Solomon Asch Conformity Line Experiment Study
Saul McLeod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul McLeod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
Solomon Asch experimented with investigating the extent to which social pressure from a majority group could affect a person to conform .
He believed the main problem with Sherif’s (1935) conformity experiment was that there was no correct answer to the ambiguous autokinetic experiment. How could we be sure that a person conformed when there was no correct answer?
Asch (1951) devised what is now regarded as a classic experiment in social psychology, whereby there was an obvious answer to a line judgment task.
If the participant gave an incorrect answer, it would be clear that this was due to group pressure.
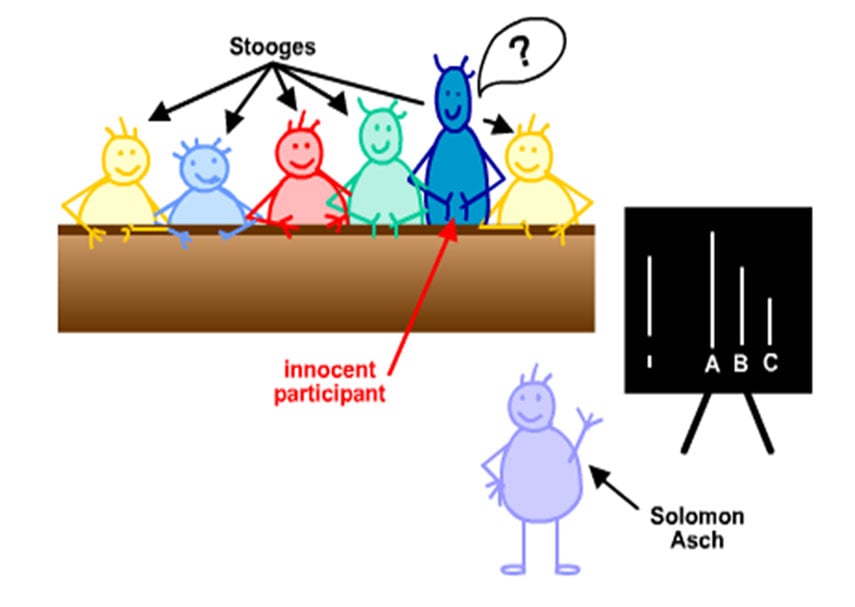

Experimental Procedure
Asch used a lab experiment to study conformity, whereby 50 male students from Swarthmore College in the USA participated in a ‘vision test.’
Using a line judgment task, Asch put a naive participant in a room with seven confederates/stooges. The confederates had agreed in advance what their responses would be when presented with the line task.
The real participant did not know this and was led to believe that the other seven confederates/stooges were also real participants like themselves.

Each person in the room had to state aloud which comparison line (A, B or C) was most like the target line. The answer was always obvious. The real participant sat at the end of the row and gave his or her answer last.
At the start, all participants (including the confederates) gave the correct answers. However, after a few rounds, the confederates started to provide unanimously incorrect answers.
There were 18 trials in total, and the confederates gave the wrong answer on 12 trials (called the critical trials). Asch was interested to see if the real participant would conform to the majority view.
Asch’s experiment also had a control condition where there were no confederates, only a “real participant.”
Asch measured the number of times each participant conformed to the majority view. On average, about one third (32%) of the participants who were placed in this situation went along and conformed with the clearly incorrect majority on the critical trials.
Over the 12 critical trials, about 75% of participants conformed at least once, and 25% of participants never conformed.
In the control group , with no pressure to conform to confederates, less than 1% of participants gave the wrong answer.
Why did the participants conform so readily? When they were interviewed after the experiment, most of them said that they did not really believe their conforming answers, but had gone along with the group for fear of being ridiculed or thought “peculiar.
A few of them said that they did believe the group’s answers were correct.
Apparently, people conform for two main reasons: because they want to fit in with the group ( normative influence ) and because they believe the group is better informed than they are ( informational influence ).
Critical Evaluation
One limitation of the study is that is used a biased sample. All the participants were male students who all belonged to the same age group. This means that the study lacks population validity and that the results cannot be generalized to females or older groups of people.
Another problem is that the experiment used an artificial task to measure conformity – judging line lengths. How often are we faced with making a judgment like the one Asch used, where the answer is plain to see?
This means that the study has low ecological validity and the results cannot be generalized to other real-life situations of conformity. Asch replied that he wanted to investigate a situation where the participants could be in no doubt what the correct answer was. In so doing he could explore the true limits of social influence.
Some critics thought the high levels of conformity found by Asch were a reflection of American, 1950’s culture and told us more about the historical and cultural climate of the USA in the 1950s than then they did about the phenomena of conformity.
In the 1950s America was very conservative, involved in an anti-communist witch-hunt (which became known as McCarthyism) against anyone who was thought to hold sympathetic left-wing views.
Perrin and Spencer
Conformity to American values was expected. Support for this comes from studies in the 1970s and 1980s that show lower conformity rates (e.g., Perrin & Spencer, 1980).
Perrin and Spencer (1980) suggested that the Asch effect was a “child of its time.” They carried out an exact replication of the original Asch experiment using engineering, mathematics, and chemistry students as subjects. They found that in only one out of 396 trials did an observer join the erroneous majority.
Perrin and Spencer argue that a cultural change has taken place in the value placed on conformity and obedience and in the position of students.
In America in the 1950s, students were unobtrusive members of society, whereas now, they occupy a free questioning role.
However, one problem in comparing this study with Asch is that very different types of participants are used. Perrin and Spencer used science and engineering students who might be expected to be more independent by training when it came to making perceptual judgments.
Finally, there are ethical issues : participants were not protected from psychological stress which may occur if they disagreed with the majority.
Evidence that participants in Asch-type situations are highly emotional was obtained by Back et al. (1963) who found that participants in the Asch situation had greatly increased levels of autonomic arousal.
This finding also suggests that they were in a conflict situation, finding it hard to decide whether to report what they saw or to conform to the opinion of others.
Asch also deceived the student volunteers claiming they were taking part in a “vision” test; the real purpose was to see how the “naive” participant would react to the behavior of the confederates. However, deception was necessary to produce valid results.
The clip below is not from the original experiment in 1951, but an acted version for television from the 1970s.
Factors Affecting Conformity
In further trials, Asch (1952, 1956) changed the procedure (i.e., independent variables) to investigate which situational factors influenced the level of conformity (dependent variable).
His results and conclusions are given below:
Asch (1956) found that group size influenced whether subjects conformed. The bigger the majority group (no of confederates), the more people conformed, but only up to a certain point.
With one other person (i.e., confederate) in the group conformity was 3%, with two others it increased to 13%, and with three or more it was 32% (or 1/3).
Optimum conformity effects (32%) were found with a majority of 3. Increasing the size of the majority beyond three did not increase the levels of conformity found. Brown and Byrne (1997) suggest that people might suspect collusion if the majority rises beyond three or four.
According to Hogg & Vaughan (1995), the most robust finding is that conformity reaches its full extent with 3-5 person majority, with additional members having little effect.
Lack of Group Unanimity / Presence of an Ally
The study also found that when any one individual differed from the majority, the power of conformity significantly decreased.
This showed that even a small dissent can reduce the power of a larger group, providing an important insight into how individuals can resist social pressure.
As conformity drops off with five members or more, it may be that it’s the unanimity of the group (the confederates all agree with each other) which is more important than the size of the group.
In another variation of the original experiment, Asch broke up the unanimity (total agreement) of the group by introducing a dissenting confederate.
Asch (1956) found that even the presence of just one confederate that goes against the majority choice can reduce conformity by as much as 80%.
For example, in the original experiment, 32% of participants conformed on the critical trials, whereas when one confederate gave the correct answer on all the critical trials conformity dropped to 5%.
This was supported in a study by Allen and Levine (1968). In their version of the experiment, they introduced a dissenting (disagreeing) confederate wearing thick-rimmed glasses – thus suggesting he was slightly visually impaired.
Even with this seemingly incompetent dissenter, conformity dropped from 97% to 64%. Clearly, the presence of an ally decreases conformity.
The absence of group unanimity lowers overall conformity as participants feel less need for social approval of the group (re: normative conformity).
Difficulty of Task
When the (comparison) lines (e.g., A, B, C) were made more similar in length it was harder to judge the correct answer and conformity increased.
When we are uncertain, it seems we look to others for confirmation. The more difficult the task, the greater the conformity.
Answer in Private
When participants were allowed to answer in private (so the rest of the group does not know their response), conformity decreased.
This is because there are fewer group pressures and normative influence is not as powerful, as there is no fear of rejection from the group.
Frequently Asked Questions
How has the asch conformity line experiment influenced our understanding of conformity.
The Asch conformity line experiment has shown that people are susceptible to conforming to group norms even when those norms are clearly incorrect. This experiment has significantly impacted our understanding of social influence and conformity, highlighting the powerful influence of group pressure on individual behavior.
It has helped researchers to understand the importance of social norms and group dynamics in shaping our beliefs and behaviors and has had a significant impact on the study of social psychology.
What are some real-world examples of conformity?
Examples of conformity in everyday life include following fashion trends, conforming to workplace norms, and adopting the beliefs and values of a particular social group. Other examples include conforming to peer pressure, following cultural traditions and customs, and conforming to societal expectations regarding gender roles and behavior.
Conformity can have both positive and negative effects on individuals and society, depending on the behavior’s context and consequences.
What are some of the negative effects of conformity?
Conformity can have negative effects on individuals and society. It can limit creativity and independent thinking, promote harmful social norms and practices, and prevent personal growth and self-expression.
Conforming to a group can also lead to “groupthink,” where the group prioritizes conformity over critical thinking and decision-making, which can result in poor choices.
Moreover, conformity can spread false information and harmful behavior within a group, as individuals may be afraid to challenge the group’s beliefs or actions.
How does conformity differ from obedience?
Conformity involves adjusting one’s behavior or beliefs to align with the norms of a group, even if those beliefs or behaviors are not consistent with one’s personal views. Obedience , on the other hand, involves following the orders or commands of an authority figure, often without question or critical thinking.
While conformity and obedience involve social influence, obedience is usually a response to an explicit request or demand from an authority figure, whereas conformity is a response to implicit social pressure from a group.
What is the Asch effect?
The Asch Effect is a term coined from the Asch Conformity Experiments conducted by Solomon Asch. It refers to the influence of a group majority on an individual’s judgment or behavior, such that the individual may conform to perceived group norms even when those norms are obviously incorrect or counter to the individual’s initial judgment.
This effect underscores the power of social pressure and the strong human tendency towards conformity in group settings.
What is Solomon Asch’s contribution to psychology?
Solomon Asch significantly contributed to psychology through his studies on social pressure and conformity.
His famous conformity experiments in the 1950s demonstrated how individuals often conform to the majority view, even when clearly incorrect.
His work has been fundamental to understanding social influence and group dynamics’ power in shaping individual behaviors and perceptions.
Allen, V. L., & Levine, J. M. (1968). Social support, dissent and conformity. Sociometry , 138-149.
Asch, S. E. (1951). Effects of group pressure upon the modification and distortion of judgment. In H. Guetzkow (ed.) Groups, leadership and men . Pittsburgh, PA: Carnegie Press.
Asch, S. E. (1952). Group forces in the modification and distortion of judgments.
Asch, S. E. (1956). Studies of independence and conformity: I. A minority of one against a unanimous majority. Psychological monographs: General and applied, 70(9) , 1-70.
Back, K. W., Bogdonoff, M. D., Shaw, D. M., & Klein, R. F. (1963). An interpretation of experimental conformity through physiological measures. Behavioral Science, 8(1) , 34.
Bond, R., & Smith, P. B. (1996). Culture and conformity : A meta-analysis of studies using Asch’s (1952b, 1956) line judgment task. Psychological bulletin , 119 (1), 111.
Longman, W., Vaughan, G., & Hogg, M. (1995). Introduction to social psychology .
Perrin, S., & Spencer, C. (1980). The Asch effect: a child of its time? Bulletin of the British Psychological Society, 32, 405-406.
Sherif, M., & Sherif, C. W. (1953). Groups in harmony and tension . New York: Harper & Row.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
The Asch Conformity Experiments
What These Experiments Say About Group Behavior
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
What Is Conformity?
Factors that influence conformity.
The Asch conformity experiments were a series of psychological experiments conducted by Solomon Asch in the 1950s. The experiments revealed the degree to which a person's own opinions are influenced by those of a group . Asch found that people were willing to ignore reality and give an incorrect answer in order to conform to the rest of the group.
At a Glance
The Asch conformity experiments are among the most famous in psychology's history and have inspired a wealth of additional research on conformity and group behavior. This research has provided important insight into how, why, and when people conform and the effects of social pressure on behavior.
Do you think of yourself as a conformist or a non-conformist? Most people believe that they are non-conformist enough to stand up to a group when they know they are right, but conformist enough to blend in with the rest of their peers.
Research suggests that people are often much more prone to conform than they believe they might be.
Imagine yourself in this situation: You've signed up to participate in a psychology experiment in which you are asked to complete a vision test.
Seated in a room with the other participants, you are shown a line segment and then asked to choose the matching line from a group of three segments of different lengths.
The experimenter asks each participant individually to select the matching line segment. On some occasions, everyone in the group chooses the correct line, but occasionally, the other participants unanimously declare that a different line is actually the correct match.
So what do you do when the experimenter asks you which line is the right match? Do you go with your initial response, or do you choose to conform to the rest of the group?
Conformity in Psychology
In psychological terms, conformity refers to an individual's tendency to follow the unspoken rules or behaviors of the social group to which they belong. Researchers have long been been curious about the degree to which people follow or rebel against social norms.
Asch was interested in looking at how pressure from a group could lead people to conform, even when they knew that the rest of the group was wrong. The purpose of the Asch conformity experiment was to demonstrate the power of conformity in groups.
Methodology of Asch's Experiments
Asch's experiments involved having people who were in on the experiment pretend to be regular participants alongside those who were actual, unaware subjects of the study. Those that were in on the experiment would behave in certain ways to see if their actions had an influence on the actual experimental participants.
In each experiment, a naive student participant was placed in a room with several other confederates who were in on the experiment. The subjects were told that they were taking part in a "vision test." All told, a total of 50 students were part of Asch’s experimental condition.
The confederates were all told what their responses would be when the line task was presented. The naive participant, however, had no inkling that the other students were not real participants. After the line task was presented, each student verbally announced which line (either 1, 2, or 3) matched the target line.
Critical Trials
There were 18 different trials in the experimental condition , and the confederates gave incorrect responses in 12 of them, which Asch referred to as the "critical trials." The purpose of these critical trials was to see if the participants would change their answer in order to conform to how the others in the group responded.
During the first part of the procedure, the confederates answered the questions correctly. However, they eventually began providing incorrect answers based on how they had been instructed by the experimenters.
Control Condition
The study also included 37 participants in a control condition . In order to ensure that the average person could accurately gauge the length of the lines, the control group was asked to individually write down the correct match. According to these results, participants were very accurate in their line judgments, choosing the correct answer 99% of the time.
Results of the Asch Conformity Experiments
Nearly 75% of the participants in the conformity experiments went along with the rest of the group at least one time.
After combining the trials, the results indicated that participants conformed to the incorrect group answer approximately one-third of the time.
The experiments also looked at the effect that the number of people present in the group had on conformity. When just one confederate was present, there was virtually no impact on participants' answers. The presence of two confederates had only a tiny effect. The level of conformity seen with three or more confederates was far more significant.
Asch also found that having one of the confederates give the correct answer while the rest of the confederates gave the incorrect answer dramatically lowered conformity. In this situation, just 5% to 10% of the participants conformed to the rest of the group (depending on how often the ally answered correctly). Later studies have also supported this finding, suggesting that having social support is an important tool in combating conformity.
At the conclusion of the Asch experiments, participants were asked why they had gone along with the rest of the group. In most cases, the students stated that while they knew the rest of the group was wrong, they did not want to risk facing ridicule. A few of the participants suggested that they actually believed the other members of the group were correct in their answers.
These results suggest that conformity can be influenced both by a need to fit in and a belief that other people are smarter or better informed.
Given the level of conformity seen in Asch's experiments, conformity can be even stronger in real-life situations where stimuli are more ambiguous or more difficult to judge.
Asch went on to conduct further experiments in order to determine which factors influenced how and when people conform. He found that:
- Conformity tends to increase when more people are present . However, there is little change once the group size goes beyond four or five people.
- Conformity also increases when the task becomes more difficult . In the face of uncertainty, people turn to others for information about how to respond.
- Conformity increases when other members of the group are of a higher social status . When people view the others in the group as more powerful, influential, or knowledgeable than themselves, they are more likely to go along with the group.
- Conformity tends to decrease, however, when people are able to respond privately . Research has also shown that conformity decreases if people have support from at least one other individual in a group.

Criticisms of the Asch Conformity Experiments
One of the major criticisms of Asch's conformity experiments centers on the reasons why participants choose to conform. According to some critics, individuals may have actually been motivated to avoid conflict, rather than an actual desire to conform to the rest of the group.
Another criticism is that the results of the experiment in the lab may not generalize to real-world situations.
Many social psychology experts believe that while real-world situations may not be as clear-cut as they are in the lab, the actual social pressure to conform is probably much greater, which can dramatically increase conformist behaviors.
Asch SE. Studies of independence and conformity: I. A minority of one against a unanimous majority . Psychological Monographs: General and Applied . 1956;70(9):1-70. doi:10.1037/h0093718
Morgan TJH, Laland KN, Harris PL. The development of adaptive conformity in young children: effects of uncertainty and consensus . Dev Sci. 2015;18(4):511-524. doi:10.1111/desc.12231
Asch SE. Effects of group pressure upon the modification and distortion of judgments . In: Guetzkow H, ed. Groups, Leadership and Men; Research in Human Relations. Carnegie Press. 1951:177–190.
Britt MA. Psych Experiments: From Pavlov's Dogs to Rorschach's Inkblots . Adams Media.
Myers DG. Exploring Psychology (9th ed.). Worth Publishers.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
The Asch Line Study (+3 Conformity Experiments)

Sheep. Complicit. Doormat. There are a lot of negative connotations associated with conformity, especially in the United States. Individualist societies push back on "going along with what everyone is doing." And yet, we conform more than we think. According to studies like the Asch Line Study, humans have a natural tendency to conform.
The Asch Line Study is one of the most well-known experiments in modern psychology, but it's not without its faults. Keep reading to learn about how the Asch Line Study worked, its criticisms, and similar experiments!
How Did the Asch Line Study Work?
In his famous “Line Experiment”, Asch showed his subjects a picture of a vertical line followed by three lines of different lengths, one of which was obviously the same length as the first one. He then asked subjects to identify which line was the same length as the first line.
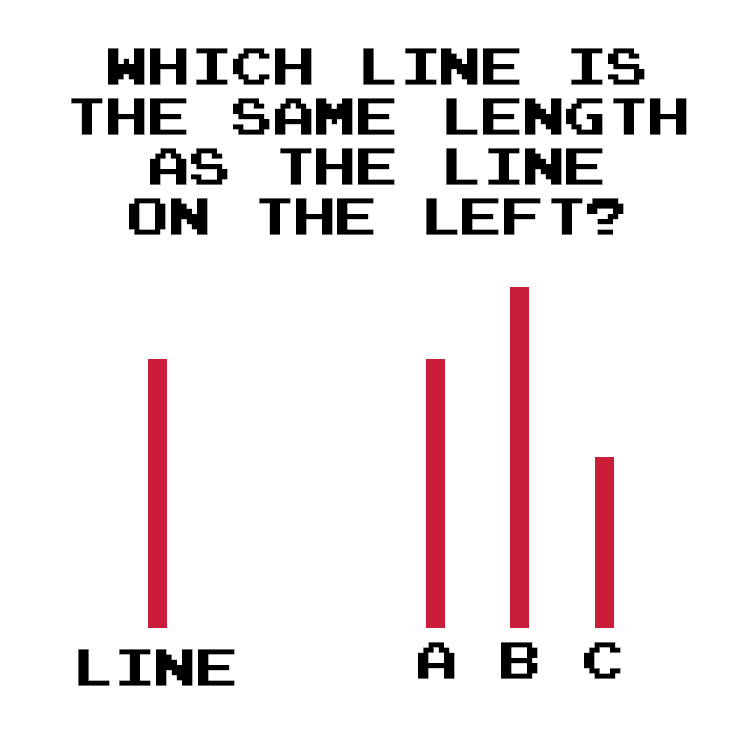
Solomon Asch used 123 male college students as his subjects, and told them that his experiment was simply a ‘vision test’. For his control group, Asch just had his subjects go through his 18 questions on their own.
However, for his experimental group, he had his subjects answer each of the same 18 questions in a group of around a dozen people, where the first 11 people intentionally said obviously incorrect answers one after another, with the final respondee being the actual subject of the experiment.
Who was Solomon Asch?
Solomon E. Asch was a pioneer in social psychology. He was born in Poland in 1907 and moved to the United States in 1920. Asch received his Ph.D. from Columbia University in 1932 and went on to perform some famous psychological experiments about conformity in the 1950s.
One of these studies is known as the “Asch Line Experiment”, where he found evidence supporting the idea that humans will conform to and accept the ideas of others around them, even if those ideas are obviously false. This study is one of the most influential studies in social psychology .
Findings of Asch's Conformity Study
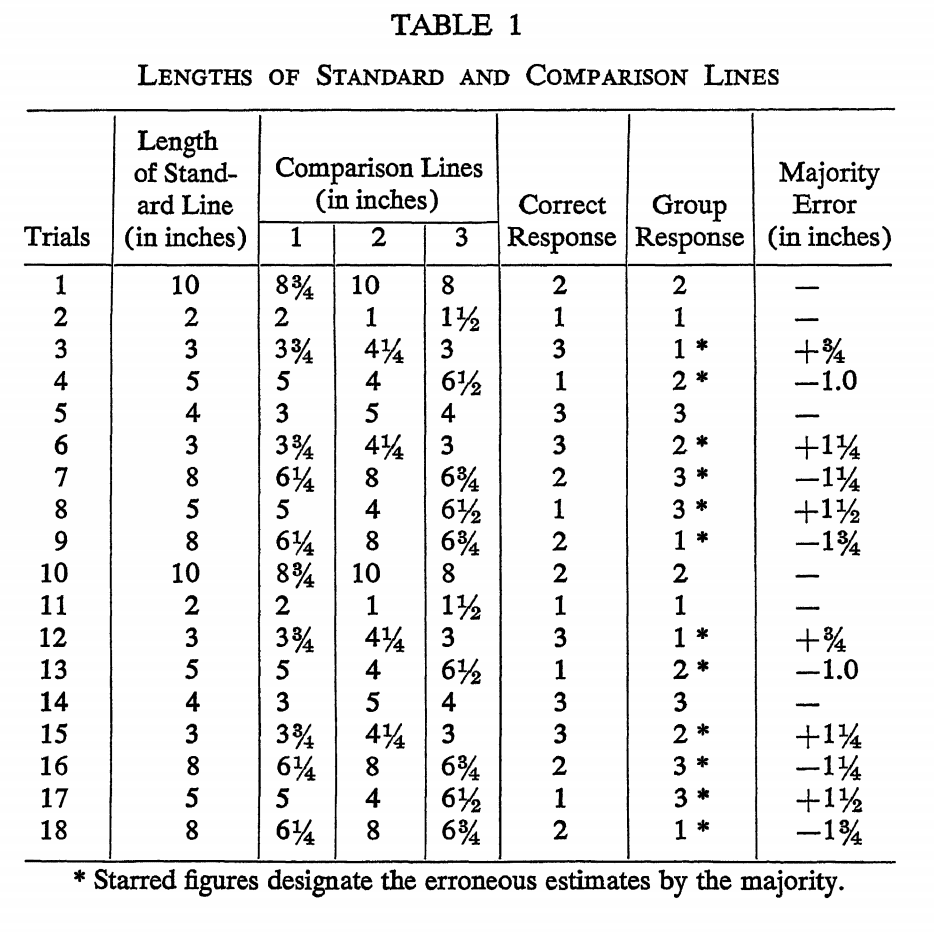
Asch found that his subjects indeed were more likely to give a false response after the other members of their group (the actors) gave false responses. As shown in this ‘Table 1’ from his experiment, during 18 trials, the ‘Majority Error’ column shows no error when the group response was the correct response, such as in Trial #1.
However, when the entire group intentionally gave a false answer (these situations are designated with an * under the “Group Response” column), the ‘Majority Error’ did exist and was slanted toward the opinion of the group.
For example, if the group answered with a line that was too long, such as in Trial #3, the ‘Majority Error’ column shows that the subjects generally estimated the line to be longer than it really was (denoted with a ‘+’), and vice-versa for when the group answered with a line that was too short, such as in Trial #4.
As for his control group, Asch found that people generally said the correct answer when they did not have a group of actors saying answers before them.
Interviewing the Participants
After the experiment, Asch revealed the true experiment to his subjects and interviewed them. Some subjects had become very agitated during the experiment, wondering why they kept disagreeing with the group. When the group pressed one particular subject on why he thought that he was correct and the entire group was wrong, he replied defiantly, exclaiming: “You're probably right, but you may be wrong!”
Other subjects admitted during the interview that they changed their answers after hearing others in their group reply differently. One was recorded saying, “If I’d been the first I probably would have responded differently.” Another subject admitted, “...at times I had the feeling: 'to heck with it, I'll go along with the rest.' "
Conclusions from the Asch Line Study
Asch found that his subjects often changed their answers when they heard the rest of the group unanimously giving a different response.
After the interviews, Asch concluded in his study that his subjects conformed to the opinions of the group for three different reasons:
Distortion of perception due to the stress of group pressure: This group of subjects always agreed with the group and said during the interview that they wholeheartedly believed that their obviously incorrect answers were correct. Asch concluded that the stress of group pressure had distorted their perception.
Distortion of judgment: This was the most common outcome, where subjects assumed that their individual answers were incorrect after seeing the rest of the group answer differently, so they changed their answer to align with the group.
Distortion of action: These subjects never doubted that they were correct and the group was wrong, but out of fear of being perceived as different, they suppressed their opinions and intentionally lied when it was their turn to give an answer.
Asch Line Study vs. Milgram Experiment
Both the Asch Line Study and the Milgram Experiment look at conformity, obedience, and the negative effects of going along with the majority opinion. Those negative effects are slightly awkward, like in the Asch Line Study, or dangerous, like in the Milgram Experiment. Both experiments were conducted in the Post-WWII world as a response to the conformity that was required for Nazi Germany to gain power. The premise of Asch's study was not nearly as dramatic. Milgram's was.
To test conformity, Milgram and his researchers instructed participants to press a button. Participants believed that the buttons would shock another "participant" in a chair, who was really an actor. (No one was shocked.) The study continued as long as participants continued to shock the participant at increasingly dangerous levels. The participants knew that they could cause serious harm to the person in the chair. Yet, many obeyed.
Further Experiments and Variations
Solomon Asch didn't just conduct one experiment and move on. He replicated his experiment with new factors, including:
- Changing the size of the actor group
- Switching to a non-unanimous actor group
- Having a unanimous actor group, except for one actor who sticks to the correct response no matter what the group or subject says
- Instructing the one actor who gives the correct response come in late
- Having one actor decide to change their answer from the group’s answer to the subject’s answer
There are also many reproductions and replications of this study online. Not all of them come to the same conclusions! Read through the following texts to get a sense of how other psychologists approached this subject:
- Mori K, Arai M. No need to fake it: reproduction of the Asch experiment without confederates. Int J Psychol. 2010 Oct 1;45(5):390-7. doi: 10.1080/00207591003774485. PMID: 22044061.
Why Is The Asch Line Study Ethnocentric? And Other Criticisms
One big issue with the Asch line study is that the subjects were all white male college students between the ages of 17 and 25, with a mean age of 20. Since the experiment only shows results for this small and specific group of people, it alone cannot be applied to other groups such as women or older men.
Experimenter Bias in the Asch Line Study
Only choosing subjects from one demographic is a form of Experimenter Bias . Of course, researchers can use one demographic if they are specifically studying that demographic. But Asch was not just looking at young, white men. If he had expanded his research to include more participants, he may have produced different answers.
We assume Asch did not go about his study with the intention of being biased. That's the tricky thing about biases. They sneak up on us! Even the way that we share information about psychology research is the result of bias. Reporter bias is the tendency to highlight certain studies due to their results. The Asch Line Study produced fascinating results. Therefore, psychology professors, reporters, and students find it fascinating and continue to share this concept. They don't always share the full story, though.
Did you know that 95% of the participants actually defied the majority at least once during the experiment? Most textbooks don't report that. Nor did they report that the interviewees knew that they were right all along! Leaving out this key information is not Asch's fault. But it should give you, a psychology student, some pause. One thing that we should take away from this study is that we have a natural tendency to conform. This tendency also takes place when we draw conclusions from famous studies! Be critical as you learn about these famous studies and look to the source if possible.
Further Criticisms of the Asch Line Study
Does the Asch Line Study stand the test of time? Not exactly. If we look at what was happening in 1950s society, we can see why Asch got his results. Young white men in the early 1950s may have responded differently to this experiment than young white men would today. In the United States, which is where this experiment was performed, the mid-1950s was a historic turning point in terms of rejecting conformity. Youth were pushing toward a more free-thinking society. This experiment was performed right around the time that the movement was just starting to blossom, so the subjects had not grown up in the middle of this new anti-conformist movement. Had Asch performed this experiment a decade later with youth who more highly valued free-thinking, he may have come across very different results.
Another thing to note is that, at least in the United States, education has evolved with this movement of encouraging free-thinking. Teachers today tell students to question everything, and many schools reject ideas of conformity. This could once again mean that, if done again today, Asch would have found very different results with this experiment.
Another problem with this experiment is that, since subjects were not told it was a psychological experiment until after it was over, subjects may have gone through emotional and psychological pain during what they thought was just a simple ‘vision test’.
Finally, it’s good to remember that the ‘Asch Line Experiment’ is just that: an experiment where people looked at lines. This can be hard to apply to other situations because humans in group settings are rarely faced with questions that have one such obvious and clear answer, as was the case in this experiment.
Related posts:
- Solomon Asch (Psychologist Biography)
- 40+ Famous Psychologists (Images + Biographies)
- Stanley Milgram (Psychologist Biography)
- Experimenter Bias (Definition + Examples)
- The Monster Study (Summary, Results, and Ethical Issues)
Reference this article:
About The Author

PracticalPie.com is a participant in the Amazon Associates Program. As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
Follow Us On:
Youtube Facebook Instagram X/Twitter
Psychology Resources
Developmental
Personality
Relationships
Psychologists
Serial Killers
Psychology Tests
Personality Quiz
Memory Test
Depression test
Type A/B Personality Test
© PracticalPsychology. All rights reserved
Privacy Policy | Terms of Use
Reference Library
Collections
- See what's new
- All Resources
- Student Resources
- Assessment Resources
- Teaching Resources
- CPD Courses
- Livestreams
Study notes, videos, interactive activities and more!
Psychology news, insights and enrichment
Currated collections of free resources
Browse resources by topic
- All Psychology Resources
Resource Selections
Currated lists of resources
Study Notes
Conformity - Asch (1951)
Last updated 6 Sept 2022
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share by Email
Asch (1951) conducted one of the most famous laboratory experiments examining conformity. He wanted to examine the extent to which social pressure from a majority, could affect a person to conform.
Asch’s sample consisted of 50 male students from Swarthmore College in America, who believed they were taking part in a vision test. Asch used a line judgement task, where he placed on real naïve participants in a room with seven confederates (actors), who had agreed their answers in advance. The real participant was deceived and was led to believe that the other seven people were also real participants. The real participant always sat second to last.
In turn, each person had to say out loud which line (A, B or C) was most like the target line in length.

Unlike Jenness’ experiment , the correct answer was always obvious. Each participant completed 18 trials and the confederates gave the same incorrect answer on 12 trials, called critical trials. Asch wanted to see if the real participant would conform to the majority view, even when the answer was clearly incorrect.
Asch measured the number of times each participant conformed to the majority view. On average, the real participants conformed to the incorrect answers on 32% of the critical trials. 74% of the participants conformed on at least one critical trial and 26% of the participants never conformed. Asch also used a control group, in which one real participant completed the same experiment without any confederates. He found that less than 1% of the participants gave an incorrect answer.
Asch interviewed his participants after the experiment to find out why they conformed. Most of the participants said that they knew their answers were incorrect, but they went along with the group in order to fit in, or because they thought they would be ridiculed. This confirms that participants conformed due to normative social influence and the desire to fit in.
Evaluation of Asch
Asch used a biased sample of 50 male students from Swarthmore College in America. Therefore, we cannot generalise the results to other populations, for example female students, and we are unable to conclude if female students would have conformed in a similar way to male students. As a result Asch’s sample lacks population validity and further research is required to determine whether males and females conform differently
Furthermore, it could be argued that Asch’s experiment has low levels of ecological validity . Asch’s test of conformity, a line judgement task, is an artificial task, which does not reflect conformity in everyday life. Consequently, we are unable to generalise the results of Asch to other real life situations, such as why people may start smoking or drinking around friends, and therefore these results are limited in their application to everyday life.
Finally, Asch’s research is ethically questionable. He broke several ethical guidelines , including: deception and protection from harm . Asch deliberately deceived his participants, saying that they were taking part in a vision test and not an experiment on conformity. Although it is seen as unethical to deceive participants, Asch’s experiment required deception in order to achieve valid results. If the participants were aware of the true aim they would have displayed demand characteristics and acted differently. In addition, Asch’s participants were not protected from psychological harm and many of the participants reporting feeling stressed when they disagreed with the majority. However, Asch interviewed all of his participants following the experiment to overcome this issue.
- Normative Social Influence
- Task Difficulty
You might also like
Ethics and psychology, role of social influence processes in social change, explanations for obedience - milgram (1963), misleading information – post-event discussion, free resource: creating evaluation burgers in the classroom.
12th January 2017
Conformity in Action: Why Our Friends Want Us to Drink?
18th January 2017
Conformity & Minority Influence: Example Answer Video for A Level SAM 2, Paper 1, Q3 (7 Marks)
Topic Videos
Explanations for Conformity Application Essay: Example Answer Video for A Level SAM 3, Paper 1, Q3 (16 Marks)
Our subjects.
- › Criminology
- › Economics
- › Geography
- › Health & Social Care
- › Psychology
- › Sociology
- › Teaching & learning resources
- › Student revision workshops
- › Online student courses
- › CPD for teachers
- › Livestreams
- › Teaching jobs
Boston House, 214 High Street, Boston Spa, West Yorkshire, LS23 6AD Tel: 01937 848885
- › Contact us
- › Terms of use
- › Privacy & cookies
© 2002-2024 Tutor2u Limited. Company Reg no: 04489574. VAT reg no 816865400.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Experimental Procedure. Asch used a lab experiment to study conformity, whereby 50 male students from Swarthmore College in the USA participated in a 'vision test.'. Using a line judgment task, Asch put a naive participant in a room with seven confederates/stooges. The confederates had agreed in advance what their responses would be when presented with the line task.
The Asch conformity experiments were a series of psychological experiments conducted by Solomon Asch in the 1950s. The experiments revealed the degree to which a person's own opinions are influenced by those of a group. Asch found that people were willing to ignore reality and give an incorrect answer in order to conform to the rest of the group.
Asch received his Ph.D. from Columbia University in 1932 and went on to perform some famous psychological experiments about conformity in the 1950s. One of these studies is known as the "Asch Line Experiment", where he found evidence supporting the idea that humans will conform to and accept the ideas of others around them, even if those ...
In psychology, the Asch conformity experiments or the Asch paradigm were a series of studies directed by Solomon Asch studying if and how individuals yielded to or defied a majority group and the effect of such influences on beliefs and opinions. [1] [2] [3] [4]Developed in the 1950s, the methodology remains in use by many researchers. Uses include the study of conformity effects of task ...
The Asch conformity experiments were a series of studies by social psychologist Solomon Asch during the 1950s. In the studies, Asch sought to learn more about how social pressure could lead to conformity. In the studies, people were asked to choose a line that matched the length of another line. When the others in the group chose the incorrect ...
The Asch Conformity Experiment. The Asch Conformity Experiment is a popular experiment that is used to study group behaviour and conformity. It was designed by the pioneering social psychologist Solomon Asch. In this test, he studied how individual cognition can be affected by external influence when in a group.
knowledge or assumptions about the situation (Asch, 1955). Contents 1 Methodology 2 Results 3 Possible Explanations 4 Variations on Size, Unanimity, and Accuracy 5 Impact 6 Criticisms 7 Works Cited Methodology Asch gathered seven to nine male college students for what he claimed was an experiment in visual perception (Asch, 1955).
Asch's research into majority influence. Asch (1955) set up a study to test conformity to the majority which remains one of the most cited and well-known social psychology studies ever Asch was interested in seeing the extent to which group pressure could influence an individual to go against what their eyes were telling them. Would the pressure of being in a group, who all agreed as to the ...
Asch (1951) conducted one of the most famous laboratory experiments examining conformity. He wanted to examine the extent to which social pressure from a majority, could affect a person to conform. Asch's sample consisted of 50 male students from Swarthmore College in America, who believed they were taking part in a vision test.
Solomon Asch conducted an experiment to investigate the extent to which social pressure from a majority group could affect a person to conform. In 1951, he created and conducted a social psychology experiment, where he asked a participant to give an answer, while the rest of the group disagreed with them to see how much the participant would ...