can use topic sentences to link back to the previous paragraph, highlighting a point of debate or critique:
“Several scholars have pointed out the flaws in this approach.” “While recent research has attempted to address the problem, many of these studies have methodological flaws that limit their validity.”
By using topic sentences, you can ensure that your paragraphs are coherent and clearly show the connections between the articles you are discussing.
As you write your paragraphs, avoid quoting directly from sources: use your own words to explain the commonalities and differences that you found in the literature.
Don’t try to cover every single point from every single source – the key to synthesizing is to extract the most important and relevant information and combine it to give your reader an overall picture of the state of knowledge on your topic.
Step 4: Revise, edit and proofread
Like any other piece of academic writing, synthesizing literature doesn’t happen all in one go – it involves redrafting, revising, editing and proofreading your work.
Checklist for Synthesis
- Do I introduce the paragraph with a clear, focused topic sentence?
- Do I discuss more than one source in the paragraph?
- Do I mention only the most relevant findings, rather than describing every part of the studies?
- Do I discuss the similarities or differences between the sources, rather than summarizing each source in turn?
- Do I put the findings or arguments of the sources in my own words?
- Is the paragraph organized around a single idea?
- Is the paragraph directly relevant to my research question or topic?
- Is there a logical transition from this paragraph to the next one?
Further Information
How to Synthesise: a Step-by-Step Approach
Help…I”ve Been Asked to Synthesize!
Learn how to Synthesise (combine information from sources)
How to write a Psychology Essay

Review of Related Literature (RRL)
Ai generator.
The Review of Related Literature (RRL) is a crucial section in research that examines existing studies and publications related to a specific topic. It summarizes and synthesizes previous findings, identifies gaps, and provides context for the current research. RRL ensures the research is grounded in established knowledge, guiding the direction and focus of new studies.
What Is Review of Related Literature (RRL)?
The Review of Related Literature (RRL) is a detailed analysis of existing research relevant to a specific topic. It evaluates, synthesizes, and summarizes previous studies to identify trends, gaps, and conflicts in the literature. RRL provides a foundation for new research, ensuring it builds on established knowledge and addresses existing gaps.
Format of Review of Related Literature (RRL)
The Review of Related Literature (RRL) is a critical part of any research paper or thesis . It provides an overview of existing research on your topic and helps to establish the context for your study. Here is a typical format for an RRL:
1. Introduction
- Purpose : Explain the purpose of the review and its importance to your research.
- Scope : Define the scope of the literature reviewed, including the time frame, types of sources, and key themes.
2. Theoretical Framework
- Concepts and Theories : Present the main theories and concepts that underpin your research.
- Relevance : Explain how these theories relate to your study.
3. Review of Empirical Studies
- Sub-theme 1 : Summarize key studies, including methodologies, findings, and conclusions.
- Sub-theme 2 : Continue summarizing studies, focusing on different aspects or variables.
- Sub-theme 3 : Include any additional relevant studies.
4. Methodological Review
- Approaches : Discuss the various methodologies used in the reviewed studies.
- Strengths and Weaknesses : Highlight the strengths and weaknesses of these methodologies.
- Gaps : Identify gaps in the existing research that your study aims to address.
5. Synthesis and Critique
- Integration : Integrate findings from the reviewed studies to show the current state of knowledge.
- Critique : Critically evaluate the literature, discussing inconsistencies, limitations, and areas for further research.
6. Conclusion
- Summary : Summarize the main findings from the literature review.
- Research Gap : Clearly state the research gap your study will address.
- Contribution : Explain how your study will contribute to the existing body of knowledge.
7. References
- Citation Style : List all the sources cited in your literature review in the appropriate citation style (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago).
Review of Related Literature (RRL) 1. Introduction This review examines research on social media’s impact on mental health, focusing on anxiety and depression across various demographics over the past ten years. 2. Theoretical Framework Anchored in Social Comparison Theory and Uses and Gratifications Theory, this review explores how individuals’ social media interactions affect their mental health. 3. Review of Empirical Studies Adolescents’ Mental Health Instagram & Body Image : Smith & Johnson (2017) found Instagram use linked to body image issues and lower self-esteem among 500 high school students. Facebook & Anxiety : Brown & Green (2016) showed Facebook use correlated with higher anxiety and depressive symptoms in a longitudinal study of 300 students. Young Adults’ Mental Health Twitter & Stress : Davis & Lee (2018) reported higher stress levels among heavy Twitter users in a survey of 400 university students. LinkedIn & Self-Esteem : Miller & White (2019) found LinkedIn use positively influenced professional self-esteem in 200 young professionals. Adult Mental Health General Social Media Use : Thompson & Evans (2020) found moderate social media use associated with better mental health outcomes, while excessive use correlated with higher anxiety and depression in 1,000 adults. 4. Methodological Review Studies used cross-sectional surveys, longitudinal designs, and mixed methods. Cross-sectional surveys provided large data sets but couldn’t infer causation. Longitudinal studies offered insights into long-term effects but were resource-intensive. Mixed methods enriched data through qualitative insights but required careful integration. 5. Synthesis and Critique The literature shows a complex relationship between social media and mental health, with platform-specific and demographic-specific effects. However, reliance on self-reported data introduces bias, and many cross-sectional studies limit causal inference. More longitudinal and experimental research is needed. 6. Conclusion Current research offers insights into social media’s mental health impact but leaves gaps, particularly regarding long-term effects and causation. This study aims to address these gaps through comprehensive longitudinal analysis. 7. References Brown, A., & Green, K. (2016). Facebook Use and Anxiety Among High School Students . Psychology in the Schools, 53(3), 257-264. Davis, R., & Lee, S. (2018). Twitter and Psychological Stress: A Study of University Students . Journal of College Student Development, 59(2), 120-135. Miller, P., & White, H. (2019). LinkedIn and Its Effect on Professional Self-Esteem . Journal of Applied Psychology, 104(1), 78-90. Smith, J., & Johnson, L. (2017). The Impact of Instagram on Teen Body Image . Journal of Adolescent Health, 60(5), 555-560. Thompson, M., & Evans, D. (2020). The Relationship Between Social Media Use and Mental Health in Adults . Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 23(4), 201-208.

Review of Related Literature (RRL) Examples
Review of related literature in research, review of related literature in research paper, review of related literature qualitative research.

Review of Related Literature Quantitative Research

More Review of Related Literature (RRL) Examples
- Impact of E-learning on Student Performance
- Effectiveness of Mindfulness in Workplace
- Green Building and Energy Efficiency
- Impact of Technology on Healthcare Delivery
- Effects of Nutrition on Cognitive Development in Children
- Impact of Employee Training Programs on Productivity
- Effects of Climate Change on Biodiversity
- Impact of Parental Involvement on Student Achievement
- Effects of Mobile Learning on Student Engagement
- Effects of Urban Green Spaces on Mental Health
Purpose of the Review of Related Literature (RRL)
The Review of Related Literature (RRL) serves several critical purposes in research:
- Establishing Context : It situates your research within the broader field, showing how your study relates to existing work.
- Identifying Gaps : It highlights gaps, inconsistencies, and areas needing further exploration in current knowledge, providing a clear rationale for your study.
- Avoiding Duplication : By reviewing what has already been done, it helps ensure your research is original and not a repetition of existing studies.
- Building on Existing Knowledge : It allows you to build on the findings of previous research, using established theories and methodologies to inform your work.
- Theoretical Foundation : It provides a theoretical basis for your research, grounding it in existing concepts and theories.
- Methodological Insights : It offers insights into the methods and approaches used in similar studies, helping you choose the most appropriate methods for your research.
- Establishing Credibility : It demonstrates your familiarity with the field, showing that you are well-informed and have a solid foundation for your research.
- Supporting Arguments : It provides evidence and support for your research questions, hypotheses, and objectives, strengthening the overall argument of your study.
How to Write Review of Related Literature (RRL)
Writing a Review of Related Literature (RRL) involves several key steps. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Define the Scope and Objectives
- Determine the Scope : Decide on the breadth of the literature you will review, including specific themes, time frame, and types of sources.
- Set Objectives : Clearly define the purpose of the review. What do you aim to achieve? Identify gaps, establish context, or build on existing knowledge.
2. Search for Relevant Literature
- Identify Keywords : Use keywords and phrases related to your research topic.
- Use Databases : Search academic databases like Google Scholar, PubMed, JSTOR, etc., for relevant articles, books, and papers.
- Select Sources : Choose sources that are credible, recent, and relevant to your research.
3. Evaluate and Select the Literature
- Read Abstracts and Summaries : Quickly determine the relevance of each source.
- Assess Quality : Consider the methodology, credibility of the authors, and publication source.
- Select Key Studies : Choose studies that are most relevant to your research questions and objectives.
4. Organize the Literature
- Thematic Organization : Group studies by themes or topics.
- Chronological Organization : Arrange studies in the order they were published to show the development of ideas over time.
- Methodological Organization : Categorize studies by the methods they used.
5. Write the Review
- State the purpose and scope of the review.
- Explain the importance of the topic.
- Theoretical Framework : Present and discuss the main theories and concepts.
- Summarize key studies, including their methodologies, findings, and conclusions.
- Organize by themes or other chosen organizational methods.
- Methodological Review : Discuss the various methodologies used, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses.
- Synthesis and Critique : Integrate findings, critically evaluate the literature, and identify gaps or inconsistencies.
- Summarize the main findings from the literature review.
- Highlight the research gaps your study will address.
- State how your research will contribute to the existing knowledge.
6. Cite the Sources
- Use Appropriate Citation Style : Follow the required citation style (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago).
- List References : Provide a complete list of all sources cited in your review.
What is an RRL?
An RRL summarizes and synthesizes existing research on a specific topic to identify gaps and guide future studies.
Why is RRL important?
It provides context, highlights gaps, and ensures new research builds on existing knowledge.
How do you write an RRL?
Organize by themes, summarize studies, evaluate methodologies, identify gaps, and conclude with relevance to current research.
What sources are used in RRL?
Peer-reviewed journals, books, conference papers, and credible online resources.
How long should an RRL be?
Length varies; typically 10-20% of the total research paper.
What are common RRL mistakes?
Lack of organization, insufficient synthesis, over-reliance on outdated sources, and failure to identify gaps.
Can an RRL include non-scholarly sources?
Primarily scholarly, but reputable non-scholarly sources can be included for context.
What is the difference between RRL and bibliography?
RRL synthesizes and analyzes the literature, while a bibliography lists sources.
How often should an RRL be updated?
Regularly, especially when new relevant research is published.
Can an RRL influence research direction?
Yes, it identifies gaps and trends that shape the focus and methodology of new research.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

IMAGES
VIDEO