95 Literature Review Topics + How-to Guide [2024]
![topics for a literature review 95 Literature Review Topics + How-to Guide [2024]](https://studycorgi.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/front-view-hardback-books-1-353x528.jpg)
A literature review is a variant of curtsy in scientific circles. It presents your acknowledgment that you are not the first to tackle the issue. Your predecessors have made progress in answering your research question, and you plan to start from the point they finished.
This article features examples of literature review topics on multiple knowledge areas. Additionally, you will find exhaustive disambiguation of all the types of a literature review, as well as its purposes, definition, outline, and formatting.
- 🔝 Top 15 Topics
- ✍️ Writing Tips
- Political Science
- Criminal Justice

🔗 References
🔝 top 15 literature review topics.
- What does the science say about extraterrestrial life?
- Redesigning organisms in synthetic biology: Where are we at now?
- Equality of human rights at the international level.
- Why do genes happen to be active or inactive?
- Legalizing physician-assisted suicide.
- Can an adult person change their native language?
- The most efficient study programs.
- The ethics of using surveillance cameras.
- The effect of reading fiction on your brain.
- British imperialism in India.
- What is kindness: A philosophical approach.
- Modern technologies can sift out fake news.
- Multiculturalism: A romantic myth or today’s reality?
- The demographics of liberal worldview in the US.
- Chronic fatigue: Literature review and hypotheses.
✍️ Literature Review Writing Tips
Speaking of a literature review , the definition is too broad to be used as writing guidance. It is an overview of credible materials on a particular research question. A literature review usually becomes chapter 1 in dissertations and theses , allowing to explore the current knowledge on the topic. It evaluates academic and professional articles, journal publications, books, and web-based resources.
A literature review is an indispensable part of a research paper. It serves many purposes, some of which are not evident.
What Is the Purpose of a Literature Review?
- To draw the background context;
- To compare your results with previous research;
- To justify your research methods;
- To frame research gaps and show the scientific novelty of your project;
- To explain the social value of your work;
- To demonstrate your knowledge of the referenced literature;
- To train your analytical thinking.
Types of Literature Review
Below you’ll find the 6 types of literature reviews.
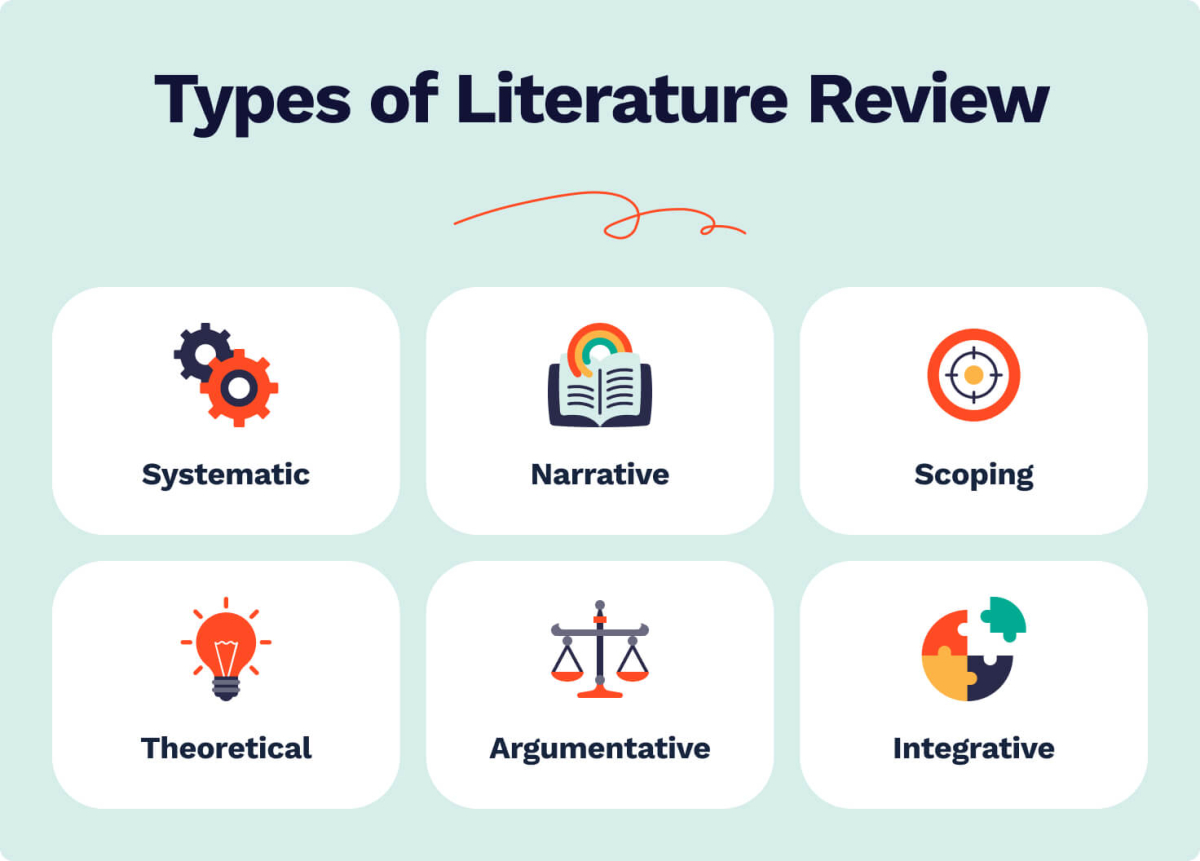
Systematic Review
A systematic literature review is a most comprehensive and data-oriented type. It defines the timeframe of the selected literature and is subdivided into two categories:
- Meta-analysis ( deductive research through standardized statistical procedures)
- Meta-synthesis (inductive study by non-statistical qualitative methods)
Narrative Review
It is also called a traditional or critical literature review. The purpose is to summarize the available material, critique it, and identify the gaps and inconsistencies. This type works well for almost any research question, provided it is sufficiently focused and limited in time or subject matter.
Scoping Review
As the name implies, it estimates the scope of available literature on a literature review topic. Unlike a systematic literature review, which aims to find the most specific research question, this type looks for the most general one. It answers the question of what else can be researched in the field.
Theoretical Review
A theoretical literature review explores the pool of theories that have so far accumulated on a concept. It lists the existing ideas, their relationships, and gaps. The purpose is to develop hypotheses to be tested in the experimental section.
Argumentative Review
This type provides the most selective literature review to prove or refute an argument already established in the research literature. However, this is also the most biased review among all types.
Integrative Review
This literature review integrates, synthesizes, and critiques the available secondary data to develop new research frameworks and perspectives.
Systematic Review vs. Literature Review vs. Annotated Bibliography
- Purpose: Eliminate bias and answer a focused question.
- Structure: Introduction – Methodology – Discussion – Conclusion – List of References.
- Number of sources: 3+
- Scope: Clearly defined (narrow) research question.
- Relationship between so urces: How do they answer my research question?
- Organization: Evidence-based inductions or deductions.
- Purpose: Summarize the most significant sources on the topic.
- Structure: Intro – Methods – Discussion – Conclusion – References.
- Number of sources: 1+
- Scope: Either a general topic or a specific question.
- Relationship between sources: Do they agree or disagree?
- Organization: Cause-and-effect, comparison or contrast, and classification.
- Purpose: List the most suitable sources for additional reading with brief explanations.
- Structure: Numbered list according to a formal citation style (APA, MLA, or Chicago) plus a brief explanation of relevance and credibility of sources.
- Number of sources: 15-20
- Scope: General topic.
- Relationship between sources: How do they relate to the topic?
- Organization: Alphabetical order.
What Are the Four Stages of Literature Review?
The process of conducting a literature review can be divided into four stages:
- Formulating the problem. Choose a topic and its specific aspects.
- Searching the literature. Make up the preliminary bibliography list to be described in the literature review.
- Evaluating the data. Decide which sources are the most significant in understanding the topic.
- Analyzing and interpreting the essential findings.
Literature Review Outline
How long should a literature review be? It depends on the assignment requirements and your outline.
A literature review is often used as a part of a more general research paper. In such a case, you can limit yourself to the standard introduction –main body – conclusion formula.
In all the other situations, use the following literature review outline.
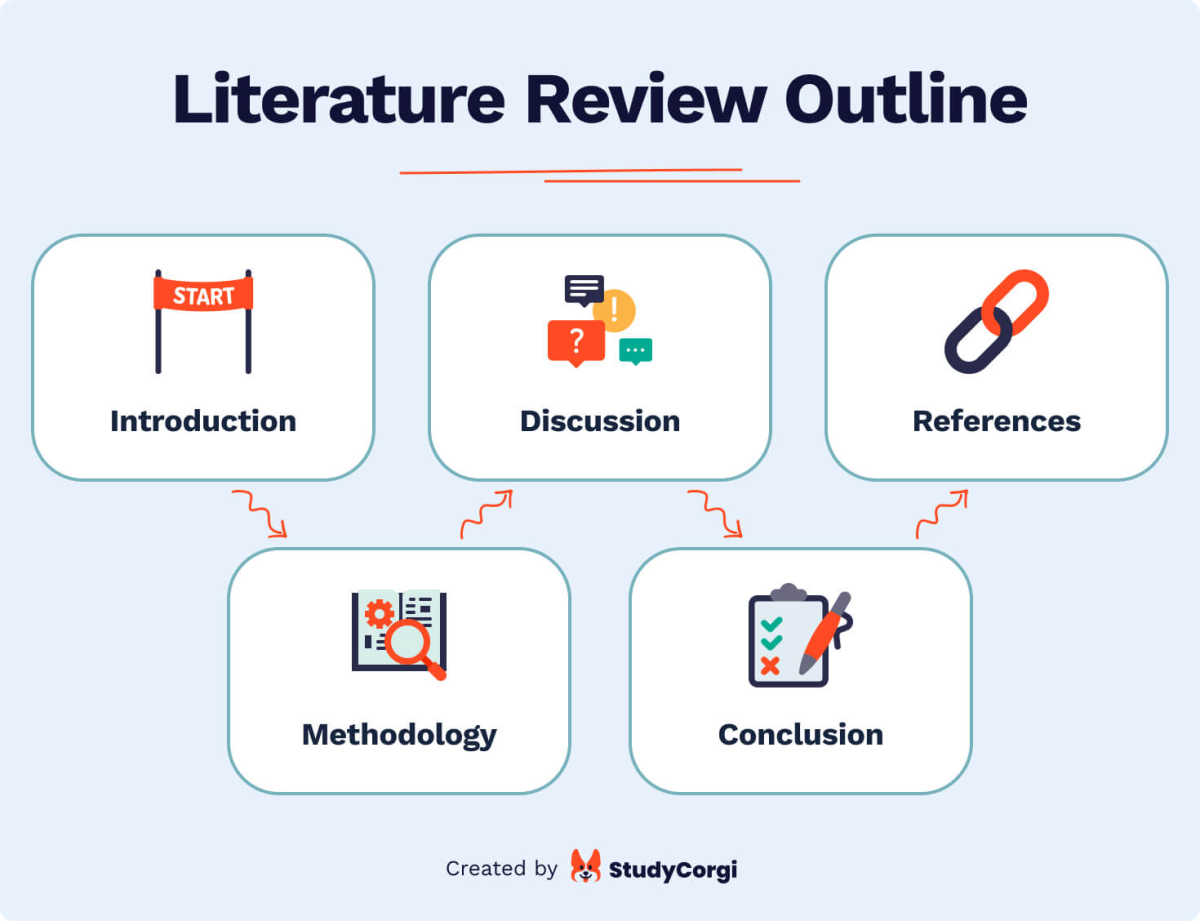
- Introduction Trace the scope and highlight the importance of your review. Why did you choose the given topic or research question? How does it contribute to the previous study?
- Methodology We have listed the types of literature review above. Depending on your purposes, select one and explain why your choice is the best. You can also specify which logic you used while choosing the sources for your review.
- Discussion It is the central part of the text which compares, contrasts, and explains the relationships between various ideas you found in the bibliography items.
- Conclusion Are you satisfied with the result of your work? How will it help further research? Which gaps have you spotted, and which hypothesis could you generate?
- List of references As in any research paper, this is an indispensable part of your literature review. Be sure to follow the format requirements as provided below.
Literature Review Format
All citation styles require you to indicate the author’s name, book title, publication year, number of pages, and volume or issue number. This data is available in any printed edition, as publishers use it to identify their products.
It may sound simple until you discover that each citation style has a multi-page list of nuanced details specific to this format and inapplicable to any other.
Browse the guides for each of the most popular types below.
APA style is a format for scholarly documents. It is particularly popular in the fields of social and behavioral sciences. APA is well-known for its simplicity in source references. Thus, a vast majority of American universities and colleges prefer this format.
MLA style manual is an abridged version of the MLA Handbook published by the Modern Language Association. It was created for students to assist in their research aspirations. Its 8 th edition is addressed to secondary-school and undergraduate university and college teachers and students. The style is popular in humanities (modern languages, literature, cultural studies, and related disciplines).
Chicago style (also called CMS or CMOS) is a style guide for American English. The University of Chicago Press first published it in 1906. Since then, it has had 17 editions and has become one of the most popular citation styles in the US. The guide instructs on editorial practice, grammar, document preparation, formatting, and even the use of the singular “they.”
💡 Literature Review Topics
Literature review topics in education.
- How can we make classrooms more inclusive ?
- Flipped classroom approach.
- Waldorf schools and their concept.
- How do ADHD symptoms affect a student’s learning abilities?
- Educational leadership.
- Methods of tracking the performance of schoolchildren.
- How can token economy diminish off-task behavior in students with autism?
- Resegregation in US schools.
- Is bilingual education realizable in contemporary schools?
- Growing violence incidents in educational institutions.
Political Science Literature Review Topics
- Gender cosmopolitanism in Sweden .
- Security policy is based on political ideology .
- The emotional effect of populism .
- The theory and classification of political speeches.
- Global measures in COVID-19 response.
- The international politics of the Arab world.
- How do we select our leaders ?
- Officials in politics: Emotional labor .
- Relational peace between countries.
- The invisible force holding countries together.
Criminal Justice Literature Review Topics
- The problematic issues of prosecution and legal enforcement in Eastern Europe.
- Track the evolution of international criminal justice practices.
- Crime prevention methods.
- The evolution of criminology as a social science.
- The cycle of domestic violence : Theory and statistics.
- The patterns in child abuse perpetrators.
- Randomized experimental designs in criminology .
- Current measures to stop human trafficking in the US.
- How should we punish environmental crimes?
- Terrorism : Approaches to its definitions.
Sociology Literature Review Topics
- Does coded language help us fight racial inequality ?
- Workplace bullying.
- International conflicts in terms of social representation theory.
- Gender and sexual activity.
- Is our society liberal or conservative ?
- Single African American parents.
- Racial salary gap in the US.
- Substance abuse and health care costs for employers.
- Does federal aid succeed at fighting urban poverty?
- How does hate speech spur desensitization?
Nursing Literature Review Topics
- Practice in the field of healthcare.
- Evidence-based nursing practice.
- Traumatic brain injury.
- Alzheimer’s disease.
- Pressure ulcers study.
- Post-operative readmission rates.
- Nursing ratios and nosocomial infections.
- Patient fall prevention study.
- Emergency room wait time.
- Electronic health records.
Psychology Literature Review Topics
- Parents’ experiences of caring for a child with ASD
- The long-term consequences of child abuse
- The neurology of depression.
- Explore the psychological effects of loud noise.
- Why is it so hard to accept what contradicts our beliefs?
- The psychological mechanisms of compulsive eating.
- Why are some people more prone to discrimination and prejudice?
- Self-protection against grief .
- Non-verbal communication rates in different cultures.
- Love : Chemistry or feeling?
Biology Literature Review Topics
- Camouflage in plants.
- Color differences in male and female bird species.
- Acceptability of genetic engineering.
- Natural reforestation: Too long to wait.
- Why are domestic plants weaker than wild ones?
- Hepcidin: importance, production, regulation.
- How can we edit DNA sequences ?
- Which anti- COVID vaccines are the most effective and why?
- Cancer : An umbrella term for many diseases.
- Species that are important to our ecology.
Easy Literature Review Topics
- Sustainable agriculture : Our future reality.
- Vegetarianism.
- The scientific background behind music therapy .
- Stono revolt.
- The latest findings in stopping brain aging.
- Articles on cyber security of young children.
- Data-driven personalization : Prospects and achievements.
- Importance of the literature review in research.
- Critical literature review of digital signature.
- Reviewing quantitative academic literature and data.
- Literature Reviews – UNC Writing Center
- Learn how to write a review of literature
- Writing a Literature Review // Purdue Writing Lab
- Types of Literature Reviews – Systematic Reviews
- Literature review | Institute for Academic Development
Discover DNP
Finding the best literature review topics: 135 good topics for a literature review for nursing research papers.
Are you a nursing student or researcher looking for inspiration for your next literature review? Whether you’re working on a dissertation, thesis, or research paper, choosing the right topic is crucial. This comprehensive guide will help you navigate the process of selecting good topics for a literature review in nursing, provide you with a wealth of topic examples, and offer insights into the literature review process.

What you'll Learn
What is a Literature Review in Nursing Research?
Before diving into topic selection, it’s essential to understand what a literature review in nursing entails. A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. In nursing, literature reviews play a vital role in advancing evidence-based practice and informing future research.
Understanding the Purpose of a Literature Review
The primary purpose of a literature review in nursing is to:
- Provide a comprehensive overview of current knowledge on a topic
- Identify gaps in existing research
- Establish a theoretical framework for further study
- Justify the need for new research
A well-conducted literature review can help you formulate a strong research question and contribute to the broader field of nursing knowledge.
Key Components of a Nursing Literature Review
A nursing literature review typically includes:
- An introduction that outlines the topic and its significance
- A clear methodology for literature searches and selection
- A synthesis of findings from relevant journal articles and academic writing
- A critical analysis of the literature, identifying themes, trends, and gaps
- A conclusion that summarizes key points and suggests areas for further research

How to Structure a Literature Review for Nursing
When structuring your literature review, consider the following steps:
- Start with a clear introduction that states your research question
- Organize your review thematically or chronologically
- Use subheadings to guide readers through different aspects of your topic
- Conclude with a summary of key findings and implications for future research
Remember, the structure should flow logically and help readers understand the current state of knowledge on your chosen topic.
How to Choose Good Topics for a Literature Review?
Selecting a good topic for your literature review is crucial. It should be interesting, relevant, and manageable within the scope of your project.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Topic
- Personal Interest : Choose a topic you’re really passionate about. Your enthusiasm will show in your writing.
- Relevance : Ensure your topic is relevant to current nursing practice or addresses emerging issues in healthcare.
- Scope : Make sure your topic is neither too broad nor too narrow. It should be manageable within your timeframe and word limit.
- Available Literature : Confirm that there’s sufficient published research on your chosen topic.
- Originality : Look for areas where you can contribute new insights or perspectives.
- Practical Implications : Consider how your review could impact nursing practice or patient care.
When brainstorming ideas, consider exploring Quora or consulting with your professor for inspiration. Remember, choosing a literature review topic is an important step in your research project, so take your time and choose wisely.
90 Examples of Good Topics for a Literature Review
To help you get started, here’s a list of potential topics for your nursing literature review. These topics span various areas of nursing and can be adapted to suit your specific interests and research requirements.
50 Best Literature Review Topics for Nursing Research Papers
- The impact of nurse-patient ratios on patient outcomes
- Effectiveness of mindfulness interventions in reducing nurse burnout
- The role of simulation in nursing education
- Cultural competence in nursing: Strategies for improvement
- Ethical considerations in end-of-life care
- The effectiveness of telehealth in rural nursing practice
- Nurse leadership styles and their impact on staff retention
- Evidence-based practices in fall prevention for elderly patients
- The role of nurse practitioners in primary care
- Strategies for improving medication adherence in chronic disease management
- The impact of 12-hour shifts on nurse performance and patient safety
- Effectiveness of pain management protocols in pediatric nursing
- The role of nurses in disaster preparedness and response
- Strategies for preventing hospital-acquired infections
- The impact of nurse education level on patient outcomes
- Evidence-based interventions for reducing medication errors
- The role of nursing in promoting health equity
- Effectiveness of family-centered care in neonatal intensive care units
- The impact of workplace violence on nurse retention and job satisfaction
- Evidence-based practices in wound care management
- The role of nursing informatics in improving patient care
- Strategies for promoting breastfeeding in diverse populations
- The impact of nurse-led clinics on chronic disease management
- Evidence-based interventions for reducing readmission rates
- The role of nurses in promoting mental health in primary care settings
- Effectiveness of interprofessional collaboration in healthcare teams
- The impact of nurse residency programs on new graduate retention
- Evidence-based practices in pain management for cancer patients
- The role of school nurses in promoting adolescent health
- Strategies for improving communication in healthcare teams
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on diabetes self-management
- Evidence-based practices in pressure ulcer prevention
- The role of nurses in promoting vaccination uptake
- Effectiveness of cognitive behavioral therapy in mental health nursing
- The impact of nurse navigators on cancer patient outcomes
- Evidence-based interventions for reducing nurse turnover
- The role of nurses in promoting healthy aging
- Strategies for improving patient safety in medication administration
- The impact of nurse-led smoking cessation interventions
- Evidence-based practices in managing postoperative pain
- The role of nurses in promoting LGBTQ+ health equity
- Effectiveness of music therapy in reducing anxiety in hospitalized patients
- The impact of nurse-led heart failure clinics on patient outcomes
- Evidence-based interventions for preventing nurse burnout
- The role of nurses in promoting environmental health
- Strategies for improving patient engagement in chronic disease management
- The impact of nurse practitioners on healthcare costs and quality
- Evidence-based practices in managing delirium in hospitalized elderly patients
- The role of nurses in promoting health literacy
- Effectiveness of mindfulness-based stress reduction for nurses
45 Trending Topics in Nursing Literature Research
- The role of artificial intelligence in nursing practice
- Nursing interventions for long COVID management
- The impact of climate change on global health: Implications for nursing
- Telenursing: Challenges and opportunities in the digital age
- The role of nurses in promoting vaccine confidence
- Addressing racial disparities in maternal health outcomes
- Nursing strategies for managing the opioid crisis
- The impact of social media on nursing education and practice
- Precision medicine: Implications for nursing care
- The role of nurses in disaster response during pandemics
- Addressing nurse burnout in the post-COVID era
- The impact of wearable technology on patient monitoring and care
- Nursing interventions for managing eco-anxiety in patients
- The role of nurses in promoting digital health literacy
- Addressing the mental health needs of healthcare workers post-pandemic
- The impact of robotics on nursing practice and patient care
- Nursing strategies for managing antimicrobial resistance
- The role of nurses in promoting health equity in underserved communities
- Addressing the nursing shortage: Innovative recruitment and retention strategies
- The impact of virtual reality on pain management in nursing
- Nursing interventions for managing chronic fatigue syndrome
- The role of nurses in promoting sustainable healthcare practices
- Addressing compassion fatigue in oncology nursing
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on reducing hospital readmissions
- Nursing strategies for managing the health impacts of air pollution
- The role of nurses in promoting LGBTQ+ inclusive healthcare
- Addressing the unique health needs of refugee populations: A nursing perspective
- The impact of nurse leadership on patient safety culture
- Nursing interventions for managing post-traumatic stress disorder in veterans
- The role of nurses in promoting health equity for individuals with disabilities
- Addressing the challenges of providing care to an aging population
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on reducing childhood obesity
- Nursing strategies for managing the health impacts of social isolation
- The role of nurses in promoting trauma-informed care
- Addressing the mental health needs of nursing students
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on improving medication adherence in chronic diseases
- Nursing strategies for managing the health impacts of heat waves
- The role of nurses in promoting cultural safety in healthcare
- Addressing the unique health needs of transgender patients: A nursing perspective
- The impact of nurse practitioners on access to primary care in rural areas
- Nursing interventions for managing post-intensive care syndrome
- The role of nurses in promoting health literacy among immigrant populations
- Addressing the challenges of providing palliative care in non-hospital settings
- The impact of nurse-led interventions on reducing stigma in mental health care
- Nursing strategies for managing the health impacts of food insecurity
30 Qualitative and Quantitative Research Topics
Qualitative Research Topics:
- Nurses’ experiences of providing end-of-life care during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Exploring patient perceptions of nurse-led chronic disease management programs
- Understanding the lived experiences of nurses working in rural settings
- Investigating the factors influencing nurse resilience in high-stress environments
- Exploring the cultural competence journey of nursing students
- Understanding the experiences of male nurses in female-dominated specialties
- Investigating the decision-making processes of nurse practitioners in primary care
- Exploring the experiences of nurses transitioning to leadership roles
- Understanding the challenges faced by nurses in promoting health literacy
- Investigating the experiences of nurses working with transgender patients
- Exploring the impact of 12-hour shifts on nurses’ work-life balance
- Understanding the experiences of nurses providing care to victims of domestic violence
- Investigating the factors influencing job satisfaction among school nurses
- Exploring the experiences of nurses working in telemedicine
- Understanding the challenges faced by nurses in implementing evidence-based practice
Quantitative Research Topics:
- The effect of nurse staffing levels on patient mortality rates
- Evaluating the impact of nurse-led interventions on diabetes management outcomes
- Assessing the effectiveness of simulation-based training on nursing students’ clinical skills
- Measuring the impact of nurse residency programs on new graduate retention rates
- Evaluating the effectiveness of mindfulness interventions on reducing nurse burnout
- Assessing the impact of nurse practitioners on healthcare costs in primary care settings
- Measuring the effectiveness of nurse-led smoking cessation programs
- Evaluating the impact of interprofessional education on nursing students’ collaboration skills
- Assessing the relationship between nurse education levels and patient satisfaction scores
- Measuring the effectiveness of nurse-led interventions in reducing hospital-acquired infections
- Evaluating the impact of nurse navigation programs on cancer patient outcomes
- Assessing the relationship between nurse workload and medication error rates
- Measuring the effectiveness of nurse-led heart failure clinics on patient readmission rates
- Evaluating the impact of nurse-led telehealth interventions on chronic disease management
- Assessing the relationship between nurse leadership styles and staff turnover rates
How to Write a Literature Review for a Research Paper?
Writing a literature review requires careful planning, thorough research, and critical analysis. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you write a comprehensive literature review for your nursing research paper.
Steps to Write a Comprehensive Literature Review
- Define your topic : Clearly articulate your research question or thesis statement.
- Conduct a thorough literature search : Use academic databases, journals, and other reliable sources to find relevant literature.
- Evaluate sources : Assess the credibility, relevance, and recency of your sources.
- Organize your findings : Group similar ideas and identify themes in the literature.
- Analyze and synthesize : Don’t just summarize; critically analyze the literature and draw connections between different sources.
- Write your review : Start with an introduction, present your findings thematically or chronologically, and conclude with a summary of key points and gaps in the literature.
- Edit and refine : Review your work for clarity, coherence, and proper citation.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Literature Review Writing
- Lack of focus or clear research question
- Over-reliance on outdated sources
- Failing to critically analyze the literature
- Poor organization of ideas
- Neglecting to identify gaps in the literature
- Plagiarism or improper citation
Using Our Writing Services for Your Literature Review
If you’re struggling with your literature review, consider seeking professional help. Our custom writing service offers expert assistance in crafting high-quality literature reviews. Our team of experienced writers can help you:
- Refine your research question
- Conduct comprehensive literature searches
- Critically analyze and synthesize findings
- Structure your review effectively
- Ensure proper citation and avoid plagiarism
Remember, while professional help can be valuable, the final work should reflect your own understanding and analysis.
What are Some Literature Research Paper Topics for Students?
As a nursing student, you might be looking for topics that are manageable yet significant. Here are some sample literature review topics suitable for nursing students at various levels:
Sample Literature Review Topics for Nursing Students
- The effectiveness of hand hygiene protocols in preventing hospital-acquired infections
- The impact of nurse-patient communication on patient satisfaction
- Evidence-based interventions for managing pediatric pain
- The role of nurse educators in promoting critical thinking skills
- Strategies for improving medication safety in geriatric nursing
- The effectiveness of nurse-led interventions in managing chronic diseases
- The impact of workplace bullying on nurse retention and job satisfaction
- The role of school nurses in managing childhood obesity
- Strategies for promoting cultural competence in nursing education
Remember, these are just starting points. Tailor your topic to your interests and the specific requirements of your course or program.
How to Conduct In-Depth Research for Your Literature Review?
Conducting thorough research is crucial for a high-quality literature review. Here are some strategies to help you find and evaluate relevant sources.
Using Databases to Find the Right Literature
- Choose the right databases : Use nursing-specific databases like CINAHL, PubMed, and Cochrane Library.
- Develop effective search strategies : Use Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT) and truncation to refine your searches.
- Use filters : Limit your search by date, publication type, or other relevant criteria.
- Keep track of your searches : Document your search strategies for future reference and to avoid duplication.
Summarizing Key Findings from Literature
- Create a matrix or table to organize key information from each source.
- Identify the main arguments, methodologies, and findings of each study.
- Look for patterns, themes, and contradictions across different sources.
- Consider how each source contributes to answering your research question.
Evaluating the Quality of Literature Sources
- Check the credibility of the authors and their affiliations.
- Assess the relevance of the source to your research question.
- Consider the methodology used and its appropriateness.
- Look at the date of publication to ensure you’re using current information.
- Evaluate the strength of the evidence presented.
- Consider any limitations or biases in the study.
By following these strategies, you’ll be well-equipped to conduct a thorough and effective literature review for your nursing research paper.
In conclusion, choosing good topics for a literature review in nursing requires careful consideration of your interests, the relevance of the topic, and the available literature. By following the guidelines provided in this comprehensive guide, you’ll be well-prepared to select an engaging topic, conduct thorough research, and write a high-quality literature review that contributes meaningfully to the field of nursing.
Remember, a well-executed literature review not only demonstrates your understanding of the current state of knowledge in your chosen area but also lays the foundation for future research and improvements in nursing practice. Whether you’re exploring the impact of nurse-patient ratios, investigating innovative interventions for chronic disease management, or examining the role of technology in nursing education, your literature review has the potential to make a significant contribution to the nursing profession.
Post navigation
Previous post.
15 Literature Review Examples

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process
Literature reviews are a necessary step in a research process and often required when writing your research proposal . They involve gathering, analyzing, and evaluating existing knowledge about a topic in order to find gaps in the literature where future studies will be needed.
Ideally, once you have completed your literature review, you will be able to identify how your research project can build upon and extend existing knowledge in your area of study.
Generally, for my undergraduate research students, I recommend a narrative review, where themes can be generated in order for the students to develop sufficient understanding of the topic so they can build upon the themes using unique methods or novel research questions.
If you’re in the process of writing a literature review, I have developed a literature review template for you to use – it’s a huge time-saver and walks you through how to write a literature review step-by-step:
Get your time-saving templates here to write your own literature review.
Literature Review Examples
For the following types of literature review, I present an explanation and overview of the type, followed by links to some real-life literature reviews on the topics.
1. Narrative Review Examples
Also known as a traditional literature review, the narrative review provides a broad overview of the studies done on a particular topic.
It often includes both qualitative and quantitative studies and may cover a wide range of years.
The narrative review’s purpose is to identify commonalities, gaps, and contradictions in the literature .
I recommend to my students that they should gather their studies together, take notes on each study, then try to group them by themes that form the basis for the review (see my step-by-step instructions at the end of the article).
Example Study
Title: Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations
Citation: Vermeir, P., Vandijck, D., Degroote, S., Peleman, R., Verhaeghe, R., Mortier, E., … & Vogelaers, D. (2015). Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations. International journal of clinical practice , 69 (11), 1257-1267.
Source: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/ijcp.12686
Overview: This narrative review analyzed themes emerging from 69 articles about communication in healthcare contexts. Five key themes were found in the literature: poor communication can lead to various negative outcomes, discontinuity of care, compromise of patient safety, patient dissatisfaction, and inefficient use of resources. After presenting the key themes, the authors recommend that practitioners need to approach healthcare communication in a more structured way, such as by ensuring there is a clear understanding of who is in charge of ensuring effective communication in clinical settings.
Other Examples
- Burnout in United States Healthcare Professionals: A Narrative Review (Reith, 2018) – read here
- Examining the Presence, Consequences, and Reduction of Implicit Bias in Health Care: A Narrative Review (Zestcott, Blair & Stone, 2016) – read here
- A Narrative Review of School-Based Physical Activity for Enhancing Cognition and Learning (Mavilidi et al., 2018) – read here
- A narrative review on burnout experienced by medical students and residents (Dyrbye & Shanafelt, 2015) – read here
2. Systematic Review Examples
This type of literature review is more structured and rigorous than a narrative review. It involves a detailed and comprehensive plan and search strategy derived from a set of specified research questions.
The key way you’d know a systematic review compared to a narrative review is in the methodology: the systematic review will likely have a very clear criteria for how the studies were collected, and clear explanations of exclusion/inclusion criteria.
The goal is to gather the maximum amount of valid literature on the topic, filter out invalid or low-quality reviews, and minimize bias. Ideally, this will provide more reliable findings, leading to higher-quality conclusions and recommendations for further research.
You may note from the examples below that the ‘method’ sections in systematic reviews tend to be much more explicit, often noting rigid inclusion/exclusion criteria and exact keywords used in searches.
Title: The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review
Citation: Roman, S., Sánchez-Siles, L. M., & Siegrist, M. (2017). The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review. Trends in food science & technology , 67 , 44-57.
Source: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092422441730122X
Overview: This systematic review included 72 studies of food naturalness to explore trends in the literature about its importance for consumers. Keywords used in the data search included: food, naturalness, natural content, and natural ingredients. Studies were included if they examined consumers’ preference for food naturalness and contained empirical data. The authors found that the literature lacks clarity about how naturalness is defined and measured, but also found that food consumption is significantly influenced by perceived naturalness of goods.
- A systematic review of research on online teaching and learning from 2009 to 2018 (Martin, Sun & Westine, 2020) – read here
- Where Is Current Research on Blockchain Technology? (Yli-Huumo et al., 2016) – read here
- Universities—industry collaboration: A systematic review (Ankrah & Al-Tabbaa, 2015) – read here
- Internet of Things Applications: A Systematic Review (Asghari, Rahmani & Javadi, 2019) – read here
3. Meta-analysis
This is a type of systematic review that uses statistical methods to combine and summarize the results of several studies.
Due to its robust methodology, a meta-analysis is often considered the ‘gold standard’ of secondary research , as it provides a more precise estimate of a treatment effect than any individual study contributing to the pooled analysis.
Furthermore, by aggregating data from a range of studies, a meta-analysis can identify patterns, disagreements, or other interesting relationships that may have been hidden in individual studies.
This helps to enhance the generalizability of findings, making the conclusions drawn from a meta-analysis particularly powerful and informative for policy and practice.
Title: Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s Disease Risk: A Meta-Meta-Analysis
Citation: Sáiz-Vazquez, O., Puente-Martínez, A., Ubillos-Landa, S., Pacheco-Bonrostro, J., & Santabárbara, J. (2020). Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease risk: a meta-meta-analysis. Brain sciences, 10(6), 386.
Source: https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060386
O verview: This study examines the relationship between cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Researchers conducted a systematic search of meta-analyses and reviewed several databases, collecting 100 primary studies and five meta-analyses to analyze the connection between cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease. They find that the literature compellingly demonstrates that low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels significantly influence the development of Alzheimer’s disease.
- The power of feedback revisited: A meta-analysis of educational feedback research (Wisniewski, Zierer & Hattie, 2020) – read here
- How Much Does Education Improve Intelligence? A Meta-Analysis (Ritchie & Tucker-Drob, 2018) – read here
- A meta-analysis of factors related to recycling (Geiger et al., 2019) – read here
- Stress management interventions for police officers and recruits (Patterson, Chung & Swan, 2014) – read here
Other Types of Reviews
- Scoping Review: This type of review is used to map the key concepts underpinning a research area and the main sources and types of evidence available. It can be undertaken as stand-alone projects in their own right, or as a precursor to a systematic review.
- Rapid Review: This type of review accelerates the systematic review process in order to produce information in a timely manner. This is achieved by simplifying or omitting stages of the systematic review process.
- Integrative Review: This review method is more inclusive than others, allowing for the simultaneous inclusion of experimental and non-experimental research. The goal is to more comprehensively understand a particular phenomenon.
- Critical Review: This is similar to a narrative review but requires a robust understanding of both the subject and the existing literature. In a critical review, the reviewer not only summarizes the existing literature, but also evaluates its strengths and weaknesses. This is common in the social sciences and humanities .
- State-of-the-Art Review: This considers the current level of advancement in a field or topic and makes recommendations for future research directions. This type of review is common in technological and scientific fields but can be applied to any discipline.
How to Write a Narrative Review (Tips for Undergrad Students)
Most undergraduate students conducting a capstone research project will be writing narrative reviews. Below is a five-step process for conducting a simple review of the literature for your project.
- Search for Relevant Literature: Use scholarly databases related to your field of study, provided by your university library, along with appropriate search terms to identify key scholarly articles that have been published on your topic.
- Evaluate and Select Sources: Filter the source list by selecting studies that are directly relevant and of sufficient quality, considering factors like credibility , objectivity, accuracy, and validity.
- Analyze and Synthesize: Review each source and summarize the main arguments in one paragraph (or more, for postgrad). Keep these summaries in a table.
- Identify Themes: With all studies summarized, group studies that share common themes, such as studies that have similar findings or methodologies.
- Write the Review: Write your review based upon the themes or subtopics you have identified. Give a thorough overview of each theme, integrating source data, and conclude with a summary of the current state of knowledge then suggestions for future research based upon your evaluation of what is lacking in the literature.
Literature reviews don’t have to be as scary as they seem. Yes, they are difficult and require a strong degree of comprehension of academic studies. But it can be feasibly done through following a structured approach to data collection and analysis. With my undergraduate research students (who tend to conduct small-scale qualitative studies ), I encourage them to conduct a narrative literature review whereby they can identify key themes in the literature. Within each theme, students can critique key studies and their strengths and limitations , in order to get a lay of the land and come to a point where they can identify ways to contribute new insights to the existing academic conversation on their topic.
Ankrah, S., & Omar, A. T. (2015). Universities–industry collaboration: A systematic review. Scandinavian Journal of Management, 31(3), 387-408.
Asghari, P., Rahmani, A. M., & Javadi, H. H. S. (2019). Internet of Things applications: A systematic review. Computer Networks , 148 , 241-261.
Dyrbye, L., & Shanafelt, T. (2016). A narrative review on burnout experienced by medical students and residents. Medical education , 50 (1), 132-149.
Geiger, J. L., Steg, L., Van Der Werff, E., & Ünal, A. B. (2019). A meta-analysis of factors related to recycling. Journal of environmental psychology , 64 , 78-97.
Martin, F., Sun, T., & Westine, C. D. (2020). A systematic review of research on online teaching and learning from 2009 to 2018. Computers & education , 159 , 104009.
Mavilidi, M. F., Ruiter, M., Schmidt, M., Okely, A. D., Loyens, S., Chandler, P., & Paas, F. (2018). A narrative review of school-based physical activity for enhancing cognition and learning: The importance of relevancy and integration. Frontiers in psychology , 2079.
Patterson, G. T., Chung, I. W., & Swan, P. W. (2014). Stress management interventions for police officers and recruits: A meta-analysis. Journal of experimental criminology , 10 , 487-513.
Reith, T. P. (2018). Burnout in United States healthcare professionals: a narrative review. Cureus , 10 (12).
Ritchie, S. J., & Tucker-Drob, E. M. (2018). How much does education improve intelligence? A meta-analysis. Psychological science , 29 (8), 1358-1369.
Roman, S., Sánchez-Siles, L. M., & Siegrist, M. (2017). The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review. Trends in food science & technology , 67 , 44-57.
Sáiz-Vazquez, O., Puente-Martínez, A., Ubillos-Landa, S., Pacheco-Bonrostro, J., & Santabárbara, J. (2020). Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease risk: a meta-meta-analysis. Brain sciences, 10(6), 386.
Vermeir, P., Vandijck, D., Degroote, S., Peleman, R., Verhaeghe, R., Mortier, E., … & Vogelaers, D. (2015). Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations. International journal of clinical practice , 69 (11), 1257-1267.
Wisniewski, B., Zierer, K., & Hattie, J. (2020). The power of feedback revisited: A meta-analysis of educational feedback research. Frontiers in Psychology , 10 , 3087.
Yli-Huumo, J., Ko, D., Choi, S., Park, S., & Smolander, K. (2016). Where is current research on blockchain technology?—a systematic review. PloS one , 11 (10), e0163477.
Zestcott, C. A., Blair, I. V., & Stone, J. (2016). Examining the presence, consequences, and reduction of implicit bias in health care: a narrative review. Group Processes & Intergroup Relations , 19 (4), 528-542

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 10 Reasons you’re Perpetually Single
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 20 Montessori Toddler Bedrooms (Design Inspiration)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 21 Montessori Homeschool Setups
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 101 Hidden Talents Examples
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

IMAGES