- U.S. Department of Health & Human Services

- Virtual Tour
- Staff Directory
- En Español

You are here
Science, health, and public trust.
September 8, 2021
Explaining How Research Works
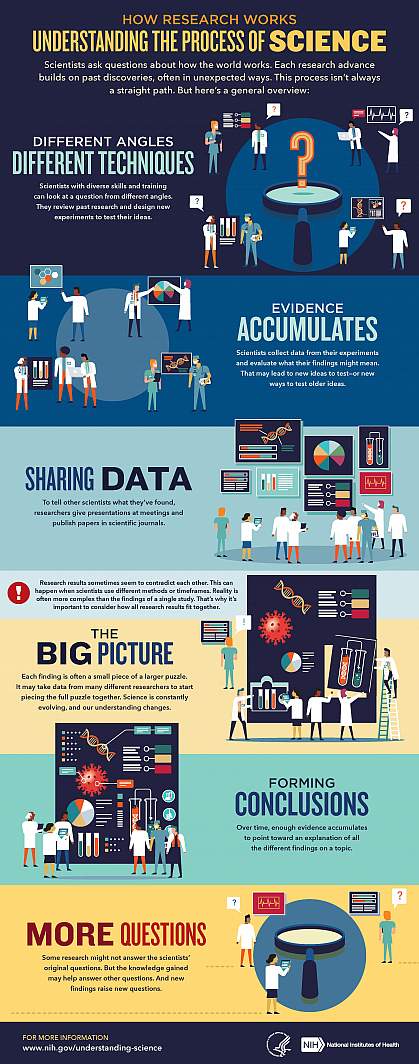
We’ve heard “follow the science” a lot during the pandemic. But it seems science has taken us on a long and winding road filled with twists and turns, even changing directions at times. That’s led some people to feel they can’t trust science. But when what we know changes, it often means science is working.

Explaining the scientific process may be one way that science communicators can help maintain public trust in science. Placing research in the bigger context of its field and where it fits into the scientific process can help people better understand and interpret new findings as they emerge. A single study usually uncovers only a piece of a larger puzzle.
Questions about how the world works are often investigated on many different levels. For example, scientists can look at the different atoms in a molecule, cells in a tissue, or how different tissues or systems affect each other. Researchers often must choose one or a finite number of ways to investigate a question. It can take many different studies using different approaches to start piecing the whole picture together.
Sometimes it might seem like research results contradict each other. But often, studies are just looking at different aspects of the same problem. Researchers can also investigate a question using different techniques or timeframes. That may lead them to arrive at different conclusions from the same data.
Using the data available at the time of their study, scientists develop different explanations, or models. New information may mean that a novel model needs to be developed to account for it. The models that prevail are those that can withstand the test of time and incorporate new information. Science is a constantly evolving and self-correcting process.
Scientists gain more confidence about a model through the scientific process. They replicate each other’s work. They present at conferences. And papers undergo peer review, in which experts in the field review the work before it can be published in scientific journals. This helps ensure that the study is up to current scientific standards and maintains a level of integrity. Peer reviewers may find problems with the experiments or think different experiments are needed to justify the conclusions. They might even offer new ways to interpret the data.
It’s important for science communicators to consider which stage a study is at in the scientific process when deciding whether to cover it. Some studies are posted on preprint servers for other scientists to start weighing in on and haven’t yet been fully vetted. Results that haven't yet been subjected to scientific scrutiny should be reported on with care and context to avoid confusion or frustration from readers.
We’ve developed a one-page guide, "How Research Works: Understanding the Process of Science" to help communicators put the process of science into perspective. We hope it can serve as a useful resource to help explain why science changes—and why it’s important to expect that change. Please take a look and share your thoughts with us by sending an email to [email protected].
Below are some additional resources:
- Discoveries in Basic Science: A Perfectly Imperfect Process
- When Clinical Research Is in the News
- What is Basic Science and Why is it Important?
- What is a Research Organism?
- What Are Clinical Trials and Studies?
- Basic Research – Digital Media Kit
- Decoding Science: How Does Science Know What It Knows? (NAS)
- Can Science Help People Make Decisions ? (NAS)
Connect with Us
- More Social Media from NIH
2.1 Why is Research Important
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Explain how scientific research addresses questions about behavior
- Discuss how scientific research guides public policy
- Appreciate how scientific research can be important in making personal decisions
Scientific research is a critical tool for successfully navigating our complex world. Without it, we would be forced to rely solely on intuition, other people’s authority, and blind luck. While many of us feel confident in our abilities to decipher and interact with the world around us, history is filled with examples of how very wrong we can be when we fail to recognize the need for evidence in supporting claims. At various times in history, we would have been certain that the sun revolved around a flat earth, that the earth’s continents did not move, and that mental illness was caused by possession (figure below). It is through systematic scientific research that we divest ourselves of our preconceived notions and superstitions and gain an objective understanding of ourselves and our world.

Some of our ancestors, across the work and over the centuries, believed that trephination – the practice of making a hole in the skull, as shown here – allowed evil spirits to leave the body, thus curing mental illness and other diseases (credit” “taiproject/Flickr)
The goal of all scientists is to better understand the world around them. Psychologists focus their attention on understanding behavior, as well as the cognitive (mental) and physiological (body) processes that underlie behavior. In contrast to other methods that people use to understand the behavior of others, such as intuition and personal experience, the hallmark of scientific research is that there is evidence to support a claim. Scientific knowledge is empirical : It is grounded in objective, tangible evidence that can be observed time and time again, regardless of who is observing.
We can easily observe the behavior of others around us. For example, if someone is crying, we can observe that behavior. However, the reason for the behavior is more difficult to determine. Is the person crying due to being sad, in pain, or happy? Sometimes, asking about the underlying cognitions is as easy as asking the subject directly: “Why are you crying?” However, there are situations in which an individual is either uncomfortable or unwilling to answer the question honestly, or is incapable of answering. For example, infants would not be able to explain why they are crying. In other situations, it may be hard to identify exactly why you feel the way you do. Think about times when you suddenly feel annoyed after a long day. There may be a specific trigger for your annoyance (a loud noise), or you may be tired, hungry, stressed, or all of the above. Human behavior is often a complicated mix of a variety of factors. In such circumstances, the psychologist must be creative in finding ways to better understand behavior. This chapter explores how scientific knowledge is generated, and how important that knowledge is in forming decisions in our personal lives and in the public domain.
USE OF RESEARCH INFORMATION
Trying to determine which theories are and are not accepted by the scientific community can be difficult, especially in an area of research as broad as psychology. More than ever before, we have an incredible amount of information at our fingertips, and a simple internet search on any given research topic might result in a number of contradictory studies. In these cases, we are witnessing the scientific community going through the process of coming to an agreement, and it could be quite some time before a consensus emerges. In other cases, rapidly developing technology is improving our ability to measure things, and changing our earlier understanding of how the mind works.
In the meantime, we should strive to think critically about the information we encounter by exercising a degree of healthy skepticism. When someone makes a claim, we should examine the claim from a number of different perspectives: what is the expertise of the person making the claim, what might they gain if the claim is valid, does the claim seem justified given the evidence, and what do other researchers think of the claim? Science is always changing and new evidence is alwaus coming to light, thus this dash of skepticism should be applied to all research you interact with from now on. Yes, that includes the research presented in this textbook.
Evaluation of research findings can have widespread impact. Imagine that you have been elected as the governor of your state. One of your responsibilities is to manage the state budget and determine how to best spend your constituents’ tax dollars. As the new governor, you need to decide whether to continue funding the D.A.R.E. (Drug Abuse Resistance Education) program in public schools (figure below). This program typically involves police officers coming into the classroom to educate students about the dangers of becoming involved with alcohol and other drugs. According to the D.A.R.E. website (www.dare.org), this program has been very popular since its inception in 1983, and it is currently operating in 75% of school districts in the United States and in more than 40 countries worldwide. Sounds like an easy decision, right? However, on closer review, you discover that the vast majority of research into this program consistently suggests that participation has little, if any, effect on whether or not someone uses alcohol or other drugs (Clayton, Cattarello, & Johnstone, 1996; Ennett, Tobler, Ringwalt, & Flewelling, 1994; Lynam et al., 1999; Ringwalt, Ennett, & Holt, 1991). If you are committed to being a good steward of taxpayer money, will you fund this particular program, or will you try to find other programs that research has consistently demonstrated to be effective?

The D.A.R.E. program continues to be popular in schools around the world despite research suggesting that it is ineffective.
It is not just politicians who can benefit from using research in guiding their decisions. We all might look to research from time to time when making decisions in our lives. Imagine you just found out that a close friend has breast cancer or that one of your young relatives has recently been diagnosed with autism. In either case, you want to know which treatment options are most successful with the fewest side effects. How would you find that out? You would probably talk with a doctor or psychologist and personally review the research that has been done on various treatment options—always with a critical eye to ensure that you are as informed as possible.
In the end, research is what makes the difference between facts and opinions. Facts are observable realities, and opinions are personal judgments, conclusions, or attitudes that may or may not be accurate. In the scientific community, facts can be established only using evidence collected through empirical research.
THE PROCESS OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH
Scientific knowledge is advanced through a process known as the scientific method . Basically, ideas (in the form of theories and hypotheses) are tested against the real world (in the form of empirical observations), and those observations lead to more ideas that are tested against the real world, and so on. In this sense, the scientific process is circular. We continually test and revise theories based on new evidence.
Two types of reasoning are used to make decisions within this model: Deductive and inductive. In deductive reasoning, ideas are tested against the empirical world. Think about a detective looking for clues and evidence to test their “hunch” about whodunit. In contrast, in inductive reasoning, empirical observations lead to new ideas. In other words, inductive reasoning involves gathering facts to create or refine a theory, rather than testing the theory by gathering facts (figure below). These processes are inseparable, like inhaling and exhaling, but different research approaches place different emphasis on the deductive and inductive aspects.

Psychological research relies on both inductive and deductive reasoning.
In the scientific context, deductive reasoning begins with a generalization—one hypothesis—that is then used to reach logical conclusions about the real world. If the hypothesis is correct, then the logical conclusions reached through deductive reasoning should also be correct. A deductive reasoning argument might go something like this: All living things require energy to survive (this would be your hypothesis). Ducks are living things. Therefore, ducks require energy to survive (logical conclusion). In this example, the hypothesis is correct; therefore, the conclusion is correct as well. Sometimes, however, an incorrect hypothesis may lead to a logical but incorrect conclusion. Consider the famous example from Greek philosophy. A philosopher decided that human beings were “featherless bipeds”. Using deductive reasoning, all two-legged creatures without feathers must be human, right? Diogenes the Cynic (named because he was, well, a cynic) burst into the room with a freshly plucked chicken from the market and held it up exclaiming “Behold! I have brought you a man!”
Deductive reasoning starts with a generalization that is tested against real-world observations; however, inductive reasoning moves in the opposite direction. Inductive reasoning uses empirical observations to construct broad generalizations. Unlike deductive reasoning, conclusions drawn from inductive reasoning may or may not be correct, regardless of the observations on which they are based. For example, you might be a biologist attempting to classify animals into groups. You notice that quite a large portion of animals are furry and produce milk for their young (cats, dogs, squirrels, horses, hippos, etc). Therefore, you might conclude that all mammals (the name you have chosen for this grouping) have hair and produce milk. This seems like a pretty great hypothesis that you could test with deductive reasoning. You go out an look at a whole bunch of things and stumble on an exception: The coconut. Coconuts have hair and produce milk, but they don’t “fit” your idea of what a mammal is. So, using inductive reasoning given the new evidence, you adjust your theory again for an other round of data collection. Inductive and deductive reasoning work in tandem to help build and improve scientific theories over time.
We’ve stated that theories and hypotheses are ideas, but what sort of ideas are they, exactly? A theory is a well-developed set of ideas that propose an explanation for observed phenomena. Theories are repeatedly checked against the world, but they tend to be too complex to be tested all at once. Instead, researchers create hypotheses to test specific aspects of a theory.
A hypothesis is a testable prediction about how the world will behave if our theory is correct, and it is often worded as an if-then statement (e.g., if I study all night, I will get a passing grade on the test). The hypothesis is extremely important because it bridges the gap between the realm of ideas and the real world. As specific hypotheses are tested, theories are modified and refined to reflect and incorporate the result of these tests (figure below).

The scientific method of research includes proposing hypotheses, conducting research, and creating or modifying theories based on results.
To see how this process works, let’s consider a specific theory and a hypothesis that might be generated from that theory. As you’ll learn in a later chapter, the James-Lange theory of emotion asserts that emotional experience relies on the physiological arousal associated with the emotional state. If you walked out of your home and discovered a very aggressive snake waiting on your doorstep, your heart would begin to race and your stomach churn. According to the James-Lange theory, these physiological changes would result in your feeling of fear. A hypothesis that could be derived from this theory might be that a person who is unaware of the physiological arousal that the sight of the snake elicits will not feel fear.
A scientific hypothesis is also falsifiable, or capable of being shown to be incorrect. Recall from the introductory chapter that Sigmund Freud had lots of interesting ideas to explain various human behaviors (figure below). However, a major criticism of Freud’s theories is that many of his ideas are not falsifiable. The essential characteristic of Freud’s building blocks of personality, the id, ego, and superego, is that they are unconscious, and therefore people can’t observe them. Because they cannot be observed or tested in any way, it is impossible to say that they don’t exist, so they cannot be considered scientific theories. Despite this, Freud’s theories are widely taught in introductory psychology texts because of their historical significance for personality psychology and psychotherapy, and these remain the root of all modern forms of therapy.

Many of the specifics of (a) Freud’s theories, such ad (b) his division on the mind into the id, ego, and superego, have fallen out of favor in recent decades because they are not falsifiable (i.e., cannot be verified through scientific investigation). In broader strokes, his views set the stage for much psychological thinking today, such as the idea that some psychological process occur at the level of the unconscious.
In contrast, the James-Lange theory does generate falsifiable hypotheses, such as the one described above. Some individuals who suffer significant injuries to their spinal columns are unable to feel the bodily changes that often accompany emotional experiences. Therefore, we could test the hypothesis by determining how emotional experiences differ between individuals who have the ability to detect these changes in their physiological arousal and those who do not. In fact, this research has been conducted and while the emotional experiences of people deprived of an awareness of their physiological arousal may be less intense, they still experience emotion (Chwalisz, Diener, & Gallagher, 1988).
Scientific research’s dependence on falsifiability allows for great confidence in the information that it produces. Typically, by the time information is accepted by the scientific community, it has been tested repeatedly.
Scientists are engaged in explaining and understanding how the world around them works, and they are able to do so by coming up with theories that generate hypotheses that are testable and falsifiable. Theories that stand up to their tests are retained and refined, while those that do not are discarded or modified. IHaving good information generated from research aids in making wise decisions both in public policy and in our personal lives.
Review Questions:
1. Scientific hypotheses are ________ and falsifiable.
a. observable
b. original
c. provable
d. testable
2. ________ are defined as observable realities.
a. behaviors
c. opinions
d. theories
3. Scientific knowledge is ________.
a. intuitive
b. empirical
c. permanent
d. subjective
4. A major criticism of Freud’s early theories involves the fact that his theories ________.
a. were too limited in scope
b. were too outrageous
c. were too broad
d. were not testable
Critical Thinking Questions:
1. In this section, the D.A.R.E. program was described as an incredibly popular program in schools across the United States despite the fact that research consistently suggests that this program is largely ineffective. How might one explain this discrepancy?
2. The scientific method is often described as self-correcting and cyclical. Briefly describe your understanding of the scientific method with regard to these concepts.
Personal Application Questions:
1. Healthcare professionals cite an enormous number of health problems related to obesity, and many people have an understandable desire to attain a healthy weight. There are many diet programs, services, and products on the market to aid those who wish to lose weight. If a close friend was considering purchasing or participating in one of these products, programs, or services, how would you make sure your friend was fully aware of the potential consequences of this decision? What sort of information would you want to review before making such an investment or lifestyle change yourself?
deductive reasoning
falsifiable
hypothesis: (plural
inductive reasoning
Answers to Exercises
Review Questions:
1. There is probably tremendous political pressure to appear to be hard on drugs. Therefore, even though D.A.R.E. might be ineffective, it is a well-known program with which voters are familiar.
2. This cyclical, self-correcting process is primarily a function of the empirical nature of science. Theories are generated as explanations of real-world phenomena. From theories, specific hypotheses are developed and tested. As a function of this testing, theories will be revisited and modified or refined to generate new hypotheses that are again tested. This cyclical process ultimately allows for more and more precise (and presumably accurate) information to be collected.
deductive reasoning: results are predicted based on a general premise
empirical: grounded in objective, tangible evidence that can be observed time and time again, regardless of who is observing
fact: objective and verifiable observation, established using evidence collected through empirical research
falsifiable: able to be disproven by experimental results
hypothesis: (plural: hypotheses) tentative and testable statement about the relationship between two or more variables
inductive reasoning: conclusions are drawn from observations
opinion: personal judgments, conclusions, or attitudes that may or may not be accurate
theory: well-developed set of ideas that propose an explanation for observed phenomena

Share This Book
- Increase Font Size
An official website of the United States government
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

Research: Articulating Questions, Generating Hypotheses, and Choosing Study Designs
Mary p tully.
- Author information
- Copyright and License information
Address correspondence to: Dr Mary P Tully, Manchester Pharmacy School, University of Manchester, Oxford Road, Manchester M13 9PT UK, e-mail: [email protected]
INTRODUCTION
Articulating a clear and concise research question is fundamental to conducting a robust and useful research study. Although “getting stuck into” the data collection is the exciting part of research, this preparation stage is crucial. Clear and concise research questions are needed for a number of reasons. Initially, they are needed to enable you to search the literature effectively. They will allow you to write clear aims and generate hypotheses. They will also ensure that you can select the most appropriate research design for your study.
This paper begins by describing the process of articulating clear and concise research questions, assuming that you have minimal experience. It then describes how to choose research questions that should be answered and how to generate study aims and hypotheses from your questions. Finally, it describes briefly how your question will help you to decide on the research design and methods best suited to answering it.

TURNING CURIOSITY INTO QUESTIONS
A research question has been described as “the uncertainty that the investigator wants to resolve by performing her study” 1 or “a logical statement that progresses from what is known or believed to be true to that which is unknown and requires validation”. 2 Developing your question usually starts with having some general ideas about the areas within which you want to do your research. These might flow from your clinical work, for example. You might be interested in finding ways to improve the pharmaceutical care of patients on your wards. Alternatively, you might be interested in identifying the best antihypertensive agent for a particular subgroup of patients. Lipowski 2 described in detail how work as a practising pharmacist can be used to great advantage to generate interesting research questions and hence useful research studies. Ideas could come from questioning received wisdom within your clinical area or the rationale behind quick fixes or workarounds, or from wanting to improve the quality, safety, or efficiency of working practice.
Alternatively, your ideas could come from searching the literature to answer a query from a colleague. Perhaps you could not find a published answer to the question you were asked, and so you want to conduct some research yourself. However, just searching the literature to generate questions is not to be recommended for novices—the volume of material can feel totally overwhelming.
Use a research notebook, where you regularly write ideas for research questions as you think of them during your clinical practice or after reading other research papers. It has been said that the best way to have a great idea is to have lots of ideas and then choose the best. The same would apply to research questions!
When you first identify your area of research interest, it is likely to be either too narrow or too broad. Narrow questions (such as “How is drug X prescribed for patients with condition Y in my hospital?”) are usually of limited interest to anyone other than the researcher. Broad questions (such as “How can pharmacists provide better patient care?”) must be broken down into smaller, more manageable questions. If you are interested in how pharmacists can provide better care, for example, you might start to narrow that topic down to how pharmacists can provide better care for one condition (such as affective disorders) for a particular subgroup of patients (such as teenagers). Then you could focus it even further by considering a specific disorder (depression) and a particular type of service that pharmacists could provide (improving patient adherence). At this stage, you could write your research question as, for example, “What role, if any, can pharmacists play in improving adherence to fluoxetine used for depression in teenagers?”
TYPES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS
Being able to consider the type of research question that you have generated is particularly useful when deciding what research methods to use. There are 3 broad categories of question: descriptive, relational, and causal.
Descriptive
One of the most basic types of question is designed to ask systematically whether a phenomenon exists. For example, we could ask “Do pharmacists ‘care’ when they deliver pharmaceutical care?” This research would initially define the key terms (i.e., describing what “pharmaceutical care” and “care” are), and then the study would set out to look for the existence of care at the same time as pharmaceutical care was being delivered.
When you know that a phenomenon exists, you can then ask description and/or classification questions. The answers to these types of questions involve describing the characteristics of the phenomenon or creating typologies of variable subtypes. In the study above, for example, you could investigate the characteristics of the “care” that pharmacists provide. Classifications usually use mutually exclusive categories, so that various subtypes of the variable will have an unambiguous category to which they can be assigned. For example, a question could be asked as to “what is a pharmacist intervention” and a definition and classification system developed for use in further research.
When seeking further detail about your phenomenon, you might ask questions about its composition. These questions necessitate deconstructing a phenomenon (such as a behaviour) into its component parts. Within hospital pharmacy practice, you might be interested in asking questions about the composition of a new behavioural intervention to improve patient adherence, for example, “What is the detailed process that the pharmacist implicitly follows during delivery of this new intervention?”
After you have described your phenomena, you may then be interested in asking questions about the relationships between several phenomena. If you work on a renal ward, for example, you may be interested in looking at the relationship between hemoglobin levels and renal function, so your question would look something like this: “Are hemoglobin levels related to level of renal function?” Alternatively, you may have a categorical variable such as grade of doctor and be interested in the differences between them with regard to prescribing errors, so your research question would be “Do junior doctors make more prescribing errors than senior doctors?” Relational questions could also be asked within qualitative research, where a detailed understanding of the nature of the relationship between, for example, the gender and career aspirations of clinical pharmacists could be sought.
Once you have described your phenomena and have identified a relationship between them, you could ask about the causes of that relationship. You may be interested to know whether an intervention or some other activity has caused a change in your variable, and your research question would be about causality. For example, you may be interested in asking, “Does captopril treatment reduce blood pressure?” Generally, however, if you ask a causality question about a medication or any other health care intervention, it ought to be rephrased as a causality–comparative question. Without comparing what happens in the presence of an intervention with what happens in the absence of the intervention, it is impossible to attribute causality to the intervention. Although a causality question would usually be answered using a comparative research design, asking a causality–comparative question makes the research design much more explicit. So the above question could be rephrased as, “Is captopril better than placebo at reducing blood pressure?”
The acronym PICO has been used to describe the components of well-crafted causality–comparative research questions. 3 The letters in this acronym stand for Population, Intervention, Comparison, and Outcome. They remind the researcher that the research question should specify the type of participant to be recruited, the type of exposure involved, the type of control group with which participants are to be compared, and the type of outcome to be measured. Using the PICO approach, the above research question could be written as “Does captopril [ intervention ] decrease rates of cardiovascular events [ outcome ] in patients with essential hypertension [ population ] compared with patients receiving no treatment [ comparison ]?”
DECIDING WHETHER TO ANSWER A RESEARCH QUESTION
Just because a question can be asked does not mean that it needs to be answered. Not all research questions deserve to have time spent on them. One useful set of criteria is to ask whether your research question is feasible, interesting, novel, ethical, and relevant. 1 The need for research to be ethical will be covered in a later paper in the series, so is not discussed here. The literature review is crucial to finding out whether the research question fulfils the remaining 4 criteria.
Conducting a comprehensive literature review will allow you to find out what is already known about the subject and any gaps that need further exploration. You may find that your research question has already been answered. However, that does not mean that you should abandon the question altogether. It may be necessary to confirm those findings using an alternative method or to translate them to another setting. If your research question has no novelty, however, and is not interesting or relevant to your peers or potential funders, you are probably better finding an alternative.
The literature will also help you learn about the research designs and methods that have been used previously and hence to decide whether your potential study is feasible. As a novice researcher, it is particularly important to ask if your planned study is feasible for you to conduct. Do you or your collaborators have the necessary technical expertise? Do you have the other resources that will be needed? If you are just starting out with research, it is likely that you will have a limited budget, in terms of both time and money. Therefore, even if the question is novel, interesting, and relevant, it may not be one that is feasible for you to answer.
GENERATING AIMS AND HYPOTHESES
All research studies should have at least one research question, and they should also have at least one aim. As a rule of thumb, a small research study should not have more than 2 aims as an absolute maximum. The aim of the study is a broad statement of intention and aspiration; it is the overall goal that you intend to achieve. The wording of this broad statement of intent is derived from the research question. If it is a descriptive research question, the aim will be, for example, “to investigate” or “to explore”. If it is a relational research question, then the aim should state the phenomena being correlated, such as “to ascertain the impact of gender on career aspirations”. If it is a causal research question, then the aim should include the direction of the relationship being tested, such as “to investigate whether captopril decreases rates of cardiovascular events in patients with essential hypertension, relative to patients receiving no treatment”.
The hypothesis is a tentative prediction of the nature and direction of relationships between sets of data, phrased as a declarative statement. Therefore, hypotheses are really only required for studies that address relational or causal research questions. For the study above, the hypothesis being tested would be “Captopril decreases rates of cardiovascular events in patients with essential hypertension, relative to patients receiving no treatment”. Studies that seek to answer descriptive research questions do not test hypotheses, but they can be used for hypothesis generation. Those hypotheses would then be tested in subsequent studies.
CHOOSING THE STUDY DESIGN
The research question is paramount in deciding what research design and methods you are going to use. There are no inherently bad research designs. The rightness or wrongness of the decision about the research design is based simply on whether it is suitable for answering the research question that you have posed.
It is possible to select completely the wrong research design to answer a specific question. For example, you may want to answer one of the research questions outlined above: “Do pharmacists ‘care’ when they deliver pharmaceutical care?” Although a randomized controlled study is considered by many as a “gold standard” research design, such a study would just not be capable of generating data to answer the question posed. Similarly, if your question was, “Is captopril better than placebo at reducing blood pressure?”, conducting a series of in-depth qualitative interviews would be equally incapable of generating the necessary data. However, if these designs are swapped around, we have 2 combinations (pharmaceutical care investigated using interviews; captopril investigated using a randomized controlled study) that are more likely to produce robust answers to the questions.
The language of the research question can be helpful in deciding what research design and methods to use. Subsequent papers in this series will cover these topics in detail. For example, if the question starts with “how many” or “how often”, it is probably a descriptive question to assess the prevalence or incidence of a phenomenon. An epidemiological research design would be appropriate, perhaps using a postal survey or structured interviews to collect the data. If the question starts with “why” or “how”, then it is a descriptive question to gain an in-depth understanding of a phenomenon. A qualitative research design, using in-depth interviews or focus groups, would collect the data needed. Finally, the term “what is the impact of” suggests a causal question, which would require comparison of data collected with and without the intervention (i.e., a before–after or randomized controlled study).
CONCLUSIONS
This paper has briefly outlined how to articulate research questions, formulate your aims, and choose your research methods. It is crucial to realize that articulating a good research question involves considerable iteration through the stages described above. It is very common that the first research question generated bears little resemblance to the final question used in the study. The language is changed several times, for example, because the first question turned out not to be feasible and the second question was a descriptive question when what was really wanted was a causality question. The books listed in the “Further Reading” section provide greater detail on the material described here, as well as a wealth of other information to ensure that your first foray into conducting research is successful.
This article is the second in the CJHP Research Primer Series, an initiative of the CJHP Editorial Board and the CSHP Research Committee. The planned 2-year series is intended to appeal to relatively inexperienced researchers, with the goal of building research capacity among practising pharmacists. The articles, presenting simple but rigorous guidance to encourage and support novice researchers, are being solicited from authors with appropriate expertise.
Previous article in this series:
Bond CM. The research jigsaw: how to get started. Can J Hosp Pharm . 2014;67(1):28–30.
Competing interests: Mary Tully has received personal fees from the UK Renal Pharmacy Group to present a conference workshop on writing research questions and nonfinancial support (in the form of travel and accommodation) from the Dubai International Pharmaceuticals and Technologies Conference and Exhibition (DUPHAT) to present a workshop on conducting pharmacy practice research.
- 1. Hulley S, Cummings S, Browner W, Grady D, Newman T. Designing clinical research. 4th ed. Philadelphia (PA): Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins; 2013. [ Google Scholar ]
- 2. Lipowski EE. Developing great research questions. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2008;65(17):1667–70. doi: 10.2146/ajhp070276. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 3. Richardson WS, Wilson MC, Nishikawa J, Hayward RS. The well-built clinical question: a key to evidence-based decisions. ACP J Club. 1995;123(3):A12–3. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
Further Reading
- Cresswell J. Research design: qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods approaches. London (UK): Sage; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Haynes RB, Sackett DL, Guyatt GH, Tugwell P. Clinical epidemiology: how to do clinical practice research. 3rd ed. Philadelphia (PA): Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins; 2006. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kumar R. Research methodology: a step-by-step guide for beginners. 3rd ed. London (UK): Sage; 2010. [ Google Scholar ]
- Smith FJ. Conducting your pharmacy practice research project. London (UK): Pharmaceutical Press; 2005. [ Google Scholar ]
- View on publisher site
- PDF (592.1 KB)
- Collections
Similar articles
Cited by other articles, links to ncbi databases.
- Download .nbib .nbib
- Format: AMA APA MLA NLM
Add to Collections

IMAGES