

7 Business Plan Templates for Kids (Free Printables!)
By: Author Amanda L. Grossman
Posted on Last updated: May 7, 2024
- Pinterest 950
- Flipboard 0
Download one of these (mostly) free business plan templates for kids to help your child focus on a business idea.
What do supersoakers, Apple computers, and Nike shoes all have in common?

They all started as a business plan.
A business plan template for kids is great for two reasons:
- Your child can play around with it and get familiar with what's required (even if they never start the business)
- It helps kids focus on just one business idea at a time, and to see if they should move forward with it
No matter which category your own child falls into – just playing with business plans, or they have an actual business idea – I’ve got just the free business plan template for you.
Honestly? I wish my own parents would’ve given me one of these when, as a kid, my childhood friend and I had come up with our first kid business idea: selling bean bags. So, good on you for getting your kids involved with business plans so early in life!
Best Business Plan Templates for Kids
Use one of the business plan templates for kids below with one of these 16 kid business ideas .
OR, help them to use one of their original ideas sending sparks in their brain. You can use these 3 kid business plan examples for help with filling it out.
1. Solid Gold Biz Plan
I’ve been in business for 7 years and I’ve made about every mistake in the book.
Probably one of the biggest? Was that I didn't sit down to write a proper business plan (or, ANY business plan) until I was several years into blogging.
Because of this, I created a free business plan template for kids and teens (on Page 6 of this free printable), so that they practice how to do it right, from the beginning!
What makes my free Solid Gold Biz Plan different is that it starts your child thinking about the problem that they want to solve – because ultimately, that is the purpose of creating a product or a service. To solve a specific problem for people.
It then goes on to ask them simple questions that will focus them in on what it takes to plan out a business idea.
For example, I raise the question of how much it will cost to not only create the product/service but to also deliver it and maintain it. These are sometimes costs forgotten costs when creating a business plan.
2. BizKids’ Guide to Writing a Business Plan
This free business plan guide for kids includes sections for your idea, your marketing (and what makes your product unique), your startup costs, and an area for pricing so that you can make sure you’ll make a profit.

At the end is a one-page summary where your child can write up their answers from the previous pages all in the same place. Great for tacking up on the wall!
3. Teen Entrepreneur Toolbox
Anthony ONeal partnered up with Dave Ramsey to create the Teen Entrepreneur Toolbox , a kid’s entrepreneur kit and small business guide for teens.
In other words, it’s so much more than just a business template for kids!
The entrepreneur kit includes the following:
- Access to the Free Entrepreneur Toolbox app
- Teen Portfolio Book
- DVD of Anthony’s Training Video
- Parent’s Guide Book
- Pack of Thank You Cards
- Deck of Conversation Starter Cards about Starting a Business
- Goal Tracker Poster
Here's my full review of the Teen Entrepreneur Toolbox .
4. Proverbial Home Maker’s Family Business Plan Guide
This is such a fun guide that you can fill out with your child, teen, tween, or even the whole family. It includes family business ideas, a sales ledger, an inventory worksheet, and much more.

Business Plan Examples
You may be wondering where you can find business plan examples to show your kids or teens.
For starters, you should look right at home. Are you a small business owner?
Then you’ll definitely want my free Take Your Child to Work Day printables – it’s got a section for you to fill in about your own business, which is a perfect business plan example to discuss with your child.
You can also find two business plan examples on the Small Business Administration’s site (scroll down until you see red buttons for Rebecca’s example business plan, and Andrew’s plan).
They’re not entirely kid-friendly but can give lots of ideas for the kind of information and research to put into a business plan.
Business Plan Activity Worksheets
Check out these free PDF Shark Tank worksheets for students . Students or kids can work through coming up with their own business ideas, create an advertisement for it, and a scoring card to judge the business ideas.
You’ll find a free 30-minute Small Business Administration course for young entrepreneurs meant for teens that you can use with your students (or have your child go through).
Hint: In Objective 3, it goes over how to create a business plan.
Are you an educator? Great – you can get a free entrepreneur curriculum for Grades 1 – 12, with lots of worksheets, from the Venture Lab .
Further resources include:
- Teen Business Video Lessons
- EverFI’s Entrepreneurial Expedition
- FEE’s Course on the Entrepreneur’s Role in Creating Value
- Business Plan Note Taker (lots of great prompts to create a business plan with)
Grab 23 more entrepreneur lesson plans here.
I hope you've found some business templates for kid resources that interest you. Below, you'll find other related kid entrepreneurship articles that will help your kids, teens, and students learn about the entrepreneur's career path.
Related Kid Entrepreneurship Resources
- 27 Youth Entrepreneur Awards and Scholarships
- 5 Kid Entrepreneur Kits
- 14 Kid Entrepreneur Books
- 11 Best Business Simulation Games for Kids
- Latest Posts
Amanda L. Grossman
Latest posts by amanda l. grossman ( see all ).
- 100 Ways to Make Money as a Kid Under 13 (Besides a Lemonade Stand) - November 12, 2024
- 7 Simple Food Market Day Ideas for Kids to Sell at School - October 25, 2024
- 11 Easy Things Kids Can Make and Sell at School (Non-Food) - September 10, 2024
Home » Teens
Business Plan Templates for Teens
If you want to launch a business, you have to have a plan! Here are some templates to help you get started.

The key to any successful business is to have a plan before getting started. Mapping out the business details is instrumental in determining if this idea is worth pursuing, which can save a lot of time and resources that could be used towards a different business that would be better suited for you and your business needs and wants.
What To Include In a Business Plan
The point of a business plan is to outline your business strategy and plan your business out on paper. As your business grows and you are looking at expansion options, lenders will want a well-defined business plan to help them determine if lending to your business is the best option. When looking at business plan template packages for teens, you are looking for business plan templates that will help you transition your business ideas to full-fledged businesses that will help adults see the vision.
The 7 parts of a business plan include:
- Executive Summary
- Business Description
- Products and Services
- Market Analysis
- Strategy and Implementation of Strategy
- Organizational Structure and Management Team
- Financial Plan and Future Projections
Best Business Plan Templates for Teenagers
Bizkids’ guide to writing a business plan.
This resource helps define the business idea and determine what to charge for the products and services that you want to offer. Learn how to evaluate your competition and what they are doing with their brand to bring value to their customers to figure out ways to make your brand unique so you can stand out in the marketplace. Determine what resources you need to build your business and how much those resources will cost you. Are there ways to bootstrap the company to make startup costs cheaper? Learn about breakeven costs and how many units you have to sell before you start making a profit with your business idea.
Teen Entrepreneur Toolbox: The Small-Business Guide for Teens
This toolbox provides 8 easy to follow, actionable steps to help teens evaluate whether or not their business idea is feasible for them to start and how to go about getting started. If you don’t currently have an idea for what business to start, this provides ideas and how to get started with them! Real teens share real business experiences and advice from their own journey, which can help you avoid making common business mistakes that will decrease your learning curve and get motivation and encouragement from teens that have faced similar challenges while building their businesses. Learn about marketing techniques that work, how to provide top-notch customer service, money management of profits, and goal setting for future growth.
Home Sweet Road’s My Business Plan
This one-page business plan is free and easily downloadable. It can be printed out and hung on the wall for easy reference. The questions asked in this document are thought-provoking and help teens determine who the target audience is for their products and services. Defining the target audience will help establish a solid marketing plan that conveys the value of the product offering while making sure that the customer’s needs are being met. Customers want to buy from businesses that understand their needs and provide an ideal solution.
Proverbial Homemaker’s Family Business Plan Guide
Families can work together to build a business that kids and teens can run themselves and are passionate about running using this comprehensive business template and associated resources. Consider first why you want to start a business and why you are choosing THIS specific business. Understanding the reason for selecting that business idea builds confidence and helps maintain the passion for the company as time goes on. Create a monetary budget based on projected profits and figure out what price is best to charge for your products and services to secure sales from your target market. Set goals and manage your time, then figure out what laws are applicable for your business venture.
Learn how to conduct market research to see if there is a need for the services you want to provide before starting by conducting surveys or soft test launches. Find out where to source materials to make products and how much that will cost.
Boss Club Kid Entrepreneur Kit
This kit is literally a business in a box, so kids and teens can get started right away as soon as they have it in their hands! Choose your kit and create the following businesses:
- Homemade dog treats
- Specialty cake pops
- Luxury bath bombs
- Delicious fudge
- Handmade soaps
If you are homeschooling, this kit counts as a homeschooling resource that you can receive credit for completing, which is a fantastic additional perk of using this tool. The intended audience is kids and teens ages 11-18, and provides over 100 videos with step-by-step instructions on how to set up and grow a business from the ground up. So far, over 100 schools across the United States are using this option for their students to learn how to set up a business that they are passionate about running. Getting teens started young on their entrepreneurial journey has been found to build self-esteem and teach decision-making early on that helps young adults make solid decisions in their lives as they mature. The benefit of this specific program is that it was created by entrepreneurs for entrepreneurs and not created by scholars that don’t have practical business knowledge. There is a quiz on their website that takes 30 seconds and helps you decide what business is best for your needs.
Small Business Administration
This is a great government resource for teens who want to learn about business for free and about what resources are available from the government, such as loans and business coaching from experienced business owners in your community. There is no absolute right or wrong way to write a business plan in business, and you can choose how your business will run or how much money you need to start it. This resource allows you to walk through your business idea and plan with an experienced business owner that can talk through the pros and cons of what you feel is the next step for your business, from expansion to new investors to additional product offerings. This resource offers two different business plan templates that walk you through example business plans.
Solid Gold Biz Plan
This free business plan template from Money Prodigy discusses the author’s mistakes during her first 7 years in business and provides insights into how she would have conducted her business affairs differently if she had to start over again knowing what she knows now. The primary goal of this template is to find a problem that your business will solve. Many new entrepreneurs focus on the product or service but not on the problem it will solve in the marketplace. The goal should be to identify the problem and then develop the solution that will be offered as a product or service by your company. After determining the primary problem, she focuses on how to best deliver the solution and how much it will cost to maintain the delivery of the product or service.
Shark Tank Lessons in Business and Entrepreneurship from Scholastic
A free lesson plan with a teacher’s guide that can be used in a group setting or as a family! Topics covered include entrepreneurship basics, writing an effective business plan, crafting persuasive pitches for investment presentations, and how to find a great business mentor. The target age group is grades 6 to 12.
Shark Tank Marketing Plan
A worksheet template that focuses on the target demographic for your business and the motivation that that demographic would have to buy a product or service that you are offering so you can establish the best way to market to them. Games are encouraged with this marketing package because this helps draw out ideas in fun ways that promote creativity and growth. Business is about finding creative solutions to problems and pivoting the company into new arenas when it becomes necessary for growth. Keeping an active marketing plan up to date as the business grows is key to expanding when necessary or finding innovative ways to keep customers engaged with your brand.
Shark Tank Analysis Worksheet
Use this worksheet when evaluating businesses to learn what investors are looking for when assessing whether or not to invest in a business. Understanding what investors are looking for in a management team, mission, vision, product/service, research and development, and strategic implementation will help you create that within your own business to make your foundation strong.
A strong business plan that is well defined will take even the novice entrepreneur to the expert level of business in no time with the proper preparation. Using a business plan template in areas of planning, marketing, product development, and strategy will assist in building a business that can be bootstrapped and stood up quickly to test the business out in ways that require little startup capital.
Related Reading
- Entrepreneurship for teens
- Teen entrepreneurs’ guide to money management
- How to earn money for teens

- Are you currently busy with school or is it summertime? Think about when the work for your business will be done. [1] X Research source
- Consider business ideas that are seasonal. For example, if it’s near Christmas, consider ideas that cater to that, like a gift wrapping service or making gift baskets.
- Are you in the middle of a very hot summer? This might be a perfect time to launch a neighborhood lemonade stand.

- Examples of product-driven businesses: baking cookies, building birdhouses, making gift baskets, creating greeting cards, selling candy, making doggie treats.
- Examples of service-driven businesses: lawn care, car washing, computer repair, pet sitting, babysitting, cleaning houses, dog walking, and teaching computer skills to older people. [3] X Research source

- Are you an animal lover? Consider offering pet sitting services.
- Maybe you’re crafty and enjoy making handmade jewelry or gift baskets. These are great products to sell. [4] X Research source

- Make sure your business name is easy to pronounce, as well.
- Clever and unique business names work well, just remember that the name needs to relate to what your business entails.

- List any specific objectives and goals for your business, as well.
- Write out what you think makes your product/service unique. [6] X Research source
Planning Your Business

- If you have a sibling that wants to help out, that would be a good place to start.
- You will be splitting your profits, so you will need to decide how much and when your employees will be paid.

- You could also ask your parents if they’d consider donating some of your future allowance as seed money for your business.
- If you bring them a solid business plan, they will be more likely to help you.

- By adding up your ongoing expenses, you will have a pretty good idea of what it will cost to keep your business running. [8] X Research source
- Another example – if you’re making cookies to sell, you will need to total up how much the ingredients cost and how often you’ll need to buy them.

- Let’s say that when you add up the cost of the ingredients, it costs you $3.50 to make a dozen chocolate chip cookies. You will want to charge more than that for each dozen in order to make a profit.
- You should also factor in how much time it takes you to make your product/perform your service. [9] X Research source You can then work out prices based upon how much you want to make. You should also factor in time that you aren't being paid (such as advertising your business or walking to a customer's home).
- For example, if it takes you a half hour to make the chocolate chip cookies mentioned above and another half hour to sell them, you will need to charge an amount that represents the amount of time you spent preparing them. This additional time is your "wage" for preparing them.
- You can work out your hourly wage by dividing your pay for a project or product (minus your expenses) by the amount of time spent working.
- In this case, if you charged $9.50 for the dozen cookies, you would be making $6 for the hour that you spent making and selling them.
- Subtract your expenses from your revenue to get your profit amount. [10] X Research source
Marketing Your Business

- You should also consider your market area. Unless you have a car (or your parents' help), market area is relatively small. This may include only areas that you can safely walk or bike to.
- These customer types are called customer profiles. Once you have your customer profiles, you will have a better idea of how to market your business to them.
- Different customer profiles sometimes require entirely different marketing strategies.

- You can market most effectively once you know these specific details about your competitors.
- Offering lower prices or providing higher quality products/services are two ways you can compete with them.
- For example, if you start a lawn care business, you will be competing with established lawn care businesses. You can build a customer base by offering better service and encouraging customer recommendations.

- Remember to keep your customer profiles in mind when choosing your marketing strategies.
- For instance, if you’re starting a pet sitting business, you could post flyers at veterinary offices and pet stores, and also hand deliver flyers to people in your neighborhood with pets.

Putting Your Business Plan on Paper

- Write the business name in large letters, or use a large font, and make it bold. It’s the most important thing on the page.
- The description paragraph can be in a normal size or standard 12 point font.

- Owner/Management example: “Kelly’s Doggy Daycare is owned by Kelly Klein. She has several years of experience pet-sitting and truly loves working with and caring for dogs of all kinds.”
- Business History example: "Kelly noticed that most of her neighbors were dog owners who worked long hours every day. Occasionally, they took vacations and/or experienced family emergencies, which could take them away from their pets for days at a time."
- "With her love for dogs, Kelly knew she could provide a pet care service that her neighbors would benefit from, and that’s how Kelly’s Doggy Daycare was born."

- You don’t need to get incredibly detailed – summarize and highlight the most important information for each.
- Example for product/service: "Kelly’s Doggy Daycare will provide hands-on pet care for today’s busy pet owner. The business will offer day rates along with in-house extended stay pet sitting. Walking services are included at no charge with every appointment."

- "It’s her mission to put your mind at ease when you have to be away from your pets. Kelly will make sure your pets are loved and cared for in your absence."
- "An email summary of every pet sitting appointment will always be sent to you via email during your absence or upon your return."

- Example: “Kelly’s Doggy Daycare caters to today’s busy adults. These are business people who work long hours every day and/or travel regularly for work, family vacationers, and anyone who finds themselves in need of last minute pet care."
- "The business has one competitor, Sam’s Sitting Service, but Kelly offers lower pricing and in-house extended stay care."
- "She plans to post flyers about the new business in her neighborhood to promote it. She will also be going door-to-door to introduce herself and inform neighbors of her services.”

- Example: "Kelly will need very few supplies to launch the business – a bag of doggie treats, 1 dog leash for a small dog and 1 dog leash for a large dog."
- "Ongoing expenses will be the replenishment of doggie treats and occasionally dog toys and/or dog blankets. The rate is $5.00 for each hour of pet care provided. The rate for in-house extended care is $25 per day."
- "Customers will need to provide their own pet food or reimburse Kelly for any food she has to purchase during pet care. Profit for each hour is approximately $3.50 after expenses."
- "Profit for each day of extended care is approximately $18.50 after expenses."
Expert Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://www.wisebread.com/create-a-business-plan-by-answering-4-simple-questions
- ↑ http://www.mikemichalowicz.com/the-37-greatest-business-ideas-for-young-entrepreneurs/
- ↑ http://www.teachingkidsbusiness.com/business-plan-example.htm
- ↑ http://content.moneyinstructor.com/664/kids-starting-business.html
About This Article

To make a business plan for kids, create a cover sheet with the business name in large, bold font and a 5-6 sentence description of the business. Have a logo? Include that, too! Start writing up the company’s management and history on the second page, talking about yourself in 1-2 sentences and how and why you came up with your business in another 2-3 sentences. Then craft 3-4 sentences, each, to describe your product or service, business goals, marketing strategy, and funding needs. To learn more from our Entrepreneur co-author, like how much to charge for your product or service, keep reading the article! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Feb 24, 2023
Did this article help you?
Molly-Claire Keely
Jan 14, 2021
Feb 11, 2018
Margret James
Feb 11, 2017
Valentina Tocasuche
Nov 24, 2018

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
- High School
- You don't have any recent items yet.
- You don't have any courses yet.
- You don't have any books yet.
- You don't have any Studylists yet.
- Information
2021 Business Studies Grade 11 Notes Chapter 16
Life sciences (lsc 431), jeppe college, students also viewed.
- Summarizing and Note taking
- Gr 9 Taalboek Nov
- Geography Gr11 Study Guide
- Case study - school
- Edexcel Igcse physics. Revision guide ( PDFDrive )
- Physics igcse 2012 exam revision notes ( PDFDrive )
Related documents
- 301 2022 4 b - law
- STDA Individual assignment
- Nov P1 2019-Memo - Memo for previous question
- NOV 2016 P1 MEMO - Life sciences questions paper
- Nutrition Notes 2020 - Summary The Department of Education
- Life Sciences P2 May-June 2016 Eng
Related Studylists
Preview text, business studies, starting a business venture on an action plan, table of contents, topics pages.
Exam guidelines for starting a business venture on an action plan
Terms and definitions 2 Aspects that must be considered when initiating a business.
Factors that must be considered before start- up
Reasons why businesses need funding 5 Sources of funding 5- Factors that influence the choice of funding 6-
This chapter consists of 7 pages
Content details for teaching, learning and assessment purposes.
Learners must be able to: Outline/Mention/Explain/Discuss aspects that must be considered when initiating a business e.: o Strategy o Operations o Productivity o Size of a business etc. Outline/Mention/Explain/Discuss factors that must be considered before start-up e.: o Culture of the organisation o Environmental changes o customer services o Business growth o Cost saving etc. Analyse the above-mentioned factors from scenarios/case studies and make recommendations for improvement. Explain/Discuss reasons why businesses need funding. Outline/Mention/Explain sources of funding. Explain/Discuss/Describe factors that influence the choice of funding e. nature of finance, amount of capital needed, risk, cost of finance etc.
TERMS AND DEFINITIONS
Terms definitions.
Strategy Plans created by the entrepreneur that is spelt out in the business plan and enforced in the action plan Collateral The asset that is pledged to the bank in case of a default in the repayment of a loan. Interest Money paid as a percentage for the use of borrowed money.
Mortgaged bond A debt instrument issued for a period of more than one year with the purpose of raising capital from borrowing.
Incentives Cash or tax relief to encourage investment in economic sectors It could also be a payment to workers to encourage productivity.
Venture capitalists Financing is given for an ownership share in the business at its start-up.
Equity Capital The total amount of money and assets invested in a business by the owner that comes from own sources. Grants Money given by government or an NGO for a specific purpose e funding small businesses. Bank overdraft A customer withdraws more than the money that is available in the bank account. Trade credit Time, usually between one and three months which a business has before it has to settle the debt.
Angel funding These are wealthy business people who want to invest in promising small business in return for a profit share in the business. Micro lenders Businesses that offer small loans to people at high interest rates without collateral.
1 Market research Businesses should conduct ongoing market research to identify profitable markets for their product. Many businesses benefit from conducting market research in local/familiar markets.
1 Business cycles Businesses obtain profit and experience losses. Changes in market & macro environment can either have a positive or negative impact on business operations. Businesses should constantly make adjustments to reduce costs where possible. Reducing cost increases profitability.
2 Factors that must be considered before start-up
2 Culture of the organisation
Establish an organisational culture so that the staff is familiar with what is acceptable. Ensure that a code of conduct is in place and enforce it from the start The staff must know the dress code and the code of conduct of the business from the start. Provided ongoing training to ensure that the staff remain skilled and able.
2 Environmental changes
Continue to network and research to avoid changes in the business environment which may upset the business operations. Consider the risk and success factors Plan for risks and minimise the impact
2 Customer service Make an effort to satisfy the needs of customers. Change the action plan accordingly to accommodate the needs of customers Establish a good relationship with customers.
2 Business Growth
Managed and backed up growth by using a solid strategy. The success of a business is often dependent on its management and staff. Devise a suitable strategy to manage and control a larger group of employees. Keep control of the quality of each employee.
2 Cost saving
Cut cost by controlling unnecessary expenditures
2 Risk and change Management and leadership teams must be flexible to adapt to changes in the market. The original action plan may need to be changed and amended several times. The introduction of new technology may influence a budget.
2 Other factors that must be considered before starting a business. Planning and minimising the environmental impact on the business. Action plan to satisfy the needs of customers. The sources of raw materials/suppliers. The sources of funding that the business would use. The forms of ownership that will be used by the business. The registration of the business. The location/business premises to be used.
3 Acquiring funding
3 Reasons why businesses need funding. Businesses require funding to: Cover the start-up costs including g premises/machinery/raw materials etc. Run the business and have enough money to pay employees/suppliers of raw material etc. Pay for cost of input such as wages, telephone other expenses Expand the business as the orders/sales increase and bigger premises need to be established.
3 Sources of funding
3.2 Equity Capital Equity capital is the total amount of money and assets invested in a business by the owner that comes from own sources Capital that is contributed by the owner is referred to as the owner’s interest. Owner’s equity increases when the owner puts in additional funds to expand the business. The benefits of putting own capital into the business is that it encourages a commitment from the owner.
3.2 Issuing of shares New companies can issue shares to obtain capital. Shareholders receive a share certificate as proof of ownership The Memorandum of Incorporation and prospectus list the details of the shares that are offered for sale Ordinary shares are the most type of share offered by companies to shareholders All shareholders receive a portion of the profits called a dividend.
3.2 Debt Capital Many businesses need to borrow funds. The business plan will indicate how much a debt capital is crucial for business funding. The following sources of finance are available to the entrepreneur:
Bank loan o The business can borrow money from the bank. o The amount will be specified for a set period. o Interest is payable on the loan. o The period can be fixed for the time of the loan or variable in line with the current interest rate.
4 Cost of finance Businesses will generally choose the funding with lower costs/interest The income earned on borrowed capital must exceed its cost otherwise it will be to the disadvantages of the holders of own capital. Borrowed capital may be cheaper because the holders of own capital require a higher income owing to the higher risk
4 Period of financing If needed for a long period might rather use own capital because borrowed would be too expensive over a long period.
4 Availability If more own capital is not available, the business might be forced to use borrowed or other way around.
4 Tax considerations
Interest on borrowed capital is tax deductible. Dividends on own capital are not deductible.
- Multiple Choice
Course : Life Sciences (LSC 431)
University : jeppe college.

- 122 Edexcel Igcse physics. Revision guide ( PDFDrive ) 100% (1)
- 34 Physics igcse 2012 exam revision notes ( PDFDrive ) Life Sciences None
- Discover more from: Life Sciences LSC 431 Jeppe College 26 Documents Go to course
- 122 Edexcel Igcse physics. Revision guide ( PDFDrive ) Life Sciences 100% (1)
- More from: Life Sciences LSC 431 Jeppe College 26 Documents Go to course
- More from: Business p2 by Maxine Fischer 11 11 documents Go to Studylist
Business Plan Examples for Students
Ajay Jagtap
- December 29, 2023
- 26 Min Read

Do you know what’s the most common mistake students and rookie entrepreneurs make while preparing their first business plan?
Of course, it’s the first business plan we’re talking about; there’ll definitely be a few. However, overcomplicating things and failing to consider a business plan example still remain the most common one.
That’s why we decided to come up with a solution. We’ve curated this list of top business plan examples for students to help you get going.
So whether you need a business plan for a college project, start a side hustle, or win a business competition, these examples are just what you need to create business plans that stand out.
Ready to dive in? Let’s start by understanding the key elements of a business plan example:
Key Elements of a Business Plan Example
Business planning is not as complicated of a process as people think it is; they’re just overcomplicating things. (Don’t think so?)
Let’s simplify the key elements that make up a comprehensive business plan; you’ll understand it better that way.
- Executive Summary: A high-level overview or summary of your plan.
- Company Overview: A detailed description of your business idea, its fundamental elements, history, and future goals.
- Market Analysis: A study of your external business environment that includes details about your industry, competitors, and target market.
- Products and Services: Description of the products or services you intend to exchange for money.
- Sales and Marketing Strategies: A section outlining sales and marketing strategies your business will implement to achieve its financial goals.
- Operations Plan: A section outlining the business processes and daily activities involved in ensuring seamless business operations.
- Management Team: Introduction to your founders, key management, and their compensation plan.
- Financial Plan: Your financial plan is a detailed breakdown of your business’s financial projections and financing needs.
That’s pretty much it about the key elements of a business plan example. Next, let’s explore the best business plan examples for students.
Say goodbye to boring templates
Build your business plan faster and easier with AI assistant
Get 30% off for Students and educators

Top Business Plan Examples for Students
Now that you already know about the components of a business plan template, let’s review some of the best business plan examples for students.
1. Startup Business Plan Example
Upmetrics’ startup business plan example is the ideal solution for students planning to start up or participate in a business plan competition. This business plan template follows the SBA-approved business planning format used by thousands of successful entrepreneurs.
Whether your startup is about a new-age AI-based application, an online shopping site, or traditional IT consulting—this sample business plan is just what you need.
Unlike any traditional small business plan, this example of a startup business plan is lean and agile in approach, focuses on innovation, and emphasizes market validation.
2. Lean Business Plan Example
Since you’re transitioning from a student to an entrepreneur, you may not have enough time to spend on creating a detailed business plan. That’s where this lean business plan template can help.
It’s a condensed version of a traditional plan summarizing all its sections with a primary focus on covering only the critical aspects of the business.
This template is best for startups or businesses uncertain about business planning and student-turned-entrepreneurs with limited time and resources to prepare a business plan.
3. SBA Business Plan Example
Following an SBA-recommended business plan format is key to securing bank loans and business grants. Since it can be time-consuming to find a template that follows a similar outline as the SBA, this SBA-approved business plan example is the way to get started.
This SBA business plan template has nine primary sections, that include executive summary, company description, market analysis, organization, product description, marketing, funding request, and financial projections.
SBA business plan examples ensure you stay on track and don’t deviate from your funding needs.
4. One-Page Business Plan Example
As you may have already guessed, a one-page business plan is a one-page version of a traditional business plan. Since it’s a condensed version of a business plan, drafting it can be quite easy and quick compared to a lean or traditional plan.
Employees, partners, and vendors often use one-page business plans as a quick overview of your company and banks and investors as a summary of your operations.
While it may not be the ideal choice for entrepreneurs seeking investment or bank loans, students with side hustles and idea-stage startups can consider this option.

5. HBS Sample Business Plan
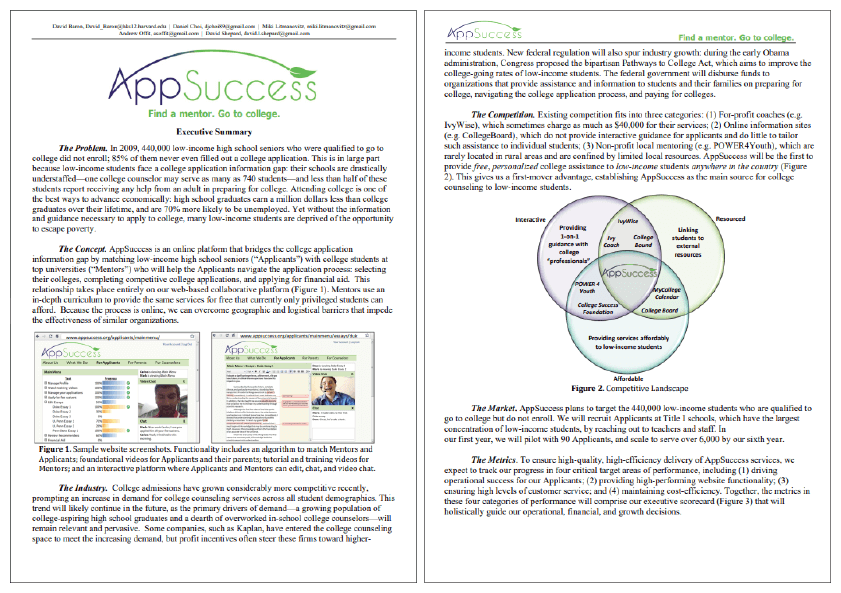
Harvard Business School’s new venture competition selected this sample business plan as a finalist in 2011.
This is a business plan of App Success, a collaborative web-based platform that connects low-income high school seniors with college students from top universities; this business will enable them to collaborate on college selection, college applications, and financial aid applications.
This example can be a great reference for those planning to start a mobile or web-based solution.
6. Kean University Sample Business Plan
Kean University organizes a business plan competition every year for its students where students prepare and present business plans to compete, and this is one of the sample business plans the University provides to participants to understand the format.
It’s a business plan of Blue Water Boatworks, Inc., a boat detailing and cleaning company specializing in servicing recreational fiberglass and aluminum watercraft.
This example can be a great reference for those planning to start a business related to housekeeping, cleaning, or maintenance.

7. UVM Sample Business Plan
If you are looking for a strategic business plan for a food business, the University of Vermont’s Fancy Foods Business Plan can be a guiding resource for you.
Despite the fact that it can be a good reference for detailed planning, it was written in 1998, so any statistics and numbers may not seem relevant to today’s market landscape. Make sure you keep that in mind.
You may closely follow this example as a reference if planning to start a food truck, restaurant, or any other business that serves food.
That was the list of best sample business plans for students. However, there’s more to talk about. You now have a business plan example, but what about pitching to investors? Let’s explore free pitch deck examples for students.
Free Pitch Deck Example for Students
Pitching to investors as a first-time founder can be exciting but also overwhelming at times. Worry not; we’ve got a solution—investor pitch templates. We’ve prepared a set of 8 investor pitch templates and examples for students and entrepreneurs to help create winning business pitches.
Whether you need a pitch to find an opportunity, ask for subject matter knowledge, or a problem-solving pitch, these investor pitch examples have got you covered. Download now.
How to write a winning plan for a business plan competition?
Creating a business plan is no different than creating one for a real business. Similar to how entrepreneurs prepare and present business plans to investors, Students in business plan competitions pitch to judges.
In short, the business planning process remains exactly the same. Let’s discuss how you can write a winning plan to help you win a business plan competition.
- Select a compelling business idea : everything starts with a compelling idea. Make sure you have a viable business idea to compete in the competition.
- Refer to winning business plan examples : Once you are sure about your business concept, refer to business plan examples from previous winners and how they planned the sections of their plan.
- Market Research & Industry Analysis : After referring to business plan examples, conduct industry research and market analysis to make your statistical and financial numbers accurate and realistic.
- Understand business model and revenue streams : Since you are preparing a business plan for a company that doesn’t exist, be sure about the business model and how the business will generate profit.
- Use AI business plan generator : Using an AI business plan generator like Upmetrics can be incredibly helpful in speeding up the business planning process. With industry-specific business plan templates and AI assistance to write your plan, you can write the first draft of your plan in literally no time.
- Presentation and visuals : Prepare visuals and graphs to make your business plan visually appealing and numbers digestible. You may not need to prepare these visuals if you use business plan software manually.
- Proofread and edit : Grammatical errors are the last thing judges want to see in a business plan. Make sure you proofread and edit your draft thoroughly before submitting it.
Easy as that, that’s the way to write a perfect business plan that can lead you to victory in any business plan competition on planet Earth. Let’s look at an example of a real-life business and financial plan.

Business and Financial Plan Example for Students
Having learned about business planning for students, let’s quickly discuss a coffee shop sample business plan and financial statements prepared using Upmetrics.
1. Executive Summary
The Cooper’s Cup will be a new cafe in Phoenix, Arizona. The 1,500 square foot café will be located in the newly constructed Market Square Plaza on the northeast corner of 135th Street and Mission Street. The anchor tenant, the Price Chopper grocery store, has already taken occupancy, and the excellent location brings more than 10,000 shoppers weekly.
The Cooper’s Cup, aptly named for the aromatic brown liquid that will fill the cup, fills the void of original cafes in the market and stands out from its corporate peers with its fast food concepts and prompt services. The Cooper’s Cup is the alternative to fast food/commercial/coffee shops and offers a much calmer, civilized gourmet coffee experience.
There are no televisions in the cafe, the background music is subtle, and work from local artists will hang on the walls. The restaurant is well-appointed, with overstuffed leather chairs and sofas in a library-like setting. The cafe is reminiscent of times gone by – yet is cutting edge technologically with WIFI and state-of-the-art espresso machines.
The Cooper’s Cup measures its financial success in terms of increased market share and earnings. This is a tremendous opportunity with a total local market of $54 million! The keys to success will be offering quality gourmet coffees, taking advantage of its small size, and relying on an outstanding barista staff.
To achieve these goals, the cafe will present some of the area’s finest gourmet beans from local distributors. Because of its small size, the restaurant can enjoy larger margins through lower overhead. The cafe will hand-select baristas and offer salaries comparable to the chains. The baristas will be trained to cross-sell and sell higher-margin products.
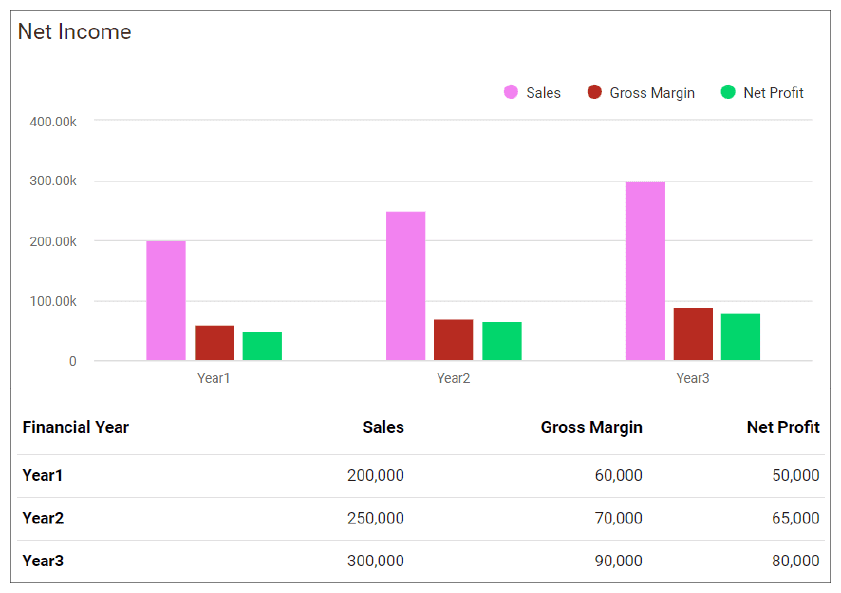
The primary objectives of the business plan for Cooper’s Cup are below:
- To increase revenues by $36,000 or 5% in Year 2 and $73,000 or 10% by Year 3
- Achieve a profit margin of 5.2% in Year 2 and 6.90% by Year 3
- Be the Cafe of Choice in the Phoenix area and the recipient of the Best Coffeehouse Award.
Guiding Principles
The Cooper’s Cup is committed to values such as excellence, passion, quality, integrity, and leadership, allowing them to navigate challenges and provide for future opportunities. These core beliefs start with their commitment to their products and their employees. Cooper’s Cup rewards excellence and cherishes loyalty. The cafe will work with its employees to build strong businesses and a secure future.
Mission statement
The Cooper’s Cup is committed to its products and employees, which they believe is the recipe for market success.
Key to success
The Cooper’s Cup stands out from the competition. Below are their Keys to Success:
- Great Products : providing exemplary products at market prices – will make customers want to return again and again.
- Hire Quality Baristas : Pay employees rates similar to the larger chains with opportunities for long-term careers and opportunities for advancement with long-term plans to open a second facility.
- Convert Customers to Connoisseurs : Only 40% of the nation’s coffee drinkers consume premium ground and whole bean coffee – this will aid in the continued growth.
Financial Summary
2. Business Overview
The Cooper’s Cup will be a coffee house/cafe located in Phoenix, Arizona. The cozy cafe will be located in the newly completed Market Square Plaza in the Arizona City area. The cafe will serve gourmet coffee, espresso, drip coffee, lattes, and smoothies. The simple pastry offerings may vary with seasonality, but the primary line will be muffins, bread, cookies, scones, and rolls. All pastries will be supplied daily by a local bakery.
The cafe will be owned and operated by Owen Jones, a veteran restaurateur with several years of experience running and managing chain restaurants. The cafe will be open for business Monday – Thursday 7-10, Fridays and Saturdays, 7-11, and closed Sundays.
The Cooper’s Cup will be formed as an S-Corporation owned by Mr. Doe.
Start-Up Summary
The Cooper’s Cup will have seating for 40 patrons. The rent is $2,075 a month, with a three-five-year lease available. The site comprises 1500 square feet of leased space consisting of a dining room, a coffee bar, two restrooms, and a storage room in the back.
This storefront needs to be plumbed and wired appropriately to be used as a restaurant. Painting, new floors, and countertops are also needed. A custom coffee bar needs to be built. With materials bought on sale and volunteer labor, the cost to renovate will be $71,725.
The coffeehouse equipment will consist of two commercial espresso machines, air pots and urns, a commercial blender, a commercial brewer, top-loading coffee bins, barista syrups, cold drink dispenser, frothing equipment, a commercial refrigerator, microwave, and stainless steel prep bar.
The cost of the equipment is $38,275. The furniture will consist of leather couches and chairs (purchased at auction), coffee tables, bookcases, and window treatments. The artwork will come from local artists and be sold on a consignment basis. The books were secured via donations. The total cost to furnish is $14,000. Other startup expenses will be dishes, furniture, rent deposit, and marketing.
Location and Facilities

The new coffeehouse is located in the highly desirable Phoenix, Arizona, area at the northeastern intersection of 135th Street and Mission Street in the Newmarket Square Plaza. The property is situated in an excellent location, with an easy 6-minute drive time to I-435 and 69 Highway.
The property is 95% leased with Price Chopper as the Anchor Tenant. Other tenants include LifeSpring Med Spa, Jane’s Canines (Pet Store & Boarding), Pride Cleaners Kahn Dental, and Swim U.
Price Chopper brings more than 10,000 shoppers per week to the center. The location comprises a population of 9,420 within a one-mile radius, 61,102 within a 2-mile radius, and 149,550 within a 5-mile radius – with a median household income of $120,856. Sprint / Nextel’s corporate office is within 2 miles of the site.
3. Market Analysis
Phoenix, Arizona, is an award-winning place to live and work and is considered the leading business community in the Midwest. National publications and organizations recognize Phoenix for its business environment and livability. Here’s a sampling: 6th Place, America’s Best Places to Live Money, Top 50 Cities to Live and Play, National Geographic Adventure, 3rd Hottest Town in the U.S., Money, Among 20 Best Places to Live & Work Employment Review, One of only 72 Sterling Tree Cities in the U.S., National Arbor Day Foundation, Top 10 best Locations to Raise a Family, Southern Business and Development, 1st Place, Kid Friendly Report Card, Population Connection, 2nd Best City in America to Live Business Development Outlook.
Phoenix is at the core of one of the most dynamic local markets in the U.S. It offers easy access to the Arizona City region’s amenities, and, as part of the Arizona City metropolitan area, it is within the most centrally located major market in the nation. I-35, I-435, I-635, and U.S. Highway 69 all pass through Phoenix, and no point in the city is more than 3.5 miles from a freeway. The city maintains an excellent arterial street network and plans to construct additional lane-miles as the area grows. Three airports serve the region. Arizona City International Airport (MCI) is just 25 interstate highway miles north of Phoenix. Johnson County Executive Airport—the second busiest in Arizona—provides complete services for private business jets and general aviation. New Century AirCenter, just 12 miles southwest of the city, offers available aviation services and accommodates cargo or passenger jets of any size.
Phoenix supplies some of the most highly educated workers in the nation, with 97% of Phoenix adults over age 25 holding at least a high school diploma. Johnson County, where Phoenix is located, ranks first among the country’s 231 counties with populations greater than 250,000. The county ranks sixth in the percentage of adults with at least a bachelor’s degree and 16th with a graduate or professional degree.
The Phoenix area has a population of 175,265, based on the 2010 census. The median household income is $77,881, and the median age is 37.9. (2010 U.S. Census)
Industry Analysis
The U.S. coffee shop industry includes about 20,000 stores with a combined annual revenue of about $10 billion. Major companies include Caribou Coffee, International Coffee & Tea (The Coffee Bean & Tea Leaf), Peet’s Coffee, and Starbucks. The industry is concentrated: the top 50 companies generate more than 70 percent of sales. Coffee shops are part of the specialty eatery industry, including retail outlets specializing in bagels, donuts, frozen yogurt, and ice cream products. (First Research)
Competitive Landscape
Consumer taste and personal income drive demand. The profitability of individual companies depends on the ability to secure prime locations, drive store traffic, and deliver high-quality products. Large companies have advantages in purchasing, finance, and marketing. Small companies can compete effectively by offering specialized products, serving a local market, or providing superior customer service. Specialty eateries, which include coffee shops, are labor-intensive: average annual revenue per worker is about $50,000. Coffee shops compete with convenience stores, gas stations, quick service, fast food restaurants, gourmet food shops, and donut shops. (First Research)
Market Size
The U.S. coffee shop industry includes about 20,000 stores with a combined annual revenue of about $10 billion. Major companies include Caribou Coffee, International Coffee & Tea (The Coffee Bean & Tea Leaf), Pet’s Coffee, and Starbucks. The industry is concentrated: the top 50 companies generate more than 70 percent of sales. (First Research)
Target Market and Segment Strategy
Most adult coffee drinkers said their lifelong habits began during their teenage years. 54% said they began drinking coffee between 13 and 19. Another 22% reported their coffee cravings started between 20 and 24. This means that 76% of adult coffee drinkers began drinking coffee by the time they were 24. So, despite a large amount of marketing and advertising directed at the younger age groups, savvy coffee shop owners will remember to cater some of their offerings to the adult and senior market. (National Coffee Drinking Study).
The Cooper’s Cup will offer a unique experience for coffee enthusiasts by providing a quiet, cozy, yet sophisticated cafe and a sense of refinement and peace in an otherwise hectic and fast-paced world. While other coffee shops cater to convenience with drive-throughs or loud music venues late into the night, the Cooper’s Cup will stand apart from its competitors with its quiet yet soothing ambiance, capturing a truly unique (and much-needed) market niche.
- Unique products (specialized roasts, local ingredients, locally-themed or named drinks, custom drinks by the star barista, etc.)
- Games, puzzles, mind benders, and other activities that encourage customers to linger over their coffee
- Hosting or sponsoring local events (entertainment, readings, book clubs, etc.)
- Using technology to creatively compete in marketing with big chains — services like FourSquare, Yelp, and Google Places can increase visibility in the local market.
- Delivering amazing service from knowledgeable baristas — spend lots of time training staff and utilizing online services like the American Coffee & Barista School.
- Selling coffee-related items (and tracking down any co-marketing opportunities with a local community college or another student-related group in the area)
4. Products and Services
Product/services descriptions.
The Cooper’s Cup’s primary offering is gourmet roasted coffees with mocha, carmelicious, white mocha, candy bar latte, and brewed coffee. Complementing the coffee will be a smoothie line including wild berry, strawberry, peach, mango, and lemonade. Rounding out the simple menu line will be pastries obtained from an outside supplier, freshly made and delivered daily. The pastry offerings may vary with seasonality, but the primary line will be muffins, bread, cookies, scones, and rolls.

Product/Service Sourcing
The Cooper’s Cup has negotiated supplier agreements with several local food-service wholesalers and coffee wholesalers in the Phoenix area that have a reputation for quality and reliability:
- Mean Beans Coffee Roasters
- Phoenix Brewers
- Healthy Harvest Bread Co.
- Mary’s Organics
If one of the abovementioned specialty suppliers cannot meet their needs, the following national suppliers can provide all the food-service products they require. In addition, the following wholesalers will supply the cafe with general restaurant supplies:
- Lawrence Food Products Corp.
- Gerry Food Supply Inc.
Future Products/Services
Young families, which comprise Phoenix’s third largest market share, are often overlooked in the coffee market. Coffeehouses traditionally have not been considered ‘kid’ friendly. To overcome this hurdle, Cooper’s Cup has long-term plans (5 years) to open a 2nd coffee shop: A combination indoor play area/coffee bar. This concept allows parents and caregivers to meet and relax with other adults while the children can enjoy the indoor playground amenities.
Additional future services will include in-store sales for home purchases and an online store.
The website will have the option to purchase a prepaid gift card program – Prepaid gift cards provide immediate cash, reduce credit card transaction charges, and draw new customers to the business.
5. Sales and Marketing Strategies
Swot analysis.
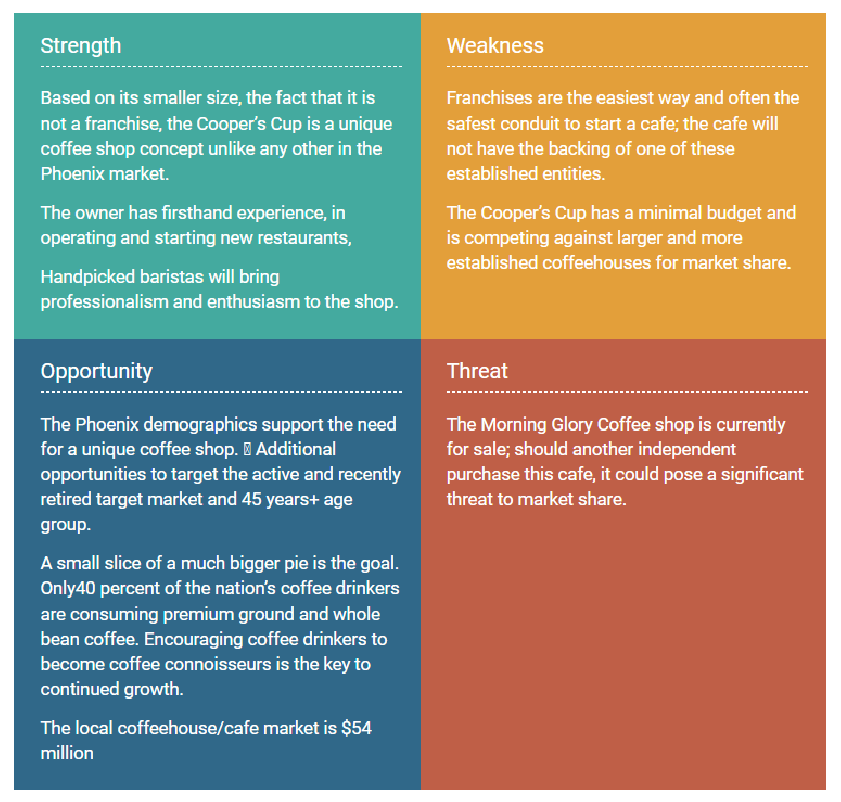
Unique Selling Proposition
The Cooper’s Cup stands out from a crowded sea of coffee chains and franchises. What sets it apart from the competition is primarily its smaller, cozier size combined with premium coffees served by knowledgeable baristas, providing so much energy and enthusiasm for its products.
Market Strategy and Positioning
The Cooper’s Cup utilizes a focus strategy on its Market. By specifically targeting three primary segments, they can cater specifically to their needs.
Senior Market (age 45+)
The Cooper’s Cup will target this Market simply by its well-selected location. Although this demographic group could readily drive downtown, they prefer a local cafe to unwind and relax and historically become some of the most loyal patrons.
Newly Hired Employees
The cafe will attract regular customers (weekly or more) – particularly the newly employed (first job) by providing free WIFI services and providing interesting games in the customer area.
Young Families
The third targeted Market, younger families, often find that coffeehouse is not ‘kid’ friendly. The company has long-term plans to create a combination coffee shop/play area so that parents and caregivers can meet with other adults while the children can enjoy the bounce houses, slides, and indoor playground equipment.
Pricing Strategy
The Cooper’s Cup primarily utilizes competition-based pricing. The cafe does not utilize coupons and discounts (other than opening promotions) because they believe that the most valuable customer demographic of daily coffee consumers is not influenced by discount programs or coupons.
Promotion and Advertising Strategy
- Online Advertising – The Cooper’s Cup will advertise regularly on popular social media sites like Facebook. Compared to traditional print advertising, this is a cost-effective tactic that will allow them to reach prospects in a highly targeted way (e.g., based on criteria such as age, gender, geography, etc.).
- Website – Cooper’s Cup will develop a simple Web site, which will provide basic information about the business, the menu, and links to their presence on the aforementioned social media channels.
- Radio Advertising – During the first six months of operation and the busy holiday shopping season, the business will advertise on local radio stations.
Sales Strategy
The Cooper’s Cup will use the following methods to increase sales revenue (as recommended by Andrew Hetzel on Better Coffee, Better Business):
- The menu will focus on the most profitable products sold. The cafe will always draw customer attention to the best products.
- As warranted, the cafe will raise prices to bolster its brand image. Prices communicate the perceived value of a product, so if set too low, the customers might assume that the beverages are inferior compared to the competition.
- Monitor flavoring inventory – Excess flavoring inventory ties up capital and valuable backroom space for storage. The cafe will utilize 4-6 varieties, including sugar-free offerings.
- Control waste and theft – audit sales and inventory reports to evaluate ingredient waste due to inefficient preparation, returned drinks, and employee consumption. Retail locations can easily waste 20% or more of their daily sales in these three key categories, which is a substantial and unnecessary loss.
- Monitor and evaluate hours of operation.
- Run employee sales contests – The baristas are the salespeople and have great influence over the customer ordering process. All baristas will have some form of sales and customer service training to make each transaction active rather than passive. Sales contests will emphasize high-margin items or cross-selling.
6. Operations Plan
Staffing and training.
An ongoing training and education program will ensure that each staff member learns and implements Cooper’s Cup’s exacting service and operational procedures standards. Staff meetings will reinforce service standards and principles. The Cafe will have detailed work descriptions and training programs for each position, from entry-level employees to the ongoing development of managers and owners. New employees will undergo an extensive training program. This ensures that each guest receives a quality experience from all employees, regardless of how long they have been employed. The Cafe embraces the concept of promoting from within. Excellence in one function typically leads to excellence in another. Regular staff evaluations and training will ensure motivation and address critical issues.
Inventory controls
The founder will be responsible for hiring and training managers who, in turn, will ensure that the day-to-day operations will comply with the standards set by Restaurant policy. Weekly management meetings will provide a forum to review and discuss financial and operational performance. Critical decisions related to purchasing, human resources, marketing, capital expenditures, and customer service will also be addressed.
Purchasing cost controls
Food preparation personnel will follow standardized recipes developed by the founders to control food costs and ensure consistency. The coffee shop will offer an innovative menu with nutritious food and beverages while achieving the most significant margin yield.
Customer Service
The hospitality business recognizes the client’s support experience is the critical driver to replicate business. The direction will Offer a superior degree of Professionalism by hiring individuals who deliver the ideal attitude to work and teaching them the skills required to accommodate guests. The restaurant will keep high levels of consumer satisfaction with talented, educated, and well-trained workers who understand and implement the fundamentals of fantastic service. Ongoing training will be provided to enable staff to perform their jobs with confidence and ability. Employees are well-spoken, well-versed, and trained to provide friendly, prompt, and professional service to each customer. This practice teaches employees who, by producing an exceptional customer experience, can optimize sales and raise their reimbursement. The team will have the knowledge and service required to create excellent daily service for every customer.
Technology & Software
While the quality of the cuisine and dining experience contributes significantly to a restaurant’s profitability, attention to business and financial details can transform small changes into significant returns. Critical sales, cost of sales, labor, inventory, marketing, and overhead metrics are monitored daily. Trends are evaluated, and constructive actions will be taken where improvement is needed. The management team will have access to the restaurant’s transactions and reports available in its real-time POS (point of sale) and accounting systems. Trends will be evaluated, and corrective action will be implemented as required.
7. Organization Structure
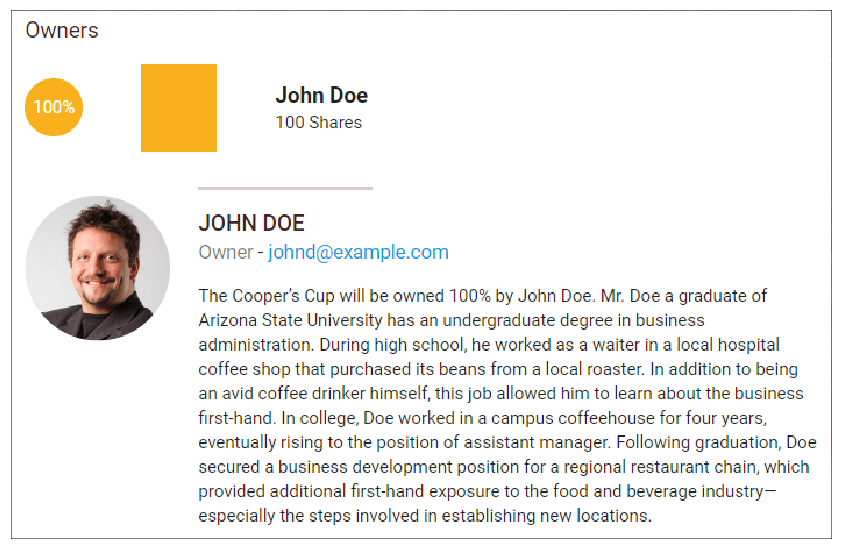
The Cooper’s Cup is formed as an S-Corporation wholly owned by John Doe.
Management Team
The Cooper’s Cup will be owned 100% by John Doe. Mr. Doe, a graduate of Arizona State University, has an undergraduate degree in business administration. During high school, he worked as a waiter in a local hospital coffee shop that purchased its beans from a local roaster. In addition to being an avid coffee drinker, this job allowed him to learn about the business first-hand. In college, Doe worked in a campus coffeehouse for four years, eventually becoming an assistant manager. Following graduation, Doe secured a business development position for a regional restaurant chain, which provided additional first-hand exposure to the food and beverage industry—especially the steps involved in establishing new locations.
Management Team Gaps
The Cooper’s Cup will rely on its POS (Point of Sale) system to generate daily accounting and cost activity reports. Mr. Doe will supply these to an outside bookkeeper for the preparation of annual income taxes.
Personnel Plan
Initially, the cafe will hire 1 manager, 5 baristas, and 2 part-time servers. In Year 2, the cafe plans to hire 1 additional full-time barista.
8. Financial Plan
Important assumptions.
- The sales forecast is conservative and assumes a 5% increase in Year 2 and a 10% in Year 3.
- The analysis accounts for economic seasonality – wherein some month’s revenues peak (such as holidays ) and wane in slower months.
- The analysis assumes the owner will not withdraw any salary till the 3rd year; at any time it is assumed that the owner’s withdrawal is available at his discretion.
- Sales are cash basis – nonaccrual accounting
- Moderate ramp-up in staff over the 5 years forecast
- Barista’s salary in the forecast is $36,000 in 2023.
- In general, most cafes have an 85% gross profit margin
- In general, most cafes have a 3% net profit margin
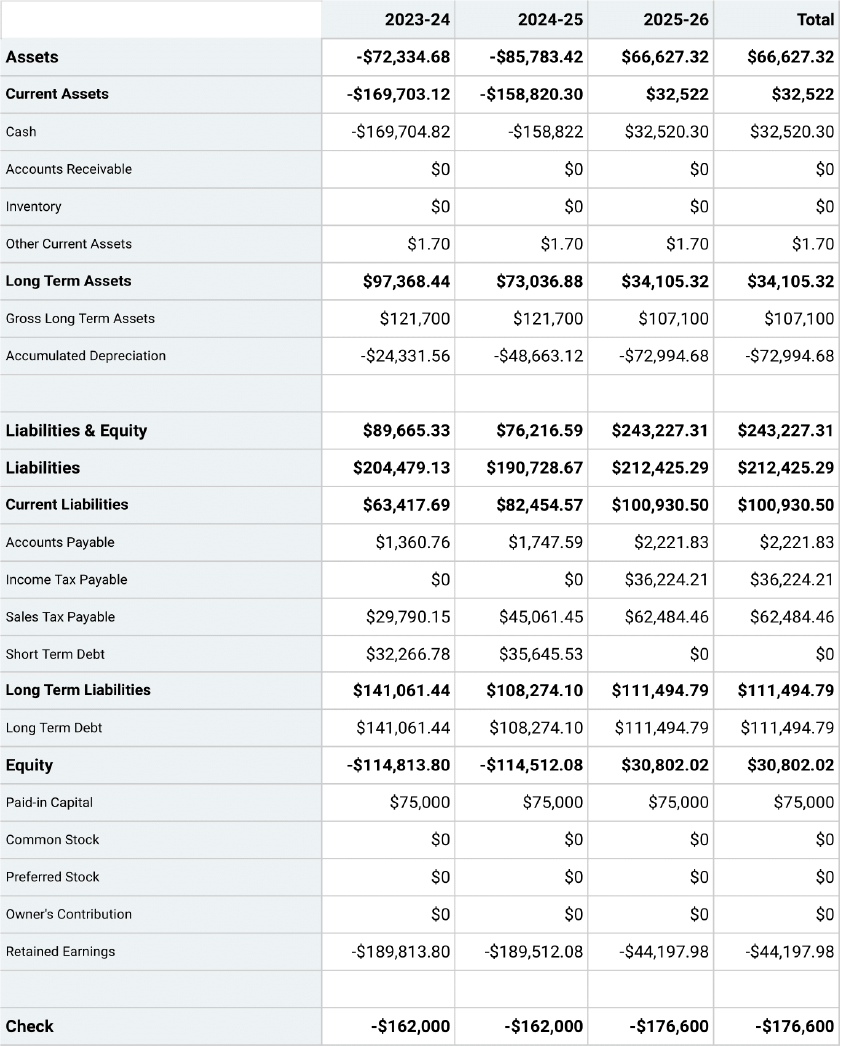
Projected Balance Sheet
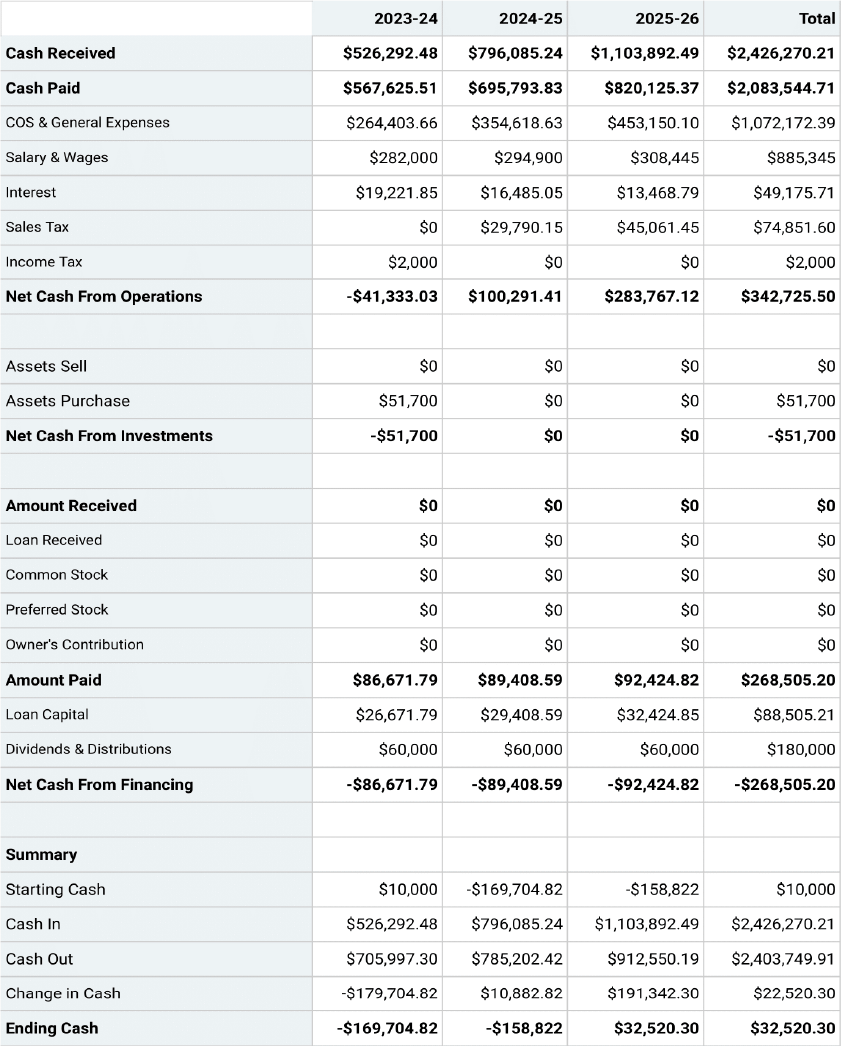
Projected Cash-Flow Statement
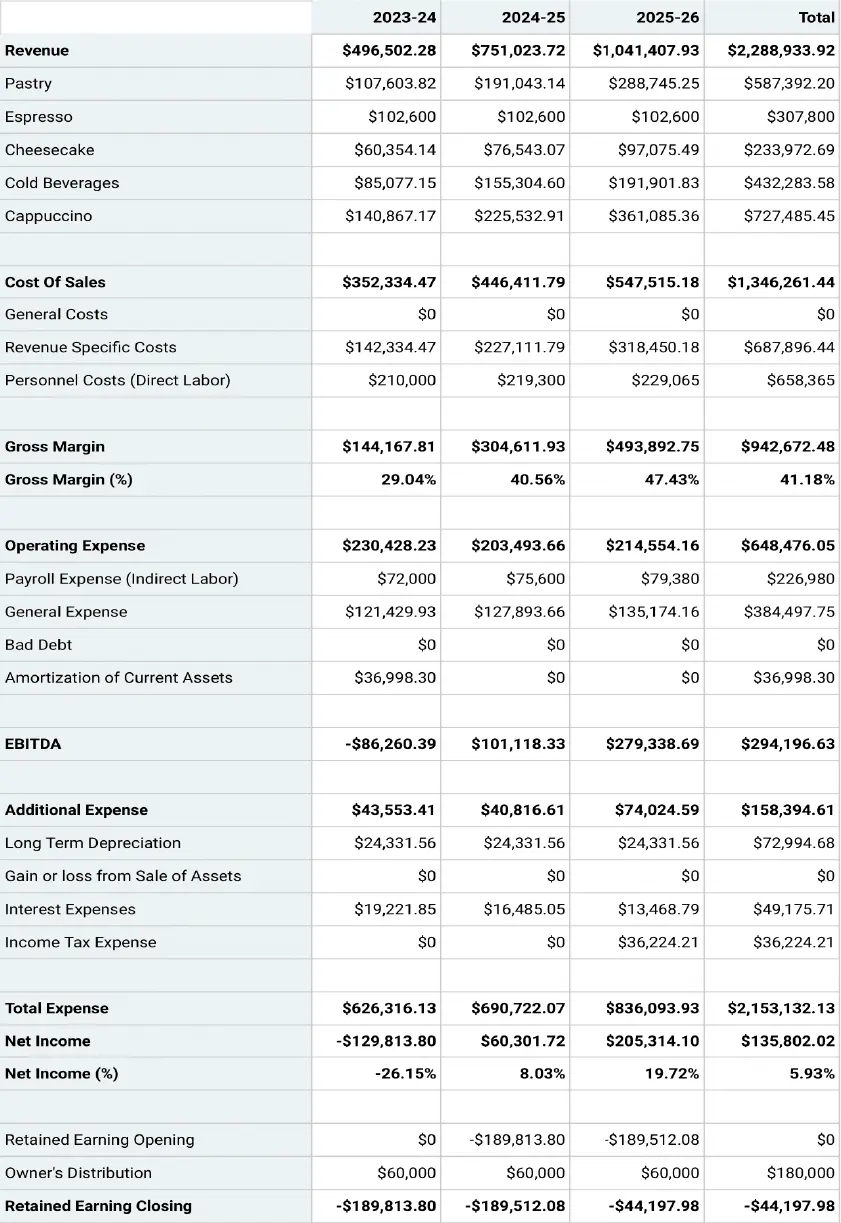
Projected Profit & Loss Statement
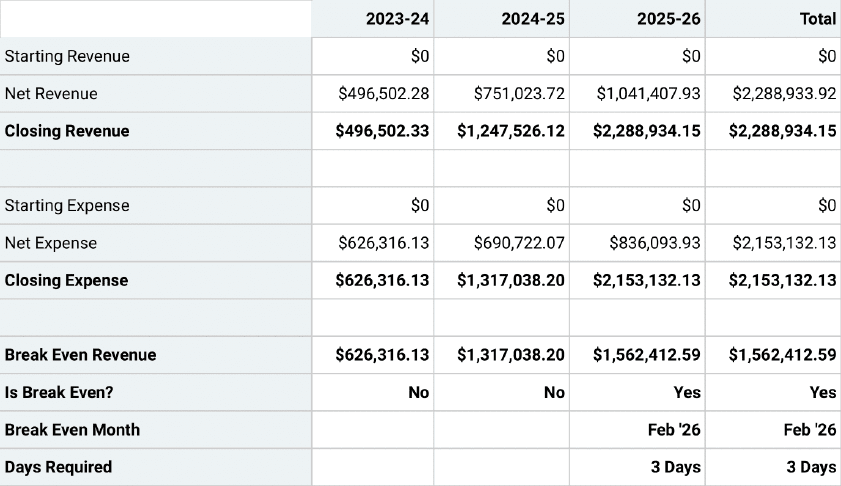
Break Even Analysis
Write Your Business Plan With Upmetrics
Whether you need a business plan to compete in a competition, win investors, or gain a competitive advantage in the market landscape, Upmetrics can help you get started.
Upmetrics is an AI business plan software that comes with AI assistance, financial forecasting features, and 400+ sample business plans so that you can prepare a business plan in no time.
So what are you waiting for? Try Upmetrics and create your business plan in a snap.
Make your plan in half the time & twice the impact with Upmetrics
Fill-in-the-blanks, AI-assistance, and automatic financials make it easy.

Frequently Asked Questions
How do you write a business plan for a college project.
As mentioned earlier in the article, business planning for a college project or competition is no different than for a real business. You can write your business plan using these step-by-step instructions.
- Select a compelling business idea
- Refer to business plan examples
- Prepare a business plan outline
- Create a company description section
- Conduct market research and industry analysis
- Describe your product and services
- Outline sales and marketing strategies
- Create an operations plan
- Introduce management team
- Prepare financial projections
- Summarize your plan with an executive summary
What is a business plan for students?
A business plan is a necessary business document that highlights its purpose, business goals, product/service offerings, go-to marketing strategies, operations and financial plan, key people involved in the business operations, and other necessary details.
As a student, consider a business plan example as a document that helps you better understand business and industry dynamics and learn how a business operates inside out.
What is a business plan competition for students?
Business plan competitions are competitions mostly organized by universities for students passionate about entrepreneurship and the business world. These competitions offer students a platform to showcase their entrepreneurial skills while also providing opportunities for mentorship and networking.
How can I increase my chances of winning a business plan competition?
There cannot be a straightforward answer to this question, but there’s surely a method that can increase your chances of winning a competition—Using AI-powered business plan software.
Why? An AI tool will make you 10X more productive while writing a business plan and preparing financial forecasts. So you can spend more time researching the market and brainstorming business ideas.
Where can I find more business plan examples for students?
Upmetrics’ library of 400+ business plan examples could be an incredible source for students to find more industry-specific business plan examples. There are examples for almost every small business category, including real estate, retail, entertainment and media, food & beverages, and more.
About the Author
Ajay is the Head of Content at Upmetrics. Before joining our team, he was a personal finance blogger and SaaS writer, covering topics such as startups, budgeting, and credit cards. If not writing, he’s probably having a power nap. Read more
Reach Your Goals with Accurate Planning
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Ready to Kickstart Your Business Planning?

– Don’t Miss It
Entrepreneurship: Starting Your Own Business Idea & Pitch PBL Unit-Grades 11-12

Description
Unleash Your Students' Entrepreneurial Spirit with this Comprehensive PBL Unit!
Looking for a fun, engaging, and NO-PREP project-based learning (PBL) unit for your high school students? Look no further! This Entrepreneurship PBL Unit is designed to guide your 11th-12th grade students through the exciting process of starting their own business .
What’s Included:
- Comprehensive Lesson Plans : 21 detailed, no-prep lessons covering financial literacy, business planning, marketing strategies, and more!
- Real-World Application : Students will develop a business idea, create a business plan, and pitch their proposal to a panel of mock investors.
- Critical Thinking & Problem-Solving : Encourages collaboration, decision-making, and the development of key entrepreneurial skills.
- Engaging Activities : Interactive lessons, group projects, real-world scenarios, and opportunities for students to present their work.
- Comprehensive Rubrics & Assessments : Clear and detailed rubrics for easy, effective grading.
- Student Handouts & Worksheet Templates : Ready-to-print resources to guide your students through each step of the project.
- No Prep for Teachers : Everything you need is included in this easy-to-follow, no-prep format!
Why Teachers Love This Unit:
✅ Promotes Financial Literacy : Teach your students the foundations of money management, budgeting, and financial planning.
✅ Hands-On Learning : Students gain practical, real-world skills that will benefit them beyond the classroom.
✅ Boosts Teamwork : Students work in teams, learning how to collaborate, delegate, and solve problems together.
✅ Engages Critical Thinking : Encourages students to think critically about real-world problems and entrepreneurial solutions.
✅ Real-Life Skills : Students gain valuable skills they can apply to future careers or even their own entrepreneurial ventures.
Perfect For:
- Business and Economics Teachers
- Career and Technical Education (CTE) Instructors
- Entrepreneurship Clubs
What’s the Result? At the end of this unit, students will have created their own business ideas, presented professional business plans, and honed skills that will serve them in their future careers. This unit is a powerful tool for preparing students for the challenges of the real world!
Ready to spark creativity and empower your students?
Buy the Entrepreneurship PBL Unit today and watch your students’ entrepreneurial spirits soar!
Happy Teaching,
CURRICU-learn Hub!
Questions & Answers
Curricu-learn hub.
- We're hiring
- Help & FAQ
- Privacy policy
- Student privacy
- Terms of service
- Tell us what you think

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here's my full review of the Teen Entrepreneur Toolbox. 4. Proverbial Home Maker's Family Business Plan Guide. This is such a fun guide that you can fill out with your child, teen, tween, or even the whole family. It includes family business ideas, a sales ledger, an inventory worksheet, and much more.
Welcome to my channelIn today's video I will be going through and discussing the topic of Transforming A Business Plan Into An Action Plan for Grade 11 in Bu...
INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS PLAN PREPARATION. This module covers the entrepreneurial activities that must be undertaken immediately prior to the opening of small. Skip to document. ... Physical education Grade 11 Module 2. Bachelor of secondary education 95% (40) 18. Earth-Science 11 Q1 MOD6 Ore-Minerals-08082020.
If you want to launch a business, you have to have a plan! Here are some templates to help you get started. ... The intended audience is kids and teens ages 11-18, and provides over 100 videos with step-by-step instructions on how to set up and grow a business from the ground up. ... The target age group is grades 6 to 12. Shark Tank Marketing ...
6. Write a short paragraph that describes your business idea and goals. As a future business owner, you'll need to know your business inside and out. You also need to be able to explain it easily to others, so get your business idea down in words. Describe what you will be offering and why your business is a good idea.
rk in small groups to brainstorm ideas. (15 min)4. As the class comes back, the teacher writes the words "Business Plan" on the board, and asks the class what they thi. k. eeds to be included in a business plan. (5 min)5. From there the teacher will pass out copies of the first part of a transcript from the article Ho.
Welcome to my channelIn today's video I will be going through and discussing the of Starting a Business on an Action Plan for Grade 11 in Business Studies. T...
BUSINESS STUDIES GRADE 11 TERM 3 CHAPTER 16 STARTING A BUSINESS VENTURE ON AN ACTION PLAN 2020 TABLE OF CONTENTS TOPICS PAGES. Exam guidelines for starting a business venture on an action plan. 3. Terms and definitions 2 Aspects that must be considered when initiating a business. 3-Factors that must be considered before start- up. 4-
Objectives. The primary objectives of the business plan for Cooper's Cup are below: To increase revenues by $36,000 or 5% in Year 2 and $73,000 or 10% by Year 3. Achieve a profit margin of 5.2% in Year 2 and 6.90% by Year 3. Be the Cafe of Choice in the Phoenix area and the recipient of the Best Coffeehouse Award.
Look no further! This Entrepreneurship PBL Unit is designed to guide your 11th-12th grade students through the exciting process of starting their own business. What's Included: Comprehensive Lesson Plans: 21 detailed, no-prep lessons covering financial literacy, business planning, marketing strategies, and more!